Triglyceride is strongly associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease among markers of hyperlipidemia and diabetes - PubMed (original) (raw)
Triglyceride is strongly associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease among markers of hyperlipidemia and diabetes
Minoru Tomizawa et al. Biomed Rep. 2014 Sep.
Abstract
The aim of the present study was to reveal the metabolic disorders most commonly associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Triglyceride (TG), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL), blood glucose (BG) and hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) were analyzed. NAFLD was diagnosed using abdominal ultrasound (US), and TG, HDL, LDL, BG and HbA1c were immediately collected on the same day and subjected to multivariate regression analysis. Stepwise analysis was performed to select the variables that were closely associated with NAFLD. The patients who were positive for the hepatitis B antigen and hepatitis C antibody were excluded from the study. Additionally, the patients who were prescribed prednisolone or methotrexate were excluded from the study as these agents may cause NAFLD or liver toxicity. The study included 168 and 125 patients with and without NAFLD, respectively. TG, BG and HbA1c were strongly correlated with NAFLD. Among these parameters, TG was the strongest predictor of NAFLD (χ2=9.89, P=0.0017). TG was the parameter that was most strongly associated with NAFLD. In conclusion, elevated TG was a marker of NAFLD.
Keywords: blood glucose; hemoglobin A1c; multivariate regression analysis; receiver operating characteristics.
Figures
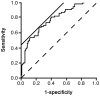
Figure 1
Receiver operator characteristic (ROC) for the prediction of nonalcoholic fatty liver with the logistic model. The ROC curve was illustrated to evaluate the usefulness of the logistic model to predict nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Solid straight line, a line with a slope of 45° to calculate the threshold value by the software (JMP 10.0.2); broken line, reference.
Similar articles
- IMPACT OF TYPE 2 DIABETES ON NONALCOHOLIC STEATOHEPATITIS AND ADVANCED FIBROSIS IN PATIENTS WITH NONALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE.
Bian H, Zhu X, Xia M, Yan H, Chang X, Hu X, Pan B, Guo W, Li X, Gao X. Bian H, et al. Endocr Pract. 2020 Apr;26(4):444-453. doi: 10.4158/EP-2019-0342. Epub 2020 Jan 22. Endocr Pract. 2020. PMID: 31968197 - Significance of Triglyceride-to-High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Ratio in Children with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease.
Kim HJ. Kim HJ. Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr. 2023 Nov;26(6):312-319. doi: 10.5223/pghn.2023.26.6.312. Epub 2023 Oct 30. Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr. 2023. PMID: 38025490 Free PMC article. - Association of serum triglyceride-to-HDL cholesterol ratio with carotid artery intima-media thickness, insulin resistance and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in children and adolescents.
Pacifico L, Bonci E, Andreoli G, Romaggioli S, Di Miscio R, Lombardo CV, Chiesa C. Pacifico L, et al. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2014 Jul;24(7):737-43. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2014.01.010. Epub 2014 Jan 29. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2014. PMID: 24656140 - Total cholesterol to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio is a significant predictor of nonalcoholic fatty liver: Jinchang cohort study.
Ren XY, Shi D, Ding J, Cheng ZY, Li HY, Li JS, Pu HQ, Yang AM, He CL, Zhang JP, Ma YB, Zhang YW, Zheng TZ, Bai YN, Cheng N. Ren XY, et al. Lipids Health Dis. 2019 Feb 11;18(1):47. doi: 10.1186/s12944-019-0984-9. Lipids Health Dis. 2019. PMID: 30744645 Free PMC article. - Effect of Nigella sativa in the treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.
Tang G, Zhang L, Tao J, Wei Z. Tang G, et al. Phytother Res. 2021 Aug;35(8):4183-4193. doi: 10.1002/ptr.7080. Epub 2021 Mar 16. Phytother Res. 2021. PMID: 33728708 Review.
Cited by
- Rural-Urban differentials in prevalence, spectrum and determinants of Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in North Indian population.
Asadullah M, Shivashankar R, Shalimar, Kandasamy D, Kondal D, Rautela G, Peerzada A, Grover B, Amarchand R, Nayak B, Sharma R, Ramakrishnan L, Prabhakaran D, Krishnan A, Tandon N. Asadullah M, et al. PLoS One. 2022 Feb 10;17(2):e0263768. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0263768. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35143562 Free PMC article. - MSC-sEV Treatment Polarizes Pro-Fibrotic M2 Macrophages without Exacerbating Liver Fibrosis in NASH.
Zhang B, Zhang B, Lai RC, Sim WK, Lam KP, Lim SK. Zhang B, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 30;24(9):8092. doi: 10.3390/ijms24098092. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37175803 Free PMC article. - Interval increase in the prevalence of symptomatic cholelithiasis-associated non-alcoholic fatty liver disease over a ten-year period in an Asian population.
Khaw KB, Choi RH, Kam JH, Chakraborty B, Chow PK. Khaw KB, et al. Singapore Med J. 2017 Dec;58(12):703-707. doi: 10.11622/smedj.2016189. Epub 2016 Dec 20. Singapore Med J. 2017. PMID: 27995261 Free PMC article. - Mean and visit-to-visit variability of glycated hemoglobin, and the risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Yoo JH, Kang M, Kim G, Hur KY, Kim JH, Sinn DH, Jin SM. Yoo JH, et al. J Diabetes Investig. 2021 Jul;12(7):1252-1262. doi: 10.1111/jdi.13455. Epub 2020 Dec 5. J Diabetes Investig. 2021. PMID: 33135331 Free PMC article. - Association between Triglyceride Glucose Index and Corrected QT Prolongation in Chinese Male Steelworkers.
Lee TL, Hsuan CF, Wu CC, Hung WC, Tsai IT, Wei CT, Yu TH, Lu IC, Chung FM, Lee YJ, Lu YC. Lee TL, et al. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Apr 12;18(8):4020. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18084020. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 33921213 Free PMC article.
References
- Chalasani N, Younossi Z, Lavine JE, et al. The diagnosis and management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: practice Guideline by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, American College of Gastroenterology, and the American Gastroenterological Association. Hepatology. 2012;55:2005–2023. - PubMed
- Adams LA, Lymp JF, St Sauver J, et al. The natural history of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a population-based cohort study. Gastroenterology. 2005;129:113–121. - PubMed
- Ascha MS, Hanouneh IA, Lopez R, Tamimi TA, Feldstein AF, Zein NN. The incidence and risk factors of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology. 2010;51:1972–1978. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous