Role of Nrf2 in chronic liver disease - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Role of Nrf2 in chronic liver disease
Wei Tang et al. World J Gastroenterol. 2014.
Abstract
Nuclear erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) is a central regulator of antioxidative response elements-mediated gene expression. It has a significant role in adaptive responses to oxidative stress by interacting with the antioxidant response element, which induces the expression of a variety of downstream targets aimed at cytoprotection. Previous studies suggested oxidative stress and associated damage could represent a common link between different forms of diseases. Oxidative stress has been implicated in various liver diseases, including viral hepatitis, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/steatohepatitis, alcoholic liver disease and drug-induced liver injury. Nrf2 activation is initiated by oxidative or electrophilic stress, and aids in the detoxification and elimination of potentially harmful exogenous chemicals and their metabolites. The expression of Nrf2 has been observed throughout human tissue, with high expression in detoxification organs, especially the liver. Thus, Nrf2 may serve as a major regulator of several cellular defense associated pathways by which hepatic cells combat oxidative stress. We review the relevant literature concerning the crucial role of Nrf2 and its signaling pathways against oxidative stress to protect hepatic cell from oxidative damage during development of common chronic liver diseases. We also review the use of Nrf2 as a therapeutic target to prevent and treat liver diseases.
Keywords: Chronic liver disease; Hepatic injury; Hepatic protection; Nuclear erythroid 2-related factor 2; Oxidative stress; Reactive oxygen species.
Figures
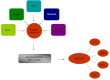
Figure 1
Nrf2 in chronic liver diseases. NRF2: Nuclear erythroid 2-related factor 2; ARE: Antioxidant response element; GST: Glutathione-S-transferases; NQO1: NAD(P)H: quinone oxidoreductase 1; HO1: Heme oxygenase-1; GCS: Group C streptococcus.
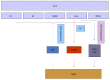
Figure 2
Nrf2 in chronic hepatitis C virus infection. HCV: Hepatitis C virus; NS4B: Nonstructural protein 4B; NS5A: Nonstructural protein 5A; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; PKC: Protein kinase C; MAPK: Mitogen activated protein kinase; PI3K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase; CK2: Casein kinase 2; NRF2: Nuclear erythroid 2-related factor 2.
Similar articles
- Nuclear erythroid 2-related factor 2: a novel potential therapeutic target for liver fibrosis.
Yang JJ, Tao H, Huang C, Li J. Yang JJ, et al. Food Chem Toxicol. 2013 Sep;59:421-7. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2013.06.018. Epub 2013 Jun 20. Food Chem Toxicol. 2013. PMID: 23793039 Review. - Free radicals, antioxidants, nuclear factor-E2-related factor-2 and liver damage.
Ramos-Tovar E, Muriel P. Ramos-Tovar E, et al. J Appl Toxicol. 2020 Jan;40(1):151-168. doi: 10.1002/jat.3880. Epub 2019 Aug 6. J Appl Toxicol. 2020. PMID: 31389060 Review. - Role of the Nrf2-ARE pathway in liver diseases.
Shin SM, Yang JH, Ki SH. Shin SM, et al. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2013;2013:763257. doi: 10.1155/2013/763257. Epub 2013 May 9. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2013. PMID: 23766860 Free PMC article. Review. - Ezetimibe, an NPC1L1 inhibitor, is a potent Nrf2 activator that protects mice from diet-induced nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.
Lee DH, Han DH, Nam KT, Park JS, Kim SH, Lee M, Kim G, Min BS, Cha BS, Lee YS, Sung SH, Jeong H, Ji HW, Lee MJ, Lee JS, Lee HY, Chun Y, Kim J, Komatsu M, Lee YH, Bae SH. Lee DH, et al. Free Radic Biol Med. 2016 Oct;99:520-532. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2016.09.009. Epub 2016 Sep 12. Free Radic Biol Med. 2016. PMID: 27634173 - Isoliquiritigenin in licorice functions as a hepatic protectant by induction of antioxidant genes through extracellular signal-regulated kinase-mediated NF-E2-related factor-2 signaling pathway.
Park SM, Lee JR, Ku SK, Cho IJ, Byun SH, Kim SC, Park SJ, Kim YW. Park SM, et al. Eur J Nutr. 2016 Dec;55(8):2431-2444. doi: 10.1007/s00394-015-1051-6. Epub 2015 Nov 22. Eur J Nutr. 2016. PMID: 26593436
Cited by
- A new NRF2 activator for the treatment of human metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease.
Hammoutene A, Laouirem S, Albuquerque M, Colnot N, Brzustowski A, Valla D, Provost N, Delerive P, Paradis V; QUID-NASH Research Group. Hammoutene A, et al. JHEP Rep. 2023 Jul 12;5(10):100845. doi: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2023.100845. eCollection 2023 Oct. JHEP Rep. 2023. PMID: 37663119 Free PMC article. - Roles of NRF2 in Fibrotic Diseases: From Mechanisms to Therapeutic Approaches.
Hao W, Li M, Cai Q, Wu S, Li X, He Q, Hu Y. Hao W, et al. Front Physiol. 2022 Jun 3;13:889792. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.889792. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35721561 Free PMC article. Review. - Genetic disruption of NRF2 promotes the development of necroinflammation and liver fibrosis in a mouse model of HFE-hereditary hemochromatosis.
Duarte TL, Caldas C, Santos AG, Silva-Gomes S, Santos-Gonçalves A, Martins MJ, Porto G, Lopes JM. Duarte TL, et al. Redox Biol. 2017 Apr;11:157-169. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2016.11.013. Epub 2016 Dec 1. Redox Biol. 2017. PMID: 27936457 Free PMC article. - Casein Glycomacropeptide Hydrolysates Exert Cytoprotective Effect against Cellular Oxidative Stress by Up-Regulating HO-1 Expression in HepG2 Cells.
Li T, Chen B, Du M, Song J, Cheng X, Wang X, Mao X. Li T, et al. Nutrients. 2017 Jan 15;9(1):31. doi: 10.3390/nu9010031. Nutrients. 2017. PMID: 28098837 Free PMC article. - Gut microbiota-derived tryptophan metabolites alleviate liver injury via AhR/Nrf2 activation in pyrrolizidine alkaloids-induced sinusoidal obstruction syndrome.
Shang H, Huang C, Xiao Z, Yang P, Zhang S, Hou X, Zhang L. Shang H, et al. Cell Biosci. 2023 Jul 8;13(1):127. doi: 10.1186/s13578-023-01078-4. Cell Biosci. 2023. PMID: 37422682 Free PMC article.
References
- Motohashi H, Yamamoto M. Nrf2-Keap1 defines a physiologically important stress response mechanism. Trends Mol Med. 2004;10:549–557. - PubMed
- Xu W, Hellerbrand C, Köhler UA, Bugnon P, Kan YW, Werner S, Beyer TA. The Nrf2 transcription factor protects from toxin-induced liver injury and fibrosis. Lab Invest. 2008;88:1068–1078. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical