Clinical role of a fixed combination of standardized Berberis aristata and Silybum marianum extracts in diabetic and hypercholesterolemic patients intolerant to statins - PubMed (original) (raw)
Clinical role of a fixed combination of standardized Berberis aristata and Silybum marianum extracts in diabetic and hypercholesterolemic patients intolerant to statins
Francesco Di Pierro et al. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2015.
Abstract
Background: Statin intolerance is a medical condition often leading patients to nonadherence to the prescribed therapy or to a relevant reduction of the statin dosage. Both situations determine a totally or partially uncontrolled lipid profile, and these conditions unquestionably increase the risk of cardiovascular events.
Methods: We enrolled hypercholesterolemic, type 2 diabetic patients complaining of intolerance to statins. Some of them had reduced the statin dose 'until the disappearance of symptoms'; others had opted for treatment with ezetimibe; and yet others were not undergoing any treatment at all. All patients of the three groups were then given a fixed combination of berberine and silymarin (Berberol(®)), known from previous papers to be able to control both lipidic and glycemic profiles.
Results: The tested product both as a single therapy and as add-on therapy to low-dose statin or to ezetimibe reduced triglycerides, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, fasting blood glucose, and glycosylated hemoglobin in a significant manner without inducing toxicity conditions that might be somehow ascribed to a statin-intolerant condition.
Conclusion: Our study demonstrates that use of Berberol(®), administered as a single or add-on therapy in statin-intolerant subjects affected by diabetes and hypercholesterolemia is a safe and effective tool capable of improving the patients' lipidic and glycemic profiles.
Keywords: Berberol®; berberine; cholesterol; ezetimibe; silymarin; type 2 diabetes.
Figures
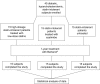
Figure 1
Scheme of the study.
Similar articles
- Preliminary study about the possible glycemic clinical advantage in using a fixed combination of Berberis aristata and Silybum marianum standardized extracts versus only Berberis aristata in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Di Pierro F, Putignano P, Villanova N, Montesi L, Moscatiello S, Marchesini G. Di Pierro F, et al. Clin Pharmacol. 2013 Nov 19;5:167-74. doi: 10.2147/CPAA.S54308. eCollection 2013. Clin Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 24277991 Free PMC article. - Berberis aristata/Silybum marianum fixed combination (Berberol(®)) effects on lipid profile in dyslipidemic patients intolerant to statins at high dosages: a randomized, placebo-controlled, clinical trial.
Derosa G, Romano D, D'Angelo A, Maffioli P. Derosa G, et al. Phytomedicine. 2015 Feb 15;22(2):231-7. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2014.11.018. Epub 2014 Dec 18. Phytomedicine. 2015. PMID: 25765827 Clinical Trial. - Retrospective analysis of the effects of a highly standardized mixture of Berberis aristata, Silybum marianum, and monacolins K and KA in patients with dyslipidemia.
Di Pierro F, Putignano P, Ferrara T, Raiola C, Rapacioli G, Villanova N. Di Pierro F, et al. Clin Pharmacol. 2016 Dec 21;9:1-7. doi: 10.2147/CPAA.S120032. eCollection 2017. Clin Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 28058034 Free PMC article. - The Effects of a Fixed Combination of Berberis aristata and Silybum marianum on Dyslipidaemia - A Meta-analysis and Systematic Review.
Tóth B, Németh D, Soós A, Hegyi P, Pham-Dobor G, Varga O, Varga V, Kiss T, Sarlós P, Erőss B, Csupor D. Tóth B, et al. Planta Med. 2020 Jan;86(2):132-143. doi: 10.1055/a-1063-1649. Epub 2019 Nov 29. Planta Med. 2020. PMID: 31784970 - Ezetimibe: a first-in-class, novel cholesterol absorption inhibitor.
Lipka LJ. Lipka LJ. Cardiovasc Drug Rev. 2003 Winter;21(4):293-312. doi: 10.1111/j.1527-3466.2003.tb00123.x. Cardiovasc Drug Rev. 2003. PMID: 14647533 Review.
Cited by
- Retrospective analysis of the effects of a highly standardized mixture of Berberis aristata, Silybum marianum, and monacolins K and KA in diabetic patients with dyslipidemia.
Di Pierro F, Putignano P, Villanova N. Di Pierro F, et al. Acta Biomed. 2018 Jan 16;88(4):462-469. doi: 10.23750/abm.v88i4.5851. Acta Biomed. 2018. PMID: 29350661 Free PMC article. - Lipid lowering nutraceuticals in clinical practice: position paper from an International Lipid Expert Panel.
Cicero AFG, Colletti A, Bajraktari G, Descamps O, Djuric DM, Ezhov M, Fras Z, Katsiki N, Langlois M, Latkovskis G, Panagiotakos DB, Paragh G, Mikhailidis DP, Mitchenko O, Paulweber B, Pella D, Pitsavos C, Reiner Ž, Ray KK, Rizzo M, Sahebkar A, Serban MC, Sperling LS, Toth PP, Vinereanu D, Vrablík M, Wong ND, Banach M. Cicero AFG, et al. Arch Med Sci. 2017 Aug;13(5):965-1005. doi: 10.5114/aoms.2017.69326. Epub 2017 Aug 4. Arch Med Sci. 2017. PMID: 28883839 Free PMC article. No abstract available. - Natural Products to Counteract the Epidemic of Cardiovascular and Metabolic Disorders.
Waltenberger B, Mocan A, Šmejkal K, Heiss EH, Atanasov AG. Waltenberger B, et al. Molecules. 2016 Jun 22;21(6):807. doi: 10.3390/molecules21060807. Molecules. 2016. PMID: 27338339 Free PMC article. Review. - Phytopharmacology and Clinical Updates of Berberis Species Against Diabetes and Other Metabolic Diseases.
Belwal T, Bisht A, Devkota HP, Ullah H, Khan H, Pandey A, Bhatt ID, Echeverría J. Belwal T, et al. Front Pharmacol. 2020 Feb 18;11:41. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00041. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32132921 Free PMC article. Review. - Natural Bioactive Compounds in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes and Metabolic (Dysfunction)-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease.
Ciobârcă D, Cătoi AF, Gavrilaș L, Banc R, Miere D, Filip L. Ciobârcă D, et al. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Feb 19;18(2):279. doi: 10.3390/ph18020279. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40006091 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Sharma SB, Garg S. Small dense LDL: risk factor for coronary artery disease (CAD) and its therapeutic modulation. Indian J Biochem Biophys. 2012;49(2):77–85. - PubMed
- Taylor FC, Huffman M, Ebrahim S. Statin therapy for primary prevention of cardiovascular disease. JAMA. 2013;310(22):2451–2452. - PubMed
- Rosenbaum D, Dallongeville J, Sabouret P, Bruckert E. Discontinuation of statin therapy due to muscular side effects: a survey in real life. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2013;23(9):871–875. - PubMed
- Alla VM, Agrawal V, DeNazareth A, Mohiuddin S, Ravilla S, Rendell M. A reappraisal of the risks and benefits of treating to target with cholesterol lowering drugs. Drugs. 2013;73(10):1025–1054. - PubMed
- Catapano AL, Farnier M, Foody JM, et al. Combination therapy in dyslipidemia: where are we now? Atherosclerosis. 2014;237(1):319–335. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources