Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms of Action of Tumour Suppressor GAS5 LncRNA - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms of Action of Tumour Suppressor GAS5 LncRNA
Mark R Pickard et al. Genes (Basel). 2015.
Abstract
It is increasingly recognised that lncRNAs play essential regulatory roles in fundamental biological processes and, consequently, that their dysregulation may contribute to major human diseases, including cancer. Better understanding of lncRNA biology may therefore offer new insights into pathogenetic mechanisms and thereby offer novel opportunities for diagnosis and therapy. Of particular interest in this regard is GAS5 lncRNA, which is down-regulated in multiple cancers, with expression levels related to both clinico-pathological characteristics and patient prognosis. Functional studies have further shown that GAS5 lncRNA both inhibits the proliferation and promotes the apoptosis of multiple cell types, and that together these cellular mechanisms of action are likely to form the basis of its tumour suppressor action. At the same time, advances have been made in our understanding of the molecular mechanisms of GAS5 lncRNA action in recent years, including riborepression of certain steroid hormone receptors and sequestration of miR-21, impacting key regulatory pathways of cell survival. Overall this accumulating knowledge has the potential to improve both the diagnosis and treatment of cancer, and ultimately patient outcome.
Keywords: GAS5; apoptosis; cancer; cell proliferation; lncRNA; tumour suppressor.
Figures
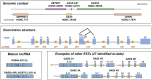
Figure 1
Genomic context, gene structure and selected products of the human GAS5 gene. For genomic context, HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee (HGNC) approved gene symbols are used, with the corresponding HGNC identity number given below each symbol. Exon/intron structure is based on published data [6]; note the presence of two alternative 5′-splice donor sites in exon 7. The two possible resulting mature lncRNAs are termed GAS5b (contains exon 7b and corresponds to the GAS5 reference sequence, NR_002578.2) and GAS5a (contains exon 7a); the latter is predicted to be 39 bases shorter than GAS5a (based on [6] and GenBank: AF141346.1). The additional GAS5 expressed sequence tags (ESTs) shown here have all been reported to induce growth arrest in lymphoid cell lines [10].
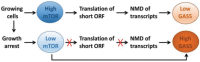
Figure 2
Interplay between mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) and nonsense-mediated decay (NMD) regulates cellular GAS5 lncRNA levels.
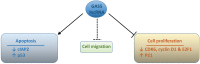
Figure 3
Summary of biological processes that are regulated by GAS5 lncRNA, including possible downstream molecular targets. ↓ and ↑ = down- and up-regulation, respectively.
Similar articles
- Novel Tumor Suppressor lncRNA Growth Arrest-Specific 5 (GAS5) In Human Cancer.
Yu Y, Hann SS. Yu Y, et al. Onco Targets Ther. 2019 Oct 11;12:8421-8436. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S221305. eCollection 2019. Onco Targets Ther. 2019. PMID: 31632088 Free PMC article. - The hormone response element mimic sequence of GAS5 lncRNA is sufficient to induce apoptosis in breast cancer cells.
Pickard MR, Williams GT. Pickard MR, et al. Oncotarget. 2016 Mar 1;7(9):10104-16. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7173. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26862727 Free PMC article. - Low expression of lncRNA-GAS5 is implicated in human primary varicose great saphenous veins.
Li L, Li X, The E, Wang LJ, Yuan TY, Wang SY, Feng J, Wang J, Liu Y, Wu YH, Ma XE, Ge J, Cui YY, Jiang XY. Li L, et al. PLoS One. 2015 Mar 25;10(3):e0120550. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0120550. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25806802 Free PMC article. - Tumor Suppressive Effects of GAS5 in Cancer Cells.
Kaur J, Salehen N, Norazit A, Rahman AA, Murad NAA, Rahman NMANA, Ibrahim K. Kaur J, et al. Noncoding RNA. 2022 May 28;8(3):39. doi: 10.3390/ncrna8030039. Noncoding RNA. 2022. PMID: 35736636 Free PMC article. Review. - Long noncoding RNA in prostate, bladder, and kidney cancer.
Martens-Uzunova ES, Böttcher R, Croce CM, Jenster G, Visakorpi T, Calin GA. Martens-Uzunova ES, et al. Eur Urol. 2014 Jun;65(6):1140-51. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2013.12.003. Epub 2013 Dec 14. Eur Urol. 2014. PMID: 24373479 Review.
Cited by
- Comparative analysis of long noncoding RNAs in long-lived mammals provides insights into natural cancer-resistance.
Jiang JJ, Kong QP. Jiang JJ, et al. RNA Biol. 2020 Nov;17(11):1657-1665. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2020.1792116. Epub 2020 Jul 17. RNA Biol. 2020. PMID: 32635806 Free PMC article. - Identification of androgen-responsive lncRNAs as diagnostic and prognostic markers for prostate cancer.
Wan X, Huang W, Yang S, Zhang Y, Pu H, Fu F, Huang Y, Wu H, Li T, Li Y. Wan X, et al. Oncotarget. 2016 Sep 13;7(37):60503-60518. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11391. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27556357 Free PMC article. - MicroRNA-210 Plays a Critical Role in the Angiogenic Effect of Isoprenaline on Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells via Regulation of Noncoding RNAs.
Yan YY, Wang ZH, Zhao L, Song DD, Qi C, Liu LL, Wang JN. Yan YY, et al. Chin Med J (Engl). 2016 Nov 20;129(22):2676-2682. doi: 10.4103/0366-6999.193452. Chin Med J (Engl). 2016. PMID: 27823999 Free PMC article. - Regulation of LncRNAs in Melanoma and Their Functional Roles in the Metastatic Process.
Melixetian M, Pelicci PG, Lanfrancone L. Melixetian M, et al. Cells. 2022 Feb 7;11(3):577. doi: 10.3390/cells11030577. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35159386 Free PMC article. Review. - Autophagy-Modulating Long Non-coding RNAs (LncRNAs) and Their Molecular Events in Cancer.
Islam Khan MZ, Tam SY, Law HKW. Islam Khan MZ, et al. Front Genet. 2019 Jan 14;9:750. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2018.00750. eCollection 2018. Front Genet. 2019. PMID: 30693021 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources