MicroRNA-320a acts as a tumor suppressor by targeting BCR/ABL oncogene in chronic myeloid leukemia - PubMed (original) (raw)
MicroRNA-320a acts as a tumor suppressor by targeting BCR/ABL oncogene in chronic myeloid leukemia
Zhu Xishan et al. Sci Rep. 2015.
Retraction in
- Retraction Note: MicroRNA-320a acts as a tumor suppressor by targeting BCR/ABL oncogene in chronic myeloid leukemia.
Xishan Z, Ziying L, Jing D, Gang L. Xishan Z, et al. Sci Rep. 2023 Mar 2;13(1):3571. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-30736-3. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36864099 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Accumulating evidences demonstrated that the induction of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and aberrant expression of microRNAs (miRNAs) are associated with tumorigenesis, tumor progression, metastasis and relapse in cancers, including chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). We found that miR-320a expression was reduced in K562 and in CML cancer stem cells. Moreover, we found that miR-320a inhibited K562 cell migration, invasion, proliferation and promoted apoptosis by targeting BCR/ABL oncogene. As an upstream regulator of BCR/ABL, miR-320a directly targets BCR/ABL. The enhanced expression of miR-320a inhibited the phosphorylation of PI3K, AKT and NF-κB; however, the expression of phosphorylated PI3K, AKT and NF-κB were restored by the overexpression of BCR/ABL. In K562, infected with miR-320a or transfected with SiBCR/ABL, the protein levels of fibronectin, vimentin, and N-cadherin were decreased, but the expression of E-cadherin was increased. The expression of mesenchymal markers in miR-320a-expressing cells was restored to normal levels by the restoration of BCR/ABL expression. Generally speaking, miR-320a acts as a novel tumor suppressor gene in CML and miR-320a can decrease migratory, invasive, proliferative and apoptotic behaviors, as well as CML EMT, by attenuating the expression of BCR/ABL oncogene.
Figures
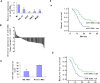
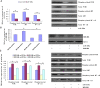
Figure 1. Downregulation of miR-320a expression in CML cell lines and CML cancer stem cells compared with the corresponding controls.
(A). Relative expression of miR-320a in 4 CML cell lines and one normal control were detected by qRT-PCR. All experiments were repeated at least three times. Each bar represents the mean of three independent experiments. *P < 0.05. (B). Relative expression of miR-320a in 70 specimens of CML cancer stem cells and normal MSCs were carried out by qRT-PCR. Data are shown as –△△CT values. (C) The mean and standard deviation of miR-320a expression levels in 70 specimens of CML cancer stem cells and normal MSCs were shown. Data are presented as 2−△Ct values (**P < 0.01). (D). Survival analysis of CML. OS and RFS curves for 90 CML patients with high or low miR-320a expression were constructed using the Kaplan-Meier method and evaluated using the log-rank test.
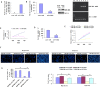
Figure 2. miR-320a inhibits CML cell migration, invasion, proliferation and induces apoptosis.
(A) The miR-320a expression was significantly increased in K562 after infection with LV-hsa-miR-320a. (B) The BCR/ABL expression was significantly decreased in K562 after infection with LV-hsa-miR-320a. (C) K562 proliferation was significantly reduced after LV-hsa-miR-320a infection compared with cont-miR infection. (D) miR-320a overexpression significantly inhibited the colony-forming ability of K562. (E–G) K562 cell migration, invasion, proliferation and apoptosis were restored after BCR/ABL restoration. The data represent the means ± s.d.; *p < 0.001, **p < 0.05, ***p < 0.01.
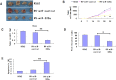
Figure 3. Overexpression of miR-320a inhibits tumorigenicity and increases apoptosis in vivo.
(A) Photographs of tumors derived from RV-miR-320a, RV-miR-control or K562 cells in nude mice. (B) Growth kinetics of tumors in nude mice. Tumor diameters were measured every 7 days. (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01).(C) Average weight of tumors in nude mice. (**p < 0.01). (D) Comparison of proliferation index. (*p < 0.05). (E) The percentage of apoptotic cells was counted. (**p < 0.01).
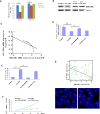
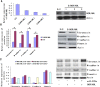
Figure 4. miR-320a directly targets BCR/ABL.
(A) The 3′-UTR element of BCR/ABL messenger RNA was partially complementary to miR-320a. miR-320a, anti-miR-320a or scramble control and luciferase reporter containing either a wild type or a mutant 3′-UTR were co-transfected into HEK-293T cells. And a Renilla luciferase expressing construct exerts as internal control. (B) Western blot analysis of BCR/ABL expression in K562 cells infected with miR-320a, and NC transfected with miR-320a inhibitors (Anti-miR-320a). The gels have been run under the same experimental conditions. (C). Analysis of correlation of miR-320a and BCR/ABL expression in CML cancer stem cells and normal MSCs. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. The analysis indicated that BCR/ABL and miR-320a were negatively correlated. (D–F) BCR/ABL abrogated the suppressive roles of miR-320a in K562 invasion and growth. K562 cells stably expressing miR-320a or scramble were transfect with or without BCR/ABL plasmids. Invasion assays (D), apoptosis analysis (E) and cell proliferation analysis (F) were performed with the above cells as described in Materials and Methods. Data are presented as mean ± s.e.m from at least three independent experiments. (G) Spearman’s correlation scatter plot of the levels of miR-320a (determined by in situ hybridization) and BCR/ABL protein (determined by immunohistochemistry) in 90 CML specimens. Representative images of BCR/ABL expression by immunohistochemistry were shown. Original magnification: ×200.
Figure 5. miR-320a down-regulates the phosphorylation of PI3K, AKT and NF-κB via BCR/ABL.
(A) The phosphorylation and total expression levels of PI3K, AKT and NF-κB in K562 cells infected with LV-hsa-miR-320a or cont-miR. (B) An immunoblot analysis of BCR/ABL expression in K562 cells infected with LV-hsa-miR-320a or cont-miR, with or without BCR/ABL restoration. (C) The phosphorylation and total expression levels of PI3K, AKT and NF-κB in K562 cells infected with LV-hsa-miR-320a or cont-miR, with or without BCR/ABL restoration. The expression levels of the phosphorylated proteins were normalized to those of the respective total proteins. The data represent the means ± s.d.; *p < 0.01. All the gels have been run under the same experimental conditions.
Figure 6. miR-320a promotes an epithelial phenotype in K562.
(A) Right panel: BCR/ABL expression was detected by western blot in K562 cells after treatment with 3 independent siRNA sequences (siNRP1) or a control (siC). Left panel: Relative expression of BCR/ABL was shown in the histogram. (B) Right panel: An immunoblot analysis of N-cadherin, vimentin, fibronectin and E-cadherin in K562 cells transfected with siNRP1 or siC. Left panel: Relative expression of proteins was shown in the histogram. (C) An immunoblot analysis of N-cadherin, vimentin, fibronectin and Ecadherin in K562 cells infected with LV-hsa-miR-320a or cont-miR, with or without BCR/ABL restoration. The protein expression levels were normalized to Actin. The data represent the means ± s.d.; *p < 0.01. All the gels have been run under the same experimental conditions.
Similar articles
- The malignancy suppression role of miR-23a by targeting the BCR/ABL oncogene in chromic myeloid leukemia.
Xishan Z, Xianjun L, Ziying L, Guangxin C, Gang L. Xishan Z, et al. Cancer Gene Ther. 2014 Sep;21(9):397-404. doi: 10.1038/cgt.2014.44. Epub 2014 Sep 12. Cancer Gene Ther. 2014. PMID: 25213664 - ApoptomiRs expression modulated by BCR-ABL is linked to CML progression and imatinib resistance.
Ferreira AF, Moura LG, Tojal I, Ambrósio L, Pinto-Simões B, Hamerschlak N, Calin GA, Ivan C, Covas DT, Kashima S, Castro FA. Ferreira AF, et al. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2014 Jun-Aug;53(1-2):47-55. doi: 10.1016/j.bcmd.2014.02.008. Epub 2014 Mar 11. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2014. PMID: 24629639 - Deregulated expression of miR-29a-3p, miR-494-3p and miR-660-5p affects sensitivity to tyrosine kinase inhibitors in CML leukemic stem cells.
Salati S, Salvestrini V, Carretta C, Genovese E, Rontauroli S, Zini R, Rossi C, Ruberti S, Bianchi E, Barbieri G, Curti A, Castagnetti F, Gugliotta G, Rosti G, Bergamaschi M, Tafuri A, Tagliafico E, Lemoli R, Manfredini R. Salati S, et al. Oncotarget. 2017 Jul 25;8(30):49451-49469. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.17706. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28533480 Free PMC article. - Chronic myelogenous leukemia: molecular and cellular aspects.
Pasternak G, Hochhaus A, Schultheis B, Hehlmann R. Pasternak G, et al. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 1998;124(12):643-60. doi: 10.1007/s004320050228. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 1998. PMID: 9879825 Review. - Emerging role of miR-320a in lung cancer: a comprehensive review.
Mohanta A, Kumar RR, Singh RK, Mandal S, Yadav R, Khatkar R, Sharma U, Uttam V, Rana MK, Rana AP, Jain A. Mohanta A, et al. Biomark Med. 2023 Sep;17(18):767-781. doi: 10.2217/bmm-2023-0215. Epub 2023 Dec 14. Biomark Med. 2023. PMID: 38095986 Review.
Cited by
- Network-based analysis implies critical roles of microRNAs in the long-term cellular responses to gold nanoparticles.
Falagan-Lotsch P , Murphy CJ . Falagan-Lotsch P , et al. Nanoscale. 2020 Nov 7;12(41):21172-21187. doi: 10.1039/d0nr04701e. Epub 2020 Sep 29. Nanoscale. 2020. PMID: 32990715 Free PMC article. - MicroRNA-320a suppresses tumor progression by targeting PBX3 in gastric cancer and is downregulated by DNA methylation.
Li YS, Zou Y, Dai DQ. Li YS, et al. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2019 Oct 15;11(10):842-856. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v11.i10.842. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31662823 Free PMC article. - Overexpression of miR-574-3p suppresses proliferation and induces apoptosis of chronic myeloid leukemia cells via targeting IL6/JAK/STAT3 pathway.
Yang H, Zhang J, Li J, Zhao F, Shen Y, Xing X. Yang H, et al. Exp Ther Med. 2018 Nov;16(5):4296-4302. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.6700. Epub 2018 Sep 5. Exp Ther Med. 2018. PMID: 30344703 Free PMC article. - Chronic myelogenous leukemia cells remodel the bone marrow niche via exosome-mediated transfer of miR-320.
Gao X, Wan Z, Wei M, Dong Y, Zhao Y, Chen X, Li Z, Qin W, Yang G, Liu L. Gao X, et al. Theranostics. 2019 Jul 28;9(19):5642-5656. doi: 10.7150/thno.34813. eCollection 2019. Theranostics. 2019. PMID: 31534508 Free PMC article. - MiR-15a-5p negatively regulates cell survival and metastasis by targeting CXCL10 in chronic myeloid leukemia.
Chen D, Wu D, Shao K, Ye B, Huang J, Gao Y. Chen D, et al. Am J Transl Res. 2017 Sep 15;9(9):4308-4316. eCollection 2017. Am J Transl Res. 2017. PMID: 28979704 Free PMC article.
References
- Joshi D., Chandrakala S., Korgaonkar S., Ghosh K. & Vundinti B. R. Down-regulation of miR-199b associated with imatinib drug resistance in 9q34.1 deleted BCR/ABL positive CML patients. Gene. 542, 109–112 (2014). - PubMed
- Shibuta T. et al.. Imatinib induces demethylation of miR-203 gene: an epigenetic mechanism of anti-tumor effect of imatinib. Leuk Res. 37, 1278–1286 (2013). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous