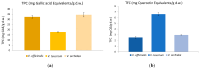Phytochemical Characterization of Veronica officinalis L., V. teucrium L. and V. orchidea Crantz from Romania and Their Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Properties - PubMed (original) (raw)
Phytochemical Characterization of Veronica officinalis L., V. teucrium L. and V. orchidea Crantz from Romania and Their Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Properties
Andrei Mocan et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2015.
Abstract
Aerial parts of Veronica species are used in Romanian traditional medicine for the treatment of various conditions like kidney diseases, cough, and catarrh, and are known for their wound-healing properties. In the present study, the phenolic and sterolic content and the antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of three Veronica species (Plantaginaceae), V. officinalis L., V. teucrium L. and V. orchidea Crantz, were studied. The identification and quantification of several phenolic compounds and phytosterols were performed using LC/MS techniques and the main components were p-coumaric acid, ferulic acid, luteoline, hispidulin and β-sitosterol. More than that, hispidulin, eupatorin and eupatilin were detected for the first time in the Veronica genus. Nevertheless, representatives of the Veronica genus were never investigated in terms of their phytosterol content. The antioxidant potential investigated by Trolox equivelents antioxidant capacity (TEAC) and EPR spectroscopy revealed that V. officinalis and V. orchidea extracts presented similar antioxidant capacities, whilst the values registered for V. teucrium extract are lower. Regarding the antimicrobial activity of the investigated species, Staphylococcus aureus, Listeria monocytogenes and Listeria ivanovii were the most sensitive strains with MIC values between 3.9 and 15.62 mg/mL. The results obtained by this study may serve to promote better use of representatives from the genus Veronica as antioxidant and antimicrobial agents.
Keywords: V. orchidea Crantz; V. teucrium L.; Veronica officinalis L.; antimicrobials; antioxidants; phytosterols.
Figures
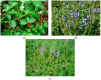
Figure 1
(a) V. officinalis L.; (b) V. teucrium L.; (c) V. orchidea Crantz.
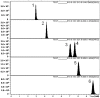
Figure 2
Tipical chromatogram of the six analyzed flavones: (1) jaceosidin; (2) hispidulin; (3) eupalitin; (4) eupatorin; (5) casticin and (6) acacetin.
Figure 3
(a) Total phenol content (TPC) and (b) total flavonoid content (TFC) of Veronica species (the bars indicate mean ± SD).
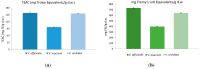
Figure 4
(a) Trolox equivelents antioxidant capacity (TEAC) and (b) antioxidant activity measured with EPR spectroscopy using Fremy’s salt as a stable synthetic radical of Veronica species (the bars indicate mean ± SD).
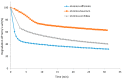
Figure 5
Degradation kinetics of the free radical Fremy’s salt by V. officinalis, V. teucrium and V. orchidea.
Similar articles
- Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Properties of Veronica spicata L. (Plantaginaceae).
Dunkić V, Kosalec I, Kosir IJ, Potocnik T, Cerenak A, Koncic MZ, Vitali D, Muller ID, Kopricanec M, Bezic N, Srecec S, Kremer D. Dunkić V, et al. Curr Drug Targets. 2015;16(14):1660-70. doi: 10.2174/1389450116666150531161820. Curr Drug Targets. 2015. PMID: 26028041 - Phytochemical Analysis, Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activities of Helichrysum arenarium (L.) Moench. and Antennaria dioica (L.) Gaertn. Flowers.
Babotă M, Mocan A, Vlase L, Crișan O, Ielciu I, Gheldiu AM, Vodnar DC, Crișan G, Păltinean R. Babotă M, et al. Molecules. 2018 Feb 13;23(2):409. doi: 10.3390/molecules23020409. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 29438342 Free PMC article. - Chemical Profiling and Assessment of Antineurodegenerative and Antioxidant Properties of Veronica teucrium L. and Veronica jacquinii Baumg.
Živković JČ, Barreira JCM, Šavikin KP, Alimpić AZ, Stojković DS, Dias MI, Santos-Buelga C, Duletić-Laušević SN, Ferreira ICFR. Živković JČ, et al. Chem Biodivers. 2017 Aug;14(8). doi: 10.1002/cbdv.201700167. Epub 2017 Jul 7. Chem Biodivers. 2017. PMID: 28488389 - Veronica Plants-Drifting from Farm to Traditional Healing, Food Application, and Phytopharmacology.
Salehi B, Shivaprasad Shetty M, V Anil Kumar N, Živković J, Calina D, Oana Docea A, Emamzadeh-Yazdi S, Sibel Kılıç C, Goloshvili T, Nicola S, Pignata G, Sharopov F, Del Mar Contreras M, Cho WC, Martins N, Sharifi-Rad J. Salehi B, et al. Molecules. 2019 Jul 4;24(13):2454. doi: 10.3390/molecules24132454. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31277407 Free PMC article. Review. - Arbutus species (Ericaceae) as source of valuable bioactive products.
Tenuta MC, Tundis R, Xiao J, Loizzo MR, Dugay A, Deguin B. Tenuta MC, et al. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2019;59(6):864-881. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2018.1551777. Epub 2018 Dec 22. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2019. PMID: 30582347 Review.
Cited by
- Identification of Phenolic Compounds Present in Three Speedwell (Veronica L.) Species and Their Antioxidant Potential.
Vrca I, Orhanović S, Pezelj I, Sušić K, Dunkić V, Kremer D, Nazlić M. Vrca I, et al. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Jun 17;13(6):738. doi: 10.3390/antiox13060738. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38929177 Free PMC article. - Isolation of Volatile Compounds by Microwave-Assisted Extraction from Six Veronica Species and Testing of Their Antiproliferative and Apoptotic Activities.
Vrca I, Čikeš Čulić V, Lozić M, Dunkić N, Kremer D, Ruščić M, Nazlić M, Dunkić V. Vrca I, et al. Plants (Basel). 2023 Sep 12;12(18):3244. doi: 10.3390/plants12183244. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37765408 Free PMC article. - Hydrosols of Veronica Species_-_Natural Source of Free Volatile Compounds with Potential Pharmacological Interest.
Nazlić M, Akrap K, Kremer D, Dunkić V. Nazlić M, et al. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Nov 9;15(11):1378. doi: 10.3390/ph15111378. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36355550 Free PMC article. - Hydrodistillation and Microwave Extraction of Volatile Compounds: Comparing Data for Twenty-One Veronica Species from Different Habitats.
Dunkić V, Nazlić M, Ruščić M, Vuko E, Akrap K, Topić S, Milović M, Vuletić N, Puizina J, Jurišić Grubešić R, Srečec S, Kremer D. Dunkić V, et al. Plants (Basel). 2022 Mar 28;11(7):902. doi: 10.3390/plants11070902. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35406882 Free PMC article. - Anti-Anemic Effect of Antioxidant-Rich Apple Vinegar against Phenylhydrazine-Induced Hemolytic Anemia in Rats.
Ousaaid D, Ghouizi AE, Laaroussi H, Bakour M, Mechchate H, Es-Safi I, Kamaly OA, Saleh A, Conte R, Lyoussi B, El Arabi I. Ousaaid D, et al. Life (Basel). 2022 Feb 4;12(2):239. doi: 10.3390/life12020239. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35207526 Free PMC article.
References
- Pratt D.E. Phenolic Compounds in Food and Their Effects on Health II. American Chemical Society; Washington, DC, USA: 1992. pp. 352–391.
- Pop A., Berce C., Bolfă P., Nagy A., Cătoi C., Dumitrescu I.B., Silaghi-Dumitrescu L., Loghin F. Evaluation of the possible endocrine disruptive effect of butylated hydroxitoluene and propyl gallate in immature female rats. Farmacia. 2013;61:202–211.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical