Antibiotic susceptibility profile of bacilli isolated from the skin of healthy humans - PubMed (original) (raw)
Antibiotic susceptibility profile of bacilli isolated from the skin of healthy humans
Prashant Tarale et al. Braz J Microbiol. 2015 Oct-Dec.
Abstract
In the present work, twelve bacilli were isolated from four different regions of human skin from Bela population of Nagpur district, India. The isolated bacilli were identified by their morphological, cultural and biochemical characteristics. Seven isolates were Gram negative rods, out of which five were belong to genus Pseudomonas. Three among the five Gram positive isolates were identified as Dermabactor and the remaining two Bacillus. Their antimicrobial susceptibility profile was determined by Kirby-Bauer disc diffusion method. The isolates showed resistance to several currently used broad-spectrum antibiotics. The Dermabactor genus was resistant to vancomycin, although it was earlier reported to be susceptible. Imipenem was found to be the most effective antibiotic for Pseudomonas while nalidixic acid, ampicillin and tetracycline were ineffective. Isolates of Bacillus displayed resistance to the extended spectrum antibiotics cephalosporin and ceftazidime. Imipenem, carbenicillin and ticarcillin were found to be the most effective antibiotics as all the investigated isolates were susceptible to them. Antibiotic resistance may be due to the overuse or misuse of antibiotics during the treatment, or following constant exposure to antibiotic-containing cosmetic formulations.
Figures
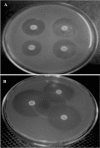
Figure 1. Representative result for antibiotic susceptibility profile. Zone of inhibition obtained on Mueller Hinton (MH) agar for (A) 10IE isolate and (B) 7IE2 isolate.
Figure 2. Representative result for lipid hydrolysis on tributyrin agar.
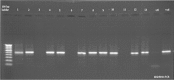
Figure 3. Agarose gel showing amplification of 16S rRNA genes from different isolates. Lane 1- 9IE, 2- 4IE, 3- 15IE, 4- 7IE2, 5- 7J, 6- 10IE, 7- 10J, 8- 14J, 9- 14FH, 10- 14C, 11- 12JY, 12- 13C, 13- 5CT.
Figure 4. Agarose gel amplification of Lipase A gene from different isolates. Lane 54- 9IE, 55- 4IE, 56- 15IE, 57- 7IE2, 58- 7J, 59- 10IE, 60- 10J, 61- 14J, 62- 14FH, 63- 14C, 64- 12JY, 65- 13C, 66- 5CT.
Similar articles
- Bacteriologic profile and antibiogram of blood culture isolates from a children's hospital in Kabul.
Tariq TM. Tariq TM. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2014 Jun;24(6):396-399. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2014. PMID: 24953929 - Antimicrobial activity and spectrum investigation of eight broad-spectrum beta-lactam drugs: a 1997 surveillance trial in 102 medical centers in the United States. Cefepime Study Group.
Jones RN, Pfaller MA, Doern GV, Erwin ME, Hollis RJ. Jones RN, et al. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1998 Mar;30(3):215-28. doi: 10.1016/s0732-8893(97)00234-4. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1998. PMID: 9572029 - Ceftobiprole: a review of a broad-spectrum and anti-MRSA cephalosporin.
Zhanel GG, Lam A, Schweizer F, Thomson K, Walkty A, Rubinstein E, Gin AS, Hoban DJ, Noreddin AM, Karlowsky JA. Zhanel GG, et al. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2008;9(4):245-54. doi: 10.2165/00128071-200809040-00004. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2008. PMID: 18572975 Review. - Cefiderocol: A Siderophore Cephalosporin with Activity Against Carbapenem-Resistant and Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacilli.
Zhanel GG, Golden AR, Zelenitsky S, Wiebe K, Lawrence CK, Adam HJ, Idowu T, Domalaon R, Schweizer F, Zhanel MA, Lagacé-Wiens PRS, Walkty AJ, Noreddin A, Lynch Iii JP, Karlowsky JA. Zhanel GG, et al. Drugs. 2019 Feb;79(3):271-289. doi: 10.1007/s40265-019-1055-2. Drugs. 2019. PMID: 30712199 Review.
Cited by
- Microbial Biosurfactants in Cosmetic and Personal Skincare Pharmaceutical Formulations.
Adu SA, Naughton PJ, Marchant R, Banat IM. Adu SA, et al. Pharmaceutics. 2020 Nov 16;12(11):1099. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12111099. Pharmaceutics. 2020. PMID: 33207832 Free PMC article. Review. - Bacterial contamination of human skin allografts and antimicrobial resistance: a skin bank problem.
Meneghetti KL, do Canto Canabarro M, Otton LM, Dos Santos Hain T, Geimba MP, Corção G. Meneghetti KL, et al. BMC Microbiol. 2018 Sep 24;18(1):121. doi: 10.1186/s12866-018-1261-1. BMC Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30249183 Free PMC article. - Antimicrobial resistance development following surgical site infections.
Călina D, Docea AO, Rosu L, Zlatian O, Rosu AF, Anghelina F, Rogoveanu O, Arsene AL, Nicolae AC, Drăgoi CM, Tsiaoussis J, Tsatsakis AM, Spandidos DA, Drakoulis N, Gofita E. Călina D, et al. Mol Med Rep. 2017 Feb;15(2):681-688. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2016.6034. Epub 2016 Dec 13. Mol Med Rep. 2017. PMID: 27959419 Free PMC article.
References
- Barak O, Treat JR, James WD. Antimicrobial peptides: Effect of innate immunity in the skin. Adv Dematol. 2005;2:357–374. - PubMed
- Berlau J, Aucken H, Malnick H, et al. Distribution of Acinetobactor species of skin of healthy human. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect. 1999;18:179–183. - PubMed
- Bojar KA, Holland KT. The human cutaneous microbiota and factors controlling colonization. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2002;18:889–903.
- Brockman ER. In: Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology. Sneath PHA, Mair NS, Sharpe ME, Holt JG, editors. Vol. 3. Williams & Wilkins; Baltimore: 1986.
- Cabello F, Godfrey H, Tomova A, et al. Antimicrobial use in aquaculture re-examined: its relevance to antimicrobial resistance and to animal and human health. Environ Microbiol. 2013;15:1917–1942. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical