Urinothorax: Case report and systematic review of the literature - PubMed (original) (raw)
Case Reports
Urinothorax: Case report and systematic review of the literature
Alexander Casallas et al. Urol Ann. 2016 Jan-Mar.
Abstract
Urinothorax, the presence of urine in the pleural space, is a rare cause of pleural effusion, usually associated with obstructive uropathy, or urinary trauma. We present the case of a 3 year-old boy and a systematic review of the literature of the 44 cases encountered. After resection of a Wilm's tumour in the right kidney our patient presented acute respiratory distress associated with radiographically confirmed pleural effusion. With the initial diagnosis of pneumonia or malignant pleural effusion, a closed thoracotomy was performed. The liquid obtained suggested urine, which was confirmed by the laboratory. Cystoscopy with retrograde pyelography detected a fistula on the posterior wall of the right kidney. The report of cases worldwide is low, probably due to its low incidence but also to underdiagnosis. Respiratory symptoms are not always present and urological symptoms usually predominate. Diagnosis requires a high degree of clinical suspicion and is confirmed by the main biochemical marker: The ratio >1.0 pleural fluid creatinine and creatinine serum.
Keywords: Pleural effusion; Wilms tumor; urinothorax; urologic surgical procedures.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: None.
Figures
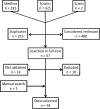
Figure 1
Systematic review flowchart
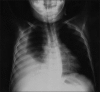
Figure 2
Chest radiography of a 3-year-old boy with right pleural effusion
Similar articles
- Shortness of Breath: An Unusual Presentation of Bladder Injury. A Case Report and Literature Review of Urinothorax.
Ramahi A, Aburayyan KM, Alqahtani A, Said Ahmed TS, Taleb M. Ramahi A, et al. Cureus. 2019 Apr 28;11(4):e4559. doi: 10.7759/cureus.4559. Cureus. 2019. PMID: 31281743 Free PMC article. - Pleural Effusion Secondary to Obstructive Uropathy: A Case of Urinothorax.
Freitas A, Coelho T, Beça S, Gregório T. Freitas A, et al. Eur J Case Rep Intern Med. 2020 Sep 16;7(12):001865. doi: 10.12890/2020_001865. eCollection 2020. Eur J Case Rep Intern Med. 2020. PMID: 33312995 Free PMC article. - Case of urinothorax - A rare presentation.
Chawla AK, Chaudhary G, Chawla MK, Chawla R, Chawla PS. Chawla AK, et al. Lung India. 2020 Jan-Feb;37(1):53-56. doi: 10.4103/lungindia.lungindia_95_19. Lung India. 2020. PMID: 31898621 Free PMC article. - Urinothorax: a new approach.
Garcia-Pachon E, Romero S. Garcia-Pachon E, et al. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2006 Jul;12(4):259-63. doi: 10.1097/01.mcp.0000230628.65515.86. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2006. PMID: 16825877 Review. - Urinothorax: case report and review of the literature with emphasis on biochemical diagnosis.
Garcia-Pachon E, Padilla-Navas I. Garcia-Pachon E, et al. Respiration. 2004 Sep-Oct;71(5):533-6. doi: 10.1159/000080642. Respiration. 2004. PMID: 15467335 Review.
Cited by
- Tension urinothorax as a reversible cause of cardiac arrest: a case report.
Wanchu A, Verma A, Jaiswal S, Khatai AA, Prasad N. Wanchu A, et al. World J Emerg Med. 2023;14(6):499-501. doi: 10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2023.097. World J Emerg Med. 2023. PMID: 37969212 Free PMC article. No abstract available. - Case report: Acute dyspnea secondary to urinothorax following ureteroscopy.
McLean A, Bartman MT, Winton EB. McLean A, et al. Urol Case Rep. 2023 Sep 13;51:102565. doi: 10.1016/j.eucr.2023.102565. eCollection 2023 Nov. Urol Case Rep. 2023. PMID: 37753456 Free PMC article. - Urinothorax, a rare complication of rupture renal calyx.
Battah A, Farouji A, DaCosta T, Ahmad A, Kazmi R, DaCosta T Jr, Miller R, Farouji I. Battah A, et al. Radiol Case Rep. 2023 Apr 29;18(7):2335-2338. doi: 10.1016/j.radcr.2023.03.043. eCollection 2023 Jul. Radiol Case Rep. 2023. PMID: 37179801 Free PMC article. - Urinothorax: A Rare Cause of Pleural Effusion.
Raja A, Dhakal A, Sinyagovskiy P, Abdalla M, Afridi SM. Raja A, et al. Cureus. 2022 May 27;14(5):e25392. doi: 10.7759/cureus.25392. eCollection 2022 May. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 35774657 Free PMC article. - Spontaneous non-obstructive nephropleural fistula with an autoimmune disorder causing massive urinothorax: a rare association.
Aeron R, Goel S, Goel A, Kumar V. Aeron R, et al. BMJ Case Rep. 2017 Sep 25;2017:bcr2017221601. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2017-221601. BMJ Case Rep. 2017. PMID: 28951516 Free PMC article.
References
- Brown B, Trotter C, Cox P, Hanlon C. Urinothorax: A rare cause of pleural effusion. W V Med J. 2011;107:16–7. - PubMed
- Ameer KA, Thomas R, Sureshkumar VK, Deepak V, Srikanth P, Arjun P, et al. An unusual complication of a common gynaecological procedure. J Assoc Physicians India. 2012;61:490–2. - PubMed
- Ansari T, Idell S. Management of undiagnosed persistent pleural effusions. Clin Chest Med. 1998;19:407–17. - PubMed
- Bramley K, Puchalski JT. Defying gravity: Subdiaphragmatic causes of pleural effusions. Clin Chest Med. 2013;34:39–46. - PubMed
- Garcia-Pachon E, Romero S. Urinothorax: A new approach. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2006;12:259–63. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources