Single nucleotide polymorphism in the microRNA-199a binding site of HIF1A gene is associated with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma risk and worse clinical outcomes - PubMed (original) (raw)
Single nucleotide polymorphism in the microRNA-199a binding site of HIF1A gene is associated with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma risk and worse clinical outcomes
Xiuchao Wang et al. Oncotarget. 2016.
Abstract
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha (HIF-1α) is over-expressed in many cancers including pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) and correlated with poor prognosis. We aim to determine the effect of germline genetic variants on the regulation of the homeostasis of the miRNA-gene regulatory loop in HIF1A gene and PDAC risk. HIF1A rs2057482 single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) was genotyped in 410 PDAC cases and 490 healthy controls. The CC genotype SNP HIF1A is significantly correlated with PDAC risk (OR = 1.719, 95% CI: 1.293-2.286) and shorter overall survival (OS, P<0.0001) compared with the CT/TT alleles group. The C/T variants of rs2057482, a SNP located near the miR-199a binding site in HIF1A, could lead to differential regulation of HIF1A by miR-199a. Specifically, the C allele of rs2057482 weakened miR-199a-induced repression of HIF-1α expression on both mRNA and protein levels. In the PDAC tissue, individuals with the rs2057482-CC genotype expressed significantly higher levels of HIF-1α protein than those with the rs2057482-CT/TT genotype (P<0.0001). Both the CC genotype of SNP HIF1A and increased HIF-1α expression are significantly associated with shorter OS of patients with PDAC. After adjusted by TNM staging, differentiation grade, and the levels of CA19-9, both SNP HIF1A and HIF-1α expression retained highly significance on OS (P<0.0001). Taken together, our study demonstrates that host genetic variants could disturb the regulation of the miR-199a/HIF1A regulatory loop and alter PDAC risk and poor prognosis. In conclusion, the rs2057482-CC genotype increases the susceptibility to PDAC and associated with cancer progression.
Keywords: hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha (HIF-1α); microRNA-199a (miR-199a); pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC); single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP).
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures
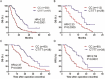
Figure 1. The association between SNP of HIF1A and survival rate in patients with PDAC
A. Kaplan–Meier survival curves of overall survival (OS) of 269 PDAC patients with the CC genotype verses the CT/TT phenotypes. B. Kaplan–Meier curves of OS for 141 advanced PDAC patients with the CC genotype verses the CT/TT phenotypes. C, D. OS (C) and relapse-free survival (RFS) (D) of 128 PDAC patients who undergoing surgical resection, presented as CC verses CT/TT genotype groups. Data were analyzed by the log-rank test and the Kaplan–Meier curves were generated by using GraphPad Prism software.
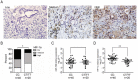
Figure 2. Relative expression levels of miR-199a and HIF-1α in PDAC tissues
A. Immunohistochemical staining of HIF-1α in PDAC with low-, medium- and high-levels of HIF-1α expression; B. The frequency distribution of levels of HIF-1α expression between CC and CT/TT genotype groups (n = 60, *P < 0.05); C. Levels of miR-199a expression in PDAC tissues of CC or CT/TT genotype groups (n=60); D. Comparison of HIF-1α protein expression in samples with the CC genotype and CT/TT genotypes (n = 60, **P< 0.01).
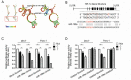
Figure 3. miR-199a differential regulation of the SNP rs2057482
A. The predicted secondary structure of the HIF-1α mRNA. The secondary structures of the 3′UTR of HIF1A were predicted by inputting two 302-nt long DNA sequences centering rs2057482 into RNA fold, with either the rs2057482-C (left) or rs2057482-T (right) allele. The figures and the values of minimum free energy (MFE) were generated by RNAfold (
); B. Schematic representation of the sequences of human miR-199a and its target site the 3′ UTR of HIF1A. The rs2057482 SNP is located 8 nucleotides (nt) downstream of the “seed complementary sequence” of miR-199a in HIF1A. C, D. Effects of rs2057482 genotypes on the expression of HIF1A gene in HEK-293T and Panc-1 cell lines. Forty-eight hours after transfection of the reporter gene and miR-199a mimic, the roles of construct with C or T allele on relative luciferase activity were compared in HEK-293T and Panc-1 cell lines (*P <0.05, **P <0.01). Data shown are mean ± SD of three independent experiments.
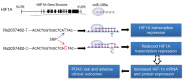
Figure 4. The role of miR-199a in the regulation of HIF1A transcription
The variant rs2057482 is a change of C-to-T located at 8bp downstream of the binding site of miR-199a in the 3 UTR of the HIF1A gene. MiR-199a is processed in pancreatic ductal epithelial cells and binds to the 3′UTR of the HIF1A gene. The rs2057482 C allele affects the miR-199a binding site at HIF1A 3′UTR, which damages the binding ability of miR-199a and results in the reduced degradation of HIF-1αmRNA and subsequently increases its translation, which may enhances PDAC risk and the development of PDAC.
Similar articles
- Polymorphisms in the hypoxia-inducible factor-1α gene confer susceptibility to pancreatic cancer.
Wang X, Liu Y, Ren H, Yuan Z, Li S, Sheng J, Zhao T, Chen Y, Liu F, Wang F, Huang H, Hao J. Wang X, et al. Cancer Biol Ther. 2011 Sep 1;12(5):383-7. doi: 10.4161/cbt.12.5.15982. Epub 2011 Sep 1. Cancer Biol Ther. 2011. PMID: 21709439 - Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 promotes pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma invasion and metastasis by activating transcription of the actin-bundling protein fascin.
Zhao X, Gao S, Ren H, Sun W, Zhang H, Sun J, Yang S, Hao J. Zhao X, et al. Cancer Res. 2014 May 1;74(9):2455-64. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-3009. Epub 2014 Mar 5. Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 24599125 - A nicotine-induced positive feedback loop between HIF1A and YAP1 contributes to epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
Ben Q, An W, Sun Y, Qian A, Liu J, Zou D, Yuan Y. Ben Q, et al. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020 Sep 7;39(1):181. doi: 10.1186/s13046-020-01689-6. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32894161 Free PMC article. - Association between HIF-1α C1772T/G1790A polymorphisms and cancer susceptibility: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis based on 40 case-control studies.
Yan Q, Chen P, Wang S, Liu N, Zhao P, Gu A. Yan Q, et al. BMC Cancer. 2014 Dec 15;14:950. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-950. BMC Cancer. 2014. PMID: 25496056 Free PMC article. Review. - Candidate microRNA biomarkers of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: meta-analysis, experimental validation and clinical significance.
Ma MZ, Kong X, Weng MZ, Cheng K, Gong W, Quan ZW, Peng CH. Ma MZ, et al. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2013 Sep 28;32(1):71. doi: 10.1186/1756-9966-32-71. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 24289824 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Serum insulin-like growth factor binding protein 2 levels as biomarker for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma-associated malnutrition and muscle wasting.
Dong J, Yu J, Li Z, Gao S, Wang H, Yang S, Wu L, Lan C, Zhao T, Gao C, Liu Z, Wang X, Hao J. Dong J, et al. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2021 Jun;12(3):704-716. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.12692. Epub 2021 Mar 24. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2021. PMID: 33763996 Free PMC article. - Genetic variation rs7930 in the miR-4273-5p target site is associated with a risk of colorectal cancer.
Lee AR, Park J, Jung KJ, Jee SH, Kim-Yoon S. Lee AR, et al. Onco Targets Ther. 2016 Nov 7;9:6885-6895. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S108787. eCollection 2016. Onco Targets Ther. 2016. PMID: 27853382 Free PMC article. - Is there a dose-dependent effect of genetic susceptibility loci for gastric cancer on prognosis of the patients?
Cheng L, Qiu LX, Jia M, Zhou F, Wang MY, Zhang RX, Yang Y, Wang X, Wang J, Jin L, Wei QY. Cheng L, et al. Oncotarget. 2017 Mar 14;8(11):18435-18443. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13123. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 27821817 Free PMC article. - MiRNA-646-mediated reciprocal repression between HIF-1α and MIIP contributes to tumorigenesis of pancreatic cancer.
Niu Y, Jin Y, Deng SC, Deng SJ, Zhu S, Liu Y, Li X, He C, Liu ML, Zeng Z, Chen HY, Zhong JX, Ye Z, Wang CY, Zhao G. Niu Y, et al. Oncogene. 2018 Mar;37(13):1743-1758. doi: 10.1038/s41388-017-0082-2. Epub 2018 Jan 18. Oncogene. 2018. PMID: 29343850 - Genetic Susceptibility in Understanding of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Risk: A Decade-Long Effort of the PANDORA Consortium.
Vodickova L, Horak J, Vodicka P. Vodickova L, et al. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2022 May 4;31(5):942-948. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-21-1340. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2022. PMID: 35506247 Free PMC article.
References
- Hidalgo M. Pancreatic cancer. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:1605–1617. - PubMed
- Song F, He M, Li H, Qian B, Wei Q, Zhang W, Chen K, Hao X. A cancer incidence survey in Tianjin: the third largest city in China-between 1981 and 2000. Cancer Causes Control. 2008;19:443–450. - PubMed
- Daemen A, Peterson D, Sahu N, McCord R, Du X, Liu B, Kowanetz K, Hong R, Moffat J, Gao M, Boudreau A, Mroue R, Corson L, et al. Metabolite profiling stratifies pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas into subtypes with distinct sensitivities to metabolic inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015;112:E4410–4417. - PMC - PubMed
- Wang X, Liu Y, Ren H, Yuan Z, Li S, Sheng J, Zhao T, Chen Y, Liu F, Wang F, Huang H, Hao J. Polymorphisms in the hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha gene confer susceptibility to pancreatic cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 2011;12:383–387. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical