MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets - PubMed (original) (raw)
MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets
Sudhir Kumar et al. Mol Biol Evol. 2016 Jul.
Abstract
We present the latest version of the Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (Mega) software, which contains many sophisticated methods and tools for phylogenomics and phylomedicine. In this major upgrade, Mega has been optimized for use on 64-bit computing systems for analyzing larger datasets. Researchers can now explore and analyze tens of thousands of sequences in Mega The new version also provides an advanced wizard for building timetrees and includes a new functionality to automatically predict gene duplication events in gene family trees. The 64-bit Mega is made available in two interfaces: graphical and command line. The graphical user interface (GUI) is a native Microsoft Windows application that can also be used on Mac OS X. The command line Mega is available as native applications for Windows, Linux, and Mac OS X. They are intended for use in high-throughput and scripted analysis. Both versions are available from www.megasoftware.net free of charge.
Keywords: evolution.; gene families; software; timetree.
© The Author 2016. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society for Molecular Biology and Evolution. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
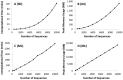
F ig . 1.
Time and memory requirements for phylogenetic analyses using the NJ method ( A , B ) and the ML analysis ( C , D ). For NJ analysis, we used the Tamura–Nei (1993) model, uniform rates of evolution among sites, and pairwise deletion option to deal with the missing data. Time usage increases polynomially with the number of sequences (third degree polynomial, R 2 = 1), as does the peak memory used ( R 2 = 1) ( A , B ). The same model and parameters were used for ML tree inference, where the time taken and the memory needs increased linearly with the number of sequences. For ML analysis, the SPR (Subtree–Pruning–Regrafting) heuristic was used for tree searching and all 5,287 sites in the sequence alignment were included. All the analyses were performed on a Dell Optiplex 9010 computer with an Intel Core-i7-3770 3.4 GHz processor, 20 GB of RAM, NVidia GeForce GT 640 graphics card, and a 64-bit Windows 7 Enterprise operating system.
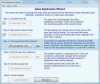
F ig . 2.
The Gene Duplication Wizard ( A ) to guide users through the process of searching gene duplication events in a gene family tree. In the first step, the user loads a gene tree from a Newick formatted text file. Second, species associated with sequences are specified using a graphical interface. In the third step, the user has the option to load a trusted species tree, in which case it will be possible to identify all duplication events in the gene tree, from a Newick file. Fourth, the user has the option to specify the root of the gene tree in a graphical interface. If the user provides a trusted species tree, then they must designate the root of that tree. Finally, the user launches the analysis and the results are displayed in the Tree Explorer window (see fig. 3 ).
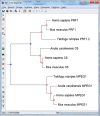
F ig . 3.
Tree Explorer window with gene duplications marked with closed blue diamonds and speciation events, if a trusted species tree is provided, are identified by open red diamonds (see fig. 2 legend for more information).
Comment in
- MEGA Evolutionary Software Re-Engineered to Handle Today's Big Data Demands.
Caspermeyer J. Caspermeyer J. Mol Biol Evol. 2016 Jul;33(7):1887. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msw074. Epub 2016 May 2. Mol Biol Evol. 2016. PMID: 27189553 No abstract available.
Similar articles
- MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 6.0.
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S. Tamura K, et al. Mol Biol Evol. 2013 Dec;30(12):2725-9. doi: 10.1093/molbev/mst197. Epub 2013 Oct 16. Mol Biol Evol. 2013. PMID: 24132122 Free PMC article. - MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms.
Kumar S, Stecher G, Li M, Knyaz C, Tamura K. Kumar S, et al. Mol Biol Evol. 2018 Jun 1;35(6):1547-1549. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msy096. Mol Biol Evol. 2018. PMID: 29722887 Free PMC article. - MEGA4: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0.
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S. Tamura K, et al. Mol Biol Evol. 2007 Aug;24(8):1596-9. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msm092. Epub 2007 May 7. Mol Biol Evol. 2007. PMID: 17488738 - Software packages for quantitative microarray-based gene expression analysis.
Dresen IM, Hüsing J, Kruse E, Boes T, Jöckel KH. Dresen IM, et al. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2003 Dec;4(6):417-37. doi: 10.2174/1389201033377436. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2003. PMID: 14683435 Review. - Alignment-free sequence comparison: benefits, applications, and tools.
Zielezinski A, Vinga S, Almeida J, Karlowski WM. Zielezinski A, et al. Genome Biol. 2017 Oct 3;18(1):186. doi: 10.1186/s13059-017-1319-7. Genome Biol. 2017. PMID: 28974235 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Disentangling the microbial genomic traits associated with aromatic hydrocarbon degradation in a jet fuel-contaminated aquifer.
Hidalgo KJ, Centurion VB, Lemos LN, Soriano AU, Valoni E, Baessa MP, Richnow HH, Vogt C, Oliveira VM. Hidalgo KJ, et al. Biodegradation. 2024 Nov 18;36(1):7. doi: 10.1007/s10532-024-10100-6. Biodegradation. 2024. PMID: 39557683 - Cryptic Diversity in Scorpaenodes xyris (Jordan & Gilbert 1882) (Scorpaeniformes: Scorpaenidae) Throughout the Tropical Eastern Pacific.
Bernal-Hernández ME, Beltrán-López RG, Robertson DR, Baldwin CC, Espinoza E, Martínez-Gómez JE, Barraza E, Angulo A, Valdiviezo-Rivera J, Acosta AFG, Domínguez-Domínguez O. Bernal-Hernández ME, et al. J Mol Evol. 2024 Nov 16. doi: 10.1007/s00239-024-10212-w. Online ahead of print. J Mol Evol. 2024. PMID: 39550524 - Taxonomy and phylogeny of rodents parasitic fleas in southeastern China with description of a new subspecies of Ctenophthalmus breviprojiciens.
Zhou S, Liu W, Zeng Z, Wang J, Han T, Xu G, Huang L, Wu S, Xiao F. Zhou S, et al. Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 16;14(1):28316. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-79492-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39550418 Free PMC article. - The chloroplast genome of Cephalanthera nanchuanica (Orchidaceae): comparative and phylogenetic analysis with other Neottieae species.
Li-Zhen L, Dong-Yan T, Wu-Fu D, Shu-Dong Z. Li-Zhen L, et al. BMC Genomics. 2024 Nov 15;25(1):1090. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-11004-8. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39548369 Free PMC article. - Epidemiological study of Newcastle disease in chicken farms in China, 2019-2022.
Wang S, Wei L, Wang J, Zhang Z. Wang S, et al. Front Vet Sci. 2024 Oct 30;11:1410878. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1410878. eCollection 2024. Front Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 39545258 Free PMC article.
References
- Kumar S Tamura K Nei M. 1994. . M ega : molecular evolutionary genetics analysis software for microcomputers . Comput Appl Biosci . 10 : 189 – 191 . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources