Specific Delivery of MiRNA for High Efficient Inhibition of Prostate Cancer by RNA Nanotechnology - PubMed (original) (raw)
Specific Delivery of MiRNA for High Efficient Inhibition of Prostate Cancer by RNA Nanotechnology
Daniel W Binzel et al. Mol Ther. 2016 Aug.
Erratum in
- Specific Delivery of MiRNA for High Efficient Inhibition of Prostate Cancer by RNA Nanotechnology.
Binzel DW, Shu Y, Li H, Sun M, Zhang Q, Shu D, Guo B, Guo P. Binzel DW, et al. Mol Ther. 2024 Jul 19:S1525-0016(24)00465-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2024.07.010. Online ahead of print. Mol Ther. 2024. PMID: 39032484 No abstract available.
Abstract
Both siRNA and miRNA can serve as powerful gene-silencing reagents but their specific delivery to cancer cells in vivo without collateral damage to healthy cells remains challenging. We report here the application of RNA nanotechnology for specific and efficient delivery of anti-miRNA seed-targeting sequence to block the growth of prostate cancer in mouse models. Utilizing the thermodynamically ultra-stable three-way junction of the pRNA of phi29 DNA packaging motor, RNA nanoparticles were constructed by bottom-up self-assembly containing the anti-prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) RNA aptamer as a targeting ligand and anti-miR17 or anti-miR21 as therapeutic modules. The 16 nm RNase-resistant and thermodynamically stable RNA nanoparticles remained intact after systemic injection in mice and strongly bound to tumors with little or no accumulation in healthy organs 8 hours postinjection, and subsequently repressed tumor growth at low doses with high efficiency.
Figures
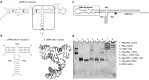
Figure 1
Design and construction of pRNA-3WJ nanoparticles harboring prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) binding aptamer and anti-miRNA LNA. (a) The sequence and secondary structure of bacteriophage phi29 packaging RNA (pRNA). (b) 3WJ core of pRNA. (c) Design of pRNA-3WJ nanoparticles harboring PSMA binding aptamer and anti-miRNA LNA. (d) 10% native TBM PAGE of A9g-3WJ-anti-miR21 nanoparticle.
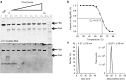
Figure 2
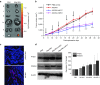
Stability and characterization of assembled pRNA-3WJ nanoparticles harboring prostate-specific membrane antigen binding aptamer and anti-miRNA LNA. (a) Assessment of chemical stability of A9g-3WJ-anti-miRNA LNA treated with 10% serum contained cell culture medium in 8% TBM native PAGE. (b) Assessment of thermodynamic stability of A9g-3WJ-anti-miRNA LNA by temperature-gradient gel electrophoresis assay. Melting profile of nanoparticle derived from PAGE with sigmoidal fitting of data to find melting temperature. (c) Hydrodynamic sizing and zeta potential measurements of the A9g-3WJ-anti-miR21 nanoparticle using a Zetasizer nano-ZS.
Figure 3
Flow cytometry assay for studying specific binding of pRNA-3WJ nanoparticles on prostate cancer cells. (a) Illustration of various design of conjugating prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) binding A9g aptamer onto the pRNA-3WJ core. Alexa647 labelled A9g-3WJ RNA nanoparticles were incubated with (b) PSMA+ LNCaP-FGC cells and (c) PSMA- PC-3 cells. Nanoparticles indicated positive binding of nanoparticles to LNCaP cells while avoiding nonspecific binding to PC-3 cells.
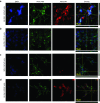
Figure 4
Confocal microscopy for assaying the binding and internalization of pRNA-3WJ nanoparticles via prostate-specific membrane antigen binding aptamer A9g. RNA nanoparticles were incubated with cell groups then fixed and stained for fluorescent imaging. (a) A9g-3WJ to LNCaP cells. (b) A9g-3WJ to PC-3 cells. (c) 3WJ control to LNCaP cells. (d) A9g aptamer control to LNCaP cells. Blue: DAPI-stained nucleus. Green: Phalloidin-Alexa 488-stained cytoplasm. Red: Alexa 647-labeled RNA nanoparticles. Overlay of three signals with z-axis scanning.
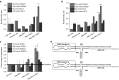
Figure 5
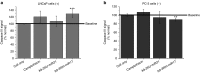
Assay for miRNA knockdown and downstream gene regulation effects of pRNA-3WJ nanoparticles harboring prostate-specific membrane antigen binding aptamer and anti-oncogenic miRNA LNA. (a) Dual-luciferase assay for evaluating delivered anti-miR21 LNA and (b) anti-miR17 LNA effects on prostate cancer cells from incubation of RNA nanoparticles. Knockdown of miRNAs led to spiked increase of reporter Renilla expression. (c) qPCR results of downstream genes PTEN and PDCD4 expression as a result of miR21 knockdown in LNCaP cells 72 hours postincubation with A9-3WJ-anti-miR21 LNA nanoparticles. (d) Design of A9g-3WJ-anti miR21 LNA and -anti-miR17 LNA nanoparticles. In all plots, *P < 0.1, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.
Figure 6
Caspase III signaling assay for apoptosis effects of pRNA-3WJ nanoparticles harboring prostate-specific membrane antigen binding aptamer and antioncogenic miRNA LNA. RNA nanoparticles with anti-miR21 and -miR17 LNA were incubated with (a) LNCaP and (b) PC-3 cells cells for 24 hours. Caspase III signaling was assayed by fluorescent reporter with peak fluorescent of 440 nm as a reporter of cell apoptosis as a result of RNA nanoparticle delivery of anti-miRNA sequences. 5 μmol/l Camptothecin was used as a positive control and benchmark of apoptosis (**P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001).
Figure 7
In vivo delivery of pRNA-3WJ nanoparticles harboring prostate-specific membrane antigen binding aptamer and anti-miRNA LNA. RNA nanoparticles were delivered as bare oligos to LNCaP C4-2 subcutaneous xenografts in nude mice. (a) Biodistribution of A9g-3WJ-Alexa647 through nude mice. B: Brain, L: Lung, S: Spleen, Lv: Liver, K: Kidney, T: Tumor. (b) Tumor-bearing nude mice were administered nanoparticles through a series of five injections through the tail vein of 20 μmol/l solution at 100 μl (indicated by arrows), while tumor volume (mm3) and total mouse weight (g) were monitored (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.0001). (c) Fluorescent confocal microscopy of tumor samples 8 hours post-i.v. administration of RNA nanoparticles. DAPI (Blue) is cell nucleus; Alexa647 (red) is RNA nanoparticle. (d) Western blot examining downstream expression of PTEN and PDCD4 from silencing of miR17 and miR21 using β-Actin as an internal control.
Similar articles
- Systemic Delivery of Anti-miRNA for Suppression of Triple Negative Breast Cancer Utilizing RNA Nanotechnology.
Shu D, Li H, Shu Y, Xiong G, Carson WE 3rd, Haque F, Xu R, Guo P. Shu D, et al. ACS Nano. 2015 Oct 27;9(10):9731-40. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.5b02471. Epub 2015 Sep 21. ACS Nano. 2015. PMID: 26387848 Free PMC article. - Fabrication of pRNA nanoparticles to deliver therapeutic RNAs and bioactive compounds into tumor cells.
Shu Y, Shu D, Haque F, Guo P. Shu Y, et al. Nat Protoc. 2013 Sep;8(9):1635-59. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2013.097. Epub 2013 Aug 1. Nat Protoc. 2013. PMID: 23928498 Free PMC article. - Using Planar Phi29 pRNA Three-Way Junction to Control Size and Shape of RNA Nanoparticles for Biodistribution Profiling in Mice.
Haque F, Xu C, Jasinski DL, Li H, Guo P. Haque F, et al. Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1632:359-380. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7138-1_23. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28730451 - RNA nanotechnology: engineering, assembly and applications in detection, gene delivery and therapy.
Guo P. Guo P. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2005 Dec;5(12):1964-82. doi: 10.1166/jnn.2005.446. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2005. PMID: 16430131 Free PMC article. Review. - Favorable biodistribution, specific targeting and conditional endosomal escape of RNA nanoparticles in cancer therapy.
Xu C, Haque F, Jasinski DL, Binzel DW, Shu D, Guo P. Xu C, et al. Cancer Lett. 2018 Feb 1;414:57-70. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2017.09.043. Epub 2017 Oct 5. Cancer Lett. 2018. PMID: 28987384 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Tuning the size, shape and structure of RNA nanoparticles for favorable cancer targeting and immunostimulation.
Guo S, Xu C, Yin H, Hill J, Pi F, Guo P. Guo S, et al. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2020 Jan;12(1):e1582. doi: 10.1002/wnan.1582. Epub 2019 Aug 27. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2020. PMID: 31456362 Free PMC article. Review. - Structure and Composition Define Immunorecognition of Nucleic Acid Nanoparticles.
Hong E, Halman JR, Shah AB, Khisamutdinov EF, Dobrovolskaia MA, Afonin KA. Hong E, et al. Nano Lett. 2018 Jul 11;18(7):4309-4321. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.8b01283. Epub 2018 Jun 20. Nano Lett. 2018. PMID: 29894623 Free PMC article. - RNA Nanotechnology to Solubilize Hydrophobic Antitumor Drug for Targeted Delivery.
Piao X, Yin H, Guo S, Wang H, Guo P. Piao X, et al. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2019 Sep 30;6(22):1900951. doi: 10.1002/advs.201900951. eCollection 2019 Nov. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2019. PMID: 31763137 Free PMC article. - Nanotechnology based approaches for detection and delivery of microRNA in healthcare and crop protection.
Chaudhary V, Jangra S, Yadav NR. Chaudhary V, et al. J Nanobiotechnology. 2018 Apr 13;16(1):40. doi: 10.1186/s12951-018-0368-8. J Nanobiotechnology. 2018. PMID: 29653577 Free PMC article. Review. - The Effect of Size and Shape of RNA Nanoparticles on Biodistribution.
Jasinski DL, Li H, Guo P. Jasinski DL, et al. Mol Ther. 2018 Mar 7;26(3):784-792. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2017.12.018. Epub 2017 Dec 22. Mol Ther. 2018. PMID: 29402549 Free PMC article.
References
- Seeman, NC (1998). DNA nanotechnology: novel DNA constructions. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct 27: 225–248. - PubMed
- Seeman, NC (2001) DNA nicks and nodes and nanotechnology. Nano Letters, 1: 22–26.
- Bellini, M, Mazzucchelli, S, Galbiati, E, Sommaruga, S, Fiandra, L, Truffi, M et al. (2014). Protein nanocages for self-triggered nuclear delivery of DNA-targeted chemotherapeutics in cancer cells. J Control Release 196: 184–196. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 EB003730/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R25 CA153954/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM114080/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA177558/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA186100/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA151648/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous