Temporal Change of the Content of 10 Oligosaccharides in the Milk of Chinese Urban Mothers - PubMed (original) (raw)
Observational Study
Temporal Change of the Content of 10 Oligosaccharides in the Milk of Chinese Urban Mothers
Sean Austin et al. Nutrients. 2016.
Abstract
Breastfed infants tend to be less prone to infections and may have improved cognitive benefits compared to formula-fed infants. Human milk oligosaccharides (HMO) are the third most abundant component of human milk, but are absent from formulae. They may be partially responsible for the benefits of breastfeeding. In this cross-sectional observational study, the HMO composition of milk from Chinese mothers was studied to determine the impact of stage of lactation, mode of delivery and geographical location. The content of 10 HMO was measured by HPLC in 446 milk samples from mothers living in three different cities in China. Around 21% of the samples contained levels of 2'-fucosyllactose (2'-FL) below the limit of quantification, which is similar to the frequency of fucosyltransferase-2 non-secretors in other populations, but 2'-FL was detected in all samples. Levels of most of the HMO studied decreased during the course of lactation, but the level of 3-fucosyllactose increased. Levels of 2'-FL and 3-fucosyllactose seem to be strongly correlated, suggesting some sort of mechanism for co-regulation. Levels of 6'-sialyllactose were higher than those of 3'-sialyllactose at early stages of lactation, but beyond 2-4 months, 3'-sialyllactose was predominant. Neither mode of delivery nor geographical location had any impact on HMO composition.
Keywords: HPLC; fucosyllactose; human milk oligosaccharides; lactation; lacto-N-fucosylpentaose; lacto-N-neotetraose; lacto-N-tetraose; sialyllactose.
Figures
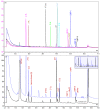
Figure 1
Chromatograms of human milk oligosaccharides (HMO). Top panel: overlay of the chromatograms of HMO standards injected individually. Lower panel: overlay of the chromatograms of pooled milk and pooled colostrum (both purchased from Lee Biosolutions, Maryland Heights, MO, USA).
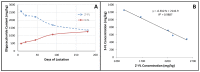
Figure 2
(A) Changes in 2′-FL and 3-FL concentration at different stages of lactation; (B) Correlation between 3-FL concentration and 2′-FL concentration.
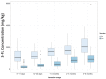
Figure 3
3-FL concentration in milk samples comparing secretor vs. non-secretor milk, where non-secretor status has been assigned to samples having 2′-FL content below the method LoQ.
Similar articles
- Human Milk Oligosaccharides Are Associated with Lactation Stage and Lewis Phenotype in a Chinese Population.
Ren X, Yan J, Bi Y, Shuttleworth PW, Wang Y, Jiang S, Wang J, Duan Y, Lai J, Yang Z. Ren X, et al. Nutrients. 2023 Mar 15;15(6):1408. doi: 10.3390/nu15061408. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 36986137 Free PMC article. - Six Oligosaccharides' Variation in Breast Milk: A Study in South China from 0 to 400 Days Postpartum.
Liu S, Cai X, Wang J, Mao Y, Zou Y, Tian F, Peng B, Hu J, Zhao Y, Wang S. Liu S, et al. Nutrients. 2021 Nov 11;13(11):4017. doi: 10.3390/nu13114017. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34836272 Free PMC article. - Major human milk oligosaccharides are absorbed into the systemic circulation after oral administration in rats.
Vazquez E, Santos-Fandila A, Buck R, Rueda R, Ramirez M. Vazquez E, et al. Br J Nutr. 2017 Jan;117(2):237-247. doi: 10.1017/S0007114516004554. Epub 2017 Feb 9. Br J Nutr. 2017. PMID: 28179042 - Weighted analysis of 2'-fucosyllactose, 3-fucosyllactose, lacto-N-tetraose, 3'-sialyllactose, and 6'-sialyllactose concentrations in human milk.
Conze DB, Kruger CL, Symonds JM, Lodder R, Schönknecht YB, Ho M, Derya SM, Parkot J, Parschat K. Conze DB, et al. Food Chem Toxicol. 2022 May;163:112877. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2022.112877. Epub 2022 Mar 16. Food Chem Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 35304182 Review. - Dynamic Changes in Human Milk Oligosaccharides in Chinese Population: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.
Zhou Y, Sun H, Li K, Zheng C, Ju M, Lyu Y, Zhao R, Wang W, Zhang W, Xu Y, Jiang S. Zhou Y, et al. Nutrients. 2021 Aug 24;13(9):2912. doi: 10.3390/nu13092912. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34578788 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Dynamics of human milk oligosaccharides in early lactation and relation with growth and appetitive traits of Filipino breastfed infants.
Samuel TM, Hartweg M, Lebumfacil JD, Buluran KB, Lawenko RB, Estorninos EM, Binia A, Sprenger N. Samuel TM, et al. Sci Rep. 2022 Oct 15;12(1):17304. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-22244-7. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36243744 Free PMC article. - Exploring the Potential of Human Milk and Formula Milk on Infants' Gut and Health.
Chong HY, Tan LT, Law JW, Hong KW, Ratnasingam V, Ab Mutalib NS, Lee LH, Letchumanan V. Chong HY, et al. Nutrients. 2022 Aug 29;14(17):3554. doi: 10.3390/nu14173554. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36079814 Free PMC article. Review. - Interactions between Bifidobacterium and Bacteroides and human milk oligosaccharides and their associations with infant cognition.
Cho S, Samuel TM, Li T, Howell BR, Baluyot K, Hazlett HC, Elison JT, Zhu H, Hauser J, Sprenger N, Lin W. Cho S, et al. Front Nutr. 2023 Jun 29;10:1216327. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1216327. eCollection 2023. Front Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37457984 Free PMC article. - Lactational and geographical variation in the concentration of six oligosaccharides in Chinese breast milk: a multicenter study over 13 months postpartum.
Liu S, Mao Y, Wang J, Tian F, Hill DR, Xiong X, Li X, Zhao Y, Wang S. Liu S, et al. Front Nutr. 2023 Sep 5;10:1267287. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1267287. eCollection 2023. Front Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37731395 Free PMC article. - Safety of lacto-_N_-tetraose (LNT) as a novel food pursuant to Regulation (EU) 2015/2283.
EFSA Panel on Nutrition, Novel Foods and Food Allergens (NDA); Turck D, Castenmiller J, De Henauw S, Hirsch-Ernst KI, Kearney J, Maciuk A, Mangelsdorf I, McArdle HJ, Naska A, Pelaez C, Pentieva K, Siani A, Thies F, Tsabouri S, Vinceti M, Cubadda F, Engel KH, Frenzel T, Heinonen M, Marchelli R, Neuhäuser-Berthold M, Poulsen M, Sanz Y, Schlatter JR, van Loveren H, Colombo P, Knutsen HK. EFSA Panel on Nutrition, Novel Foods and Food Allergens (NDA), et al. EFSA J. 2019 Dec 3;17(12):e05907. doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2019.5907. eCollection 2019 Dec. EFSA J. 2019. PMID: 32626198 Free PMC article.
References
- Eidelman A.I., Schanler R.J.J.M., Landers S., Noble L., Szucs K., Viehmann L., Feldman-Winter L., Lawrence R., Kim S., Onyema N. Breastfeeding and the use of human milk. Pediatrics. 2012;129:e827–e841. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources