Exposure to fine particulate matter associated with senile lentigo in Chinese women: a cross-sectional study - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2017 Feb;31(2):355-360.
doi: 10.1111/jdv.13834. Epub 2016 Sep 5.
Affiliations
- PMID: 27593207
- PMCID: PMC6084310
- DOI: 10.1111/jdv.13834
Exposure to fine particulate matter associated with senile lentigo in Chinese women: a cross-sectional study
F Peng et al. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2017 Feb.
Abstract
Background: Skin ageing especially senile lentigo directly affects self-esteem. For decades, senile lentigo has been associated with chronic exposure to solar radiation. However, a study conducted recently in Caucasian subjects suggested that exposure to air pollution was significantly correlated with extrinsic skin ageing, in particular senile lentigines.
Objective: To investigate the association between fine particulate matter (PM2.5 ) and skin ageing, particularly senile lentigo and seborrheic keratosis.
Methods: The study enrolled 400 Chinese women aged 40-90 years including 210 from the Yanqing county in Beijing (low PM2.5 exposure group) and 190 from the Xuanwumen in Beijing (high PM2.5 exposure group). Skin ageing symptoms, particularly senile lentigines and seborrheic keratoses, were clinically assessed using scores of intrinsic and extrinsic skin ageing. An ordinal logistic regression model was used to analyse the effect of PM2.5 on skin ageing adjusted for factors underlying skin ageing.
Results: In the study population of Xuanwumen, we found that senile lentigo on cheeks and back of hands was 1.48 times and 2.8 times higher, respectively, compared with those from Yanqing county. However, no association was found between PM2.5 and seborrheic keratosis. We found that other variables such as smoking, second-hand smoking, contact with fossil fuels and skin types were significantly associated with skin ageing.
Conclusion: These results indicate that PM2.5 was another extrinsic factor promoting skin ageing.
© 2016 European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
Figures
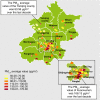
Figure 1
The average
PM
2.5 values over the past decades in a few areas of Beijing monitored by the Beijing Environmental Protection Monitoring Center.
Figure 2
Skin ageing analysis based on
SCINEXA
scores.
Similar articles
- Facial skin characteristics and concerns in Indonesia: A cross-sectional observational study.
Du Y, Doraiswamy C, Mao J, Zhang Q, Liang Y, Du Z, Vasantharaghavan R, Joshi MK. Du Y, et al. Skin Res Technol. 2022 Sep;28(5):719-728. doi: 10.1111/srt.13189. Epub 2022 Jul 4. Skin Res Technol. 2022. PMID: 35785442 Free PMC article. - Extrinsic skin ageing symptoms in seafarers subject to high work-related exposure to UV radiation.
Oldenburg M, Kuechmeister B, Ohnemus U, Baur X, Moll I. Oldenburg M, et al. Eur J Dermatol. 2013 Sep-Oct;23(5):663-70. doi: 10.1684/ejd.2013.2142. Eur J Dermatol. 2013. PMID: 24135214 - Clinical study of a retinoic acid-loaded microneedle patch for seborrheic keratosis or senile lentigo.
Hirobe S, Otsuka R, Iioka H, Quan YS, Kamiyama F, Asada H, Okada N, Nakagawa S. Hirobe S, et al. Life Sci. 2017 Jan 1;168:24-27. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2015.12.051. Epub 2016 Jan 3. Life Sci. 2017. PMID: 26757104 - Targeting SDF-1 as an efficient strategy to resolve skin hyperpigmentation issues with Himanthalia elongata extract.
Meunier M, Bracq M, Chapuis E, Lapierre L, Humeau A, Bernard S, Lambert C, Paulus C, Auriol P, Lemagnen P, Sandré J, Auriol D, Scandolera A, Reynaud R. Meunier M, et al. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2023 Feb;22(2):383-394. doi: 10.1111/jocd.15357. Epub 2022 Sep 16. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2023. PMID: 36062379 Free PMC article. Review. - Expanding Our Understanding of Human Skin Aging.
Chang ALS. Chang ALS. J Invest Dermatol. 2016 May;136(5):897-899. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2016.02.020. J Invest Dermatol. 2016. PMID: 27107374 Review.
Cited by
- Oxidative contribution of air pollution to extrinsic skin ageing.
Fussell JC, Kelly FJ. Fussell JC, et al. Free Radic Biol Med. 2020 May 1;151:111-122. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2019.11.038. Epub 2019 Dec 23. Free Radic Biol Med. 2020. PMID: 31874249 Free PMC article. Review. - Identification of Differentially Expressed Genes and Elucidation of Pathophysiological Relevance of ABCA1 in HaCaT Cells Induced by PM2.5.
Peng F, Xue CH, Yang XJ, Huang JY, Chen Z, Zhang JZ. Peng F, et al. Bioinorg Chem Appl. 2021 Apr 20;2021:8862564. doi: 10.1155/2021/8862564. eCollection 2021. Bioinorg Chem Appl. 2021. PMID: 33986791 Free PMC article. - Particulate Matter and Its Molecular Effects on Skin: Implications for Various Skin Diseases.
Paik K, Na JI, Huh CH, Shin JW. Paik K, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 13;25(18):9888. doi: 10.3390/ijms25189888. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39337376 Free PMC article. Review. - Protective effects of Camellia japonica flower extract against urban air pollutants.
Kim M, Son D, Shin S, Park D, Byun S, Jung E. Kim M, et al. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2019 Jan 28;19(1):30. doi: 10.1186/s12906-018-2405-4. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2019. PMID: 30691451 Free PMC article. - Bio-derived hydroxystearic acid ameliorates skin age spots and conspicuous pores.
Schütz R, Rawlings AV, Wandeler E, Jackson E, Trevisan S, Monneuse JM, Bendik I, Massironi M, Imfeld D. Schütz R, et al. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2019 Jun;41(3):240-256. doi: 10.1111/ics.12529. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2019. PMID: 30955220 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
- Vierkötter A, Ranft U, Krämer U et al The SCINEXA: a novel, validated score to simultaneously assess and differentiate between intrinsic and extrinsic skin ageing. J Dermatol Sci 2009; 53: 207–211. - PubMed
- Chung JH. Photoaging in Asians. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed 2003; 19: 109–121. - PubMed
- Vierkötter A, Schikowski T, Ranft U et al Airborne particle exposure and extrinsic skin aging. J Invest Dermatol 2010; 130: 2719–2726. - PubMed
- Nakamura M, Morita A, Seité S et al Environment‐induced lentigines: formation of solar lentigines beyond ultraviolet radiation. Exp Dermatol 2015; 24: 407–411. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources