Identification of Metabolites of 6'-Hydroxy-3,4,5,2',4'-pentamethoxychalcone in Rats by a Combination of Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Linear Ion Trap-Orbitrap Mass Spectrometry Based on Multiple Data Processing Techniques - PubMed (original) (raw)
Identification of Metabolites of 6'-Hydroxy-3,4,5,2',4'-pentamethoxychalcone in Rats by a Combination of Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Linear Ion Trap-Orbitrap Mass Spectrometry Based on Multiple Data Processing Techniques
Siyi Liu et al. Molecules. 2016.
Abstract
In this study, an efficient strategy was established using ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with linear ion trap-Orbitrap mass spectrometry (UHPLC-LTQ-Orbitrap MS) to profile the in vivo metabolic fate of 6'-hydroxy-3,4,5,2',4'-pentamethoxychalcone (PTC) in rat urine and feces. The UHPLC-LTQ-Orbitrap method combines the high trapping capacity and MS(n) scanning function of the linear ion trap along with accurate mass measurements within 5 ppm and a resolving power of up to 30,000 over a wider dynamic range compared to many other mass spectrometers. In order to reduce the potential interferences of endogenous substances, the post-acquisition processing method including high-resolution extracted ion chromatogram (HREIC) and multiple mass defect filters (MMDF) were developed for metabolite detection. As a result, a total of 60 and 35 metabolites were detected in the urine and feces, respectively. The corresponding in vivo reactions such as methylation, hydroxylation, hydrogenation, decarbonylation, demethylation, dehydration, methylation, demethoxylation, sulfate conjugation, glucuronide conjugation, and their composite reactions were all detected in this study. The result on PTC metabolites significantly expanded the understanding of its pharmacological effects, and could be targets for future studies on the important chemical constituents from herbal medicines.
Keywords: 6′-hydroxy-3,4,5,2′,4′-pentamethoxychalcone (PTC); UHPLC-LTQ-Orbitrap MS; metabolite identification; multiple data processing method.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
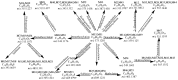
Figure 1
The proposed major metabolic pathway of PTC in the rat urine and feces.
Figure 2
ESI-MSn spectra of four reference standards and M16: (A) MS2 spectrum of PTC; (B) MS2 spectrum of 6′-hydroxy-3,4,5,2′,3′,4′-hexamethoxychalcone; (C) MS2 spectrum of 4,6′-dihydroxy-3,2′,4′-trimythoxychalcone; (D) MS3 spectrum of 4,6′-dihydroxy-3,2′,4′-trimethoxychalcone (precursor-ion was m/z 149); (E) MS2 spectrum of velutin; (F) MS3 spectrum of velutin (precursor-ion was m/z 298); (G) MS2 spectrum of M16.
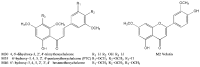
Figure 3
Chemical structures of the reference standards.
Similar articles
- Profiling and identification of the metabolites of baicalin and study on their tissue distribution in rats by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography with linear ion trap-Orbitrap mass spectrometer.
Zhang J, Cai W, Zhou Y, Liu Y, Wu X, Li Y, Lu J, Qiao Y. Zhang J, et al. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2015 Mar 15;985:91-102. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2015.01.018. Epub 2015 Jan 23. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2015. PMID: 25661005 - Profiling and identification of (-)-epicatechin metabolites in rats using ultra-high performance liquid chromatography coupled with linear trap-Orbitrap mass spectrometer.
Shang Z, Wang F, Dai S, Lu J, Wu X, Zhang J. Shang Z, et al. Drug Test Anal. 2017 Aug;9(8):1224-1235. doi: 10.1002/dta.2155. Epub 2017 Feb 10. Drug Test Anal. 2017. PMID: 28042917 - Rapid characterization and identification of the chemical constituents and the metabolites of Du-zhi pill using UHPLC coupled with quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry.
Lai H, Ouyang Y, Tian G, Zhao J, Zhang J, Zhang J, Tang L, Wu H, Yang H. Lai H, et al. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2022 Oct 15;1209:123433. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2022.123433. Epub 2022 Aug 23. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 36055062 Review. - Screening of synthetic PDE-5 inhibitors and their analogues as adulterants: analytical techniques and challenges.
Patel DN, Li L, Kee CL, Ge X, Low MY, Koh HL. Patel DN, et al. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2014 Jan;87:176-90. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2013.04.037. Epub 2013 May 6. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2014. PMID: 23721687 Review.
Cited by
- Bio-fabricated zinc oxide nanoparticles mediated by endophytic fungus Aspergillus sp. SA17 with antimicrobial and anticancer activities: in vitro supported by in silico studies.
Abdelrahman SESAH, El Hawary S, Mohsen E, El Raey MA, Selim HMRM, Hamdan AME, Ghareeb MA, Hamed AA. Abdelrahman SESAH, et al. Front Microbiol. 2024 May 13;15:1366614. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1366614. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38803373 Free PMC article. - Comprehensive Metabolite Identification of Genipin in Rats Using Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled with High Resolution Mass Spectrometry.
Cui Z, Li Z, Dong W, Qiu L, Zhang J, Wang S. Cui Z, et al. Molecules. 2023 Aug 29;28(17):6307. doi: 10.3390/molecules28176307. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37687136 Free PMC article. - Exploring stereoselective excretion and metabolism studies of novel 2-(2-hydroxypropanamido)-5-trifluoromethyl benzoic acid enantiomers.
Rong R, Zhang QL, Zhang RZ, Dan YH, Wang X, Zhao YL, Yu ZG. Rong R, et al. RSC Adv. 2020 Jul 21;10(46):27267-27279. doi: 10.1039/d0ra03500a. eCollection 2020 Jul 21. RSC Adv. 2020. PMID: 35516918 Free PMC article. - Comprehensive Identification of Guan-Xin-Shu-Tong Capsule via a Mass Defect and Fragment Filtering Approach by High Resolution Mass Spectrometry: In Vitro and In Vivo Study.
Gao X, Mu J, Li Q, Guan S, Liu R, Du Y, Zhang H, Bi K. Gao X, et al. Molecules. 2017 Jun 16;22(6):1007. doi: 10.3390/molecules22061007. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28621737 Free PMC article.
References
- Zhang J.Y., Li N., Zhou Y., Jiang Y., Tu P.F. Simultaneous qualitative and quantitative determination of major polymethoxylated flavonoids in the leaves of Murraya paniculata by RRLC-DAD-ESI-MSn. Anal. Methods. 2012;4:3399–3406. doi: 10.1039/c2ay25242b. - DOI
- Olawore N.O., Ogunwander I.A., Ekundayo O. Chemical composition of the leaf and fruit essential oils of Murraya paniculata (L.) Jack (Syn. Murraya exotica Linn.) Flavour Frag. J. 2005;20:54–56. doi: 10.1002/ffj.1365. - DOI
- Zhang J.Y., Li N., Che Y.Y., Zhang Y., Liang S.X., Zhao M.B., Jiang Y., Tu P.F. Characterization of seventy polymethoxylated flavonoids (PMFs) in the leaves of Murraya paniculata by on-line high-performance liquid chromatography coupled to photodiode array detection and electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. J. Pharmaceut. Biomed. 2011;56:950–961. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2011.08.019. - DOI - PubMed
- Zhang J.Y., Zhang Q., Zhang H.X., Ma Q., Lu J.Q., Qiao Y.J. Characterization of polymethoxylated flavonoids (PMFs) in the peels of “Shatangju” mandarin (Citrus reticulata Blanco) by online high-performance liquid chromatography coupled to photodiode array detection and electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012;60:9023–9034. doi: 10.1021/jf302713c. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous