Four Weeks of Supplementation With Isolated Soy Protein Attenuates Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage and Enhances Muscle Recovery in Well Trained Athletes: A Randomized Trial - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2016 May 23;7(3):e33528.
doi: 10.5812/asjsm.33528. eCollection 2016 Sep.
Affiliations
- PMID: 27826398
- PMCID: PMC5098124
- DOI: 10.5812/asjsm.33528
Four Weeks of Supplementation With Isolated Soy Protein Attenuates Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage and Enhances Muscle Recovery in Well Trained Athletes: A Randomized Trial
Shweta Shenoy et al. Asian J Sports Med. 2016.
Abstract
Background: The effects of consumption of isolated soy protein (ISP) for a chronic period (4 weeks) on exercise induced muscle damage (EIMD) in athletic population have never been explored.
Objectives: To examine the effects of ISP on muscle damage indices elicited via a bout of damaging exercise.
Patients and methods: Forty males (20 boxers, 20 cyclists) aged 18 - 28 years were randomly assigned to two groups (ISP and Placebo) (n = 20). All participants who engaged themselves in specific, regular training of 30 hours a week during the competitive season were included in the study. Participants consumed the supplement and the placebo for 4 weeks. The damaging exercise consisted of 100 consecutive drop-jumps. Pre and post supplementation readings of the criterion variables, highly sensitive C reactive protein (hs-cRP), creatine Kinase (CK), myeloperoxidase (MPO), isometric muscle strength, maximum aerobic capacity (VO2 max), heart rate (HR) and muscle soreness were obtained at baseline (Day 1), at 24 hours (Day 2) and at 48 hours (Day 3) following EIMD.
Results: Differences were observed in pre and post supplementation values (P < 0.05) indicating the effectiveness of soy protein in attenuating muscle damage and enhancing muscle recovery.
Conclusions: Our findings suggest that soy protein; a vegetable based supplement is effective, in ameliorating the negative effects of EIMD in trained athletic population.
Keywords: Amino Acids; C-Reactive Protein; Creatine Kinase; Exercise; Soybean Proteins.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest:None declared.
Figures
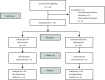
Figure 1.. Flow Diagram of Participant Recruitment and Allocation Into Groups
Similar articles
- Impact of varying doses of omega-3 supplementation on muscle damage and recovery after eccentric resistance exercise.
Visconti LM, Cotter JA, Schick EE, Daniels N, Viray FE, Purcell CA, Brotman CBR, Ruhman KE, Escobar KA. Visconti LM, et al. Metabol Open. 2021 Oct 3;12:100133. doi: 10.1016/j.metop.2021.100133. eCollection 2021 Dec. Metabol Open. 2021. PMID: 34693240 Free PMC article. - Fish oil supplementation fails to modulate indices of muscle damage and muscle repair during acute recovery from eccentric exercise in trained young males.
Mackay J, Bowles E, Macgregor LJ, Prokopidis K, Campbell C, Barber E, Galloway SDR, Witard OC. Mackay J, et al. Eur J Sport Sci. 2023 Aug;23(8):1666-1676. doi: 10.1080/17461391.2023.2199282. Epub 2023 Apr 25. Eur J Sport Sci. 2023. PMID: 37010103 - Exercise-induced muscle damage is reduced in resistance-trained males by branched chain amino acids: a randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled study.
Howatson G, Hoad M, Goodall S, Tallent J, Bell PG, French DN. Howatson G, et al. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2012 Jul 12;9:20. doi: 10.1186/1550-2783-9-20. eCollection 2012. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2012. PMID: 22569039 Free PMC article. - Attenuating Muscle Damage Biomarkers and Muscle Soreness After an Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage with Branched-Chain Amino Acid (BCAA) Supplementation: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis with Meta-regression.
Salem A, Ben Maaoui K, Jahrami H, AlMarzooqi MA, Boukhris O, Messai B, Clark CCT, Glenn JM, Ghazzaoui HA, Bragazzi NL, Ammar A, Trabelsi K, Chtourou H. Salem A, et al. Sports Med Open. 2024 Apr 16;10(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s40798-024-00686-9. Sports Med Open. 2024. PMID: 38625669 Free PMC article. - The Effects of Pre-conditioning on Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.
Boyd L, Deakin GB, Devantier-Thomas B, Singh U, Doma K. Boyd L, et al. Sports Med. 2023 Aug;53(8):1537-1557. doi: 10.1007/s40279-023-01839-8. Epub 2023 May 9. Sports Med. 2023. PMID: 37160563 Free PMC article.
Cited by
- Protein-Based Supplementation to Enhance Recovery in Team Sports: What is the Evidence?
Poulios A, Georgakouli K, Draganidis D, Deli CK, Tsimeas PD, Chatzinikolaou A, Papanikolaou K, Batrakoulis A, Mohr M, Jamurtas AZ, Fatouros IG. Poulios A, et al. J Sports Sci Med. 2019 Aug 1;18(3):523-536. eCollection 2019 Sep. J Sports Sci Med. 2019. PMID: 31427875 Free PMC article. Review. - Supplementation with Whey Protein, but Not Pea Protein, Reduces Muscle Damage Following Long-Distance Walking in Older Adults.
Spoelder M, Koopmans L, Hartman YAW, Bongers CCWG, Schoofs MCA, Eijsvogels TMH, Hopman MTE. Spoelder M, et al. Nutrients. 2023 Jan 10;15(2):342. doi: 10.3390/nu15020342. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 36678213 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Potential Relevance of Bioactive Peptides in Sports Nutrition.
König D, Kohl J, Jerger S, Centner C. König D, et al. Nutrients. 2021 Nov 10;13(11):3997. doi: 10.3390/nu13113997. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34836255 Free PMC article. Review. - Disentangling the dynamic interplay between muscle damage and energetics in male boxers during a short training block.
Obmiński Z, Crewther BT, Cook CJ. Obmiński Z, et al. Biol Sport. 2024 Jan;41(1):69-75. doi: 10.5114/biolsport.2024.127383. Epub 2023 May 30. Biol Sport. 2024. PMID: 38188101 Free PMC article.
References
- Istfan N, Murray E, Janghorbani M, Evans WJ, Young VR. The nutritional value of a soy protein concentrate (STAPRO-3200) for long-term protein nutritional maintenance in young men. J Nutr. 1983;113(12):2524–34. - PubMed
- Ruiz-Larrea MB, Mohan AR, Paganga G, Miller NJ, Bolwell GP, Rice-Evans CA. Antioxidant activity of phytoestrogenic isoflavones. Free Radic Res. 1997;26(1):63–70. - PubMed
- Meng Q, Lewis P, Wahala K, Adlercreutz H, Tikkanen MJ. Incorporation of esterified soybean isoflavones with antioxidant activity into low density lipoprotein. Biochem Biophys Acta. 1999;1438(3):369–76. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous