Sub-clinical Alcohol Consumption and Gambling Disorder - PubMed (original) (raw)
Sub-clinical Alcohol Consumption and Gambling Disorder
Michael D Harries et al. J Gambl Stud. 2017 Jun.
Abstract
While it is well established that gambling disorder is associated with alcohol use disorder, less is known regarding whether sub-clinical alcohol consumption increases gambling behavior. This study examined the effects of varying levels of alcohol consumption on clinical and cognitive measures. The sample consisted of 572 non-treatment seeking gamblers age 18-29 who were divided into three groups: non-current drinkers, current drinkers who did not qualify for an alcohol use disorder, and those with an alcohol use disorder (AUD). All subjects were assessed on gambling pathology, severity and impulsivity using the Structured Clinical Interview for Gambling Disorder, Yale Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale for Pathologic Gambling and the Barratt Impulsive Scale-11 and select cognitive tests. In all of the clinical measures, controlling for age, gender and education, the AUD group was significantly more likely than the non-current and current drinkers to be a pathologic gambler and to be impulsive, compulsive and depressed. On cognitive tasks, controlling for age, gender and education, the AUD group had significantly worse strategy use on a spatial working memory task than both other groups. This study suggests that the relationship between alcohol and gambling may only exist when pathology in both alcohol consumption and gambling behavior is present. Examining this relationship with alcohol consumption as a continuous variable would provide additional insight into the potential effects alcohol consumption has on gambling behavior.
Keywords: Alcohol; Alcohol use disorder; Cognition; Compulsivity; Gambling disorder; Impulsivity.
Figures
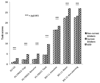
Fig. 1
Gambling pathology (SCI-GD, max score=5), gambling severity (PG-YBOCS, max score=40), and impulsivity (BIS-11, max score=30) compared across drinking groups within MANOVA examining clinical variables. Age, gender and education were included as covariates. All measures were statistically significant (p≤0.001) in the between subjects effect. AUD = Alcohol Use Disorder.
Similar articles
- An Analysis of Treatment-Seeking Behavior in Individuals with Gambling Disorder.
Harries MD, Redden SA, Grant JE. Harries MD, et al. J Gambl Stud. 2018 Sep;34(3):999-1012. doi: 10.1007/s10899-017-9730-2. J Gambl Stud. 2018. PMID: 29134496 - Latent class analysis of gambling subtypes and impulsive/compulsive associations: Time to rethink diagnostic boundaries for gambling disorder?
Chamberlain SR, Stochl J, Redden SA, Odlaug BL, Grant JE. Chamberlain SR, et al. Addict Behav. 2017 Sep;72:79-85. doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2017.03.020. Epub 2017 Mar 28. Addict Behav. 2017. PMID: 28384607 Free PMC article. - Cognitive task performance and frequency of alcohol usage in young adults.
Harvanko AM, Odlaug BL, Schreiber LR, Grant JE. Harvanko AM, et al. J Addict Med. 2012 Jun;6(2):106-11. doi: 10.1097/ADM.0b013e31823ae56d. J Addict Med. 2012. PMID: 22124290 - Pathological gambling: an impulse control disorder? Measurement of impulsivity using neurocognitive tests.
Dannon PN, Shoenfeld N, Rosenberg O, Kertzman S, Kotler M. Dannon PN, et al. Isr Med Assoc J. 2010 Apr;12(4):243-8. Isr Med Assoc J. 2010. PMID: 20803888 Review. - The latest achievements in the pharmacotherapy of gambling disorder.
Łabuzek K, Beil S, Beil-Gawełczyk J, Gabryel B, Franik G, Okopień B. Łabuzek K, et al. Pharmacol Rep. 2014 Oct;66(5):811-20. doi: 10.1016/j.pharep.2014.05.003. Epub 2014 May 23. Pharmacol Rep. 2014. PMID: 25149985 Review.
Cited by
- Changes in Gambling Behavior during the COVID-19 Pandemic-A Web Survey Study in Sweden.
Håkansson A. Håkansson A. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Jun 5;17(11):4013. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17114013. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32516880 Free PMC article. - An Analysis of Treatment-Seeking Behavior in Individuals with Gambling Disorder.
Harries MD, Redden SA, Grant JE. Harries MD, et al. J Gambl Stud. 2018 Sep;34(3):999-1012. doi: 10.1007/s10899-017-9730-2. J Gambl Stud. 2018. PMID: 29134496
References
- Aron AR. The neural basis of inhibition in cognitive control. Neuroscientist. 2007;13(3):214–28. - PubMed
- Del Boca FK, Darkes J. The validity of self-reports of alcohol consumption: state of the science and challenges for research. Addiction. 2003;98:21–12. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical