Nivolumab in patients with metastatic DNA mismatch repair-deficient or microsatellite instability-high colorectal cancer (CheckMate 142): an open-label, multicentre, phase 2 study - PubMed (original) (raw)
Clinical Trial
. 2017 Sep;18(9):1182-1191.
doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30422-9. Epub 2017 Jul 19.
Ray McDermott 2, Joseph L Leach 3, Sara Lonardi 4, Heinz-Josef Lenz 5, Michael A Morse 6, Jayesh Desai 7, Andrew Hill 8, Michael Axelson 9, Rebecca A Moss 9, Monica V Goldberg 9, Z Alexander Cao 9, Jean-Marie Ledeine 10, Gregory A Maglinte 9, Scott Kopetz 11, Thierry André 12
Affiliations
- PMID: 28734759
- PMCID: PMC6207072
- DOI: 10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30422-9
Clinical Trial
Nivolumab in patients with metastatic DNA mismatch repair-deficient or microsatellite instability-high colorectal cancer (CheckMate 142): an open-label, multicentre, phase 2 study
Michael J Overman et al. Lancet Oncol. 2017 Sep.
Erratum in
- Correction to Lancet Oncol 2017; 18: 1182-91.
[No authors listed] [No authors listed] Lancet Oncol. 2017 Sep;18(9):510. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30638-1. Lancet Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28884691 No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Metastatic DNA mismatch repair-deficient (dMMR)/microsatellite instability-high (MSI-H) colorectal cancer has a poor prognosis after treatment with conventional chemotherapy and exhibits high levels of tumour neoantigens, tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes, and checkpoint regulators. All of these features are associated with the response to PD-1 blockade in other tumour types. Therefore, we aimed to study nivolumab, a PD-1 immune checkpoint inhibitor, in patients with dMMR/MSI-H metastatic colorectal cancer.
Methods: In this ongoing, multicentre, open-label, phase 2 trial, we enrolled adults (aged ≥18 years) with histologically confirmed recurrent or metastatic colorectal cancer locally assessed as dMMR/MSI-H from 31 sites (academic centres and hospitals) in eight countries (Australia, Belgium, Canada, France, Ireland, Italy, Spain, and the USA). Eligible patients had progressed on or after, or been intolerant of, at least one previous line of treatment, including a fluoropyrimidine and oxaliplatin or irinotecan. Patients were given 3 mg/kg nivolumab every 2 weeks until disease progression, death, unacceptable toxic effects, or withdrawal from study. The primary endpoint was investigator-assessed objective response as per Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (version 1.1). All patients who received at least one dose of study drug were included in all analyses. This trial is registered with ClinicalTrials.gov, number NCT02060188.
Findings: Of the 74 patients who were enrolled between March 12, 2014, and March 16, 2016, 40 (54%) had received three or more previous treatments. At a median follow-up of 12·0 months (IQR 8·6-18·0), 23 (31·1%, 95% CI 20·8-42·9) of 74 patients achieved an investigator-assessed objective response and 51 (69%, 57-79) patients had disease control for 12 weeks or longer. Median duration of response was not yet reached; all responders were alive, and eight had responses lasting 12 months or longer (Kaplan-Meier 12-month estimate 86%, 95% CI 62-95). The most common grade 3 or 4 drug-related adverse events were increased concentrations of lipase (six [8%]) and amylase (two [3%]). 23 (31%) patients died during the study; none of these deaths were deemed to be treatment related by the investigator.
Interpretation: Nivolumab provided durable responses and disease control in pre-treated patients with dMMR/MSI-H metastatic colorectal cancer, and could be a new treatment option for these patients.
Funding: Bristol-Myers Squibb.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
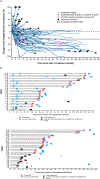
Figure 1:. Plots of change from baseline in target lesion size over time in patients with metastatic or recurrent colorectal cancer locally assessed as dMMR/MSI-H
(A) Percentage change from baseline in the sum of the tumour burden for target lesions over time per investigator assessment for evaluable patients treated with nivolumab. Triangles indicate complete response or partial response per Response Evaluation Criteria In Solid Tumors v1·1; plus signs indicate the first occurrence of a new lesion; solid circle indicate patient who were off treatment; squares indicate percentage change truncated to 100%. (B) Characteristics of response (top panel) or stable disease (bottom panel) evaluated per investigator assessment per Response Evaluation Criteria In Solid Tumors v1·1. The lines represent length of progression-free survival. Triangles indicate censored observations; solid circle indicate the first response; solid black square indicate the last dose when the patient was off treatment; dagger signs indicate death. dMMR/MSI-H=DNA mismatch repair deficient/microsatellite instability–high.
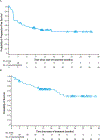
Figure 2:. Plots of progression-free survival per investigator assessment and overall survival in patients with metastatic or recurrent colorectal cancer locally assessed as dMMR/MSI-H
(A) Kaplan-Meier curve for progression-free survival per investigator assessment in patients treated with nivolumab. Triangles indicate censored observations. (B) Kaplan-Meier curve for overall survival in all patients treated with nivolumab. Triangles indicate censored observations. dMMR/MSI-H=DNA mismatch repair deficient/microsatellite instability–high; NE=not estimable.
Comment in
- PD-1 inhibition in metastatic dMMR/MSI-H colorectal cancer.
Sclafani F. Sclafani F. Lancet Oncol. 2017 Sep;18(9):1141-1142. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30512-0. Epub 2017 Jul 19. Lancet Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28734760 No abstract available.
Similar articles
- Nivolumab plus relatlimab in patients with previously treated microsatellite instability-high/mismatch repair-deficient metastatic colorectal cancer: the phase II CheckMate 142 study.
Overman MJ, Gelsomino F, Aglietta M, Wong M, Limon Miron ML, Leonard G, García-Alfonso P, Hill AG, Cubillo Gracian A, Van Cutsem E, El-Rayes B, McCraith SM, He B, Lei M, Lonardi S. Overman MJ, et al. J Immunother Cancer. 2024 May 31;12(5):e008689. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2023-008689. J Immunother Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38821718 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Nivolumab plus low-dose ipilimumab in previously treated patients with microsatellite instability-high/mismatch repair-deficient metastatic colorectal cancer: 4-year follow-up from CheckMate 142.
André T, Lonardi S, Wong KYM, Lenz HJ, Gelsomino F, Aglietta M, Morse MA, Van Cutsem E, McDermott R, Hill A, Sawyer MB, Hendlisz A, Neyns B, Abdullaev S, Memaj A, Lei M, Dixon M, Kopetz S, Overman MJ. André T, et al. Ann Oncol. 2022 Oct;33(10):1052-1060. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2022.06.008. Epub 2022 Jun 25. Ann Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35764271 - First-Line Nivolumab Plus Low-Dose Ipilimumab for Microsatellite Instability-High/Mismatch Repair-Deficient Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: The Phase II CheckMate 142 Study.
Lenz HJ, Van Cutsem E, Luisa Limon M, Wong KYM, Hendlisz A, Aglietta M, García-Alfonso P, Neyns B, Luppi G, Cardin DB, Dragovich T, Shah U, Abdullaev S, Gricar J, Ledeine JM, Overman MJ, Lonardi S. Lenz HJ, et al. J Clin Oncol. 2022 Jan 10;40(2):161-170. doi: 10.1200/JCO.21.01015. Epub 2021 Oct 12. J Clin Oncol. 2022. PMID: 34637336 Clinical Trial. - Perspectives on Treatment of Metastatic Colorectal Cancer with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy.
Morse MA, Hochster H, Benson A. Morse MA, et al. Oncologist. 2020 Jan;25(1):33-45. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2019-0176. Epub 2019 Aug 5. Oncologist. 2020. PMID: 31383813 Free PMC article. Review. - Clinical Development of Immunotherapy for Deficient Mismatch Repair Colorectal Cancer.
Thomas J, Leal A, Overman MJ. Thomas J, et al. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2020 Jun;19(2):73-81. doi: 10.1016/j.clcc.2020.02.002. Epub 2020 Feb 10. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32173280 Review.
Cited by
- IL-12 drives the expression of the inhibitory receptor NKG2A on human tumor-reactive CD8 T cells.
Fesneau O, Samson KA, Rosales W, Jones B, Moudgil T, Fox BA, Rajamanickam V, Duhen T. Fesneau O, et al. Nat Commun. 2024 Nov 18;15(1):9988. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-54420-w. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39557863 - Insights into the historical trajectory and research trends of immune checkpoint blockade in colorectal cancer: visualization and bibliometric analysis.
Chang Y, Zhou X, Nie K, Liu J, Zhang S. Chang Y, et al. Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 31;15:1478773. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1478773. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39544944 Free PMC article. - Genomic instability as a driver and suppressor of anti-tumor immunity.
Requesens M, Foijer F, Nijman HW, de Bruyn M. Requesens M, et al. Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 11;15:1462496. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1462496. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39544936 Free PMC article. Review. - Dietary pattern and the corresponding gut microbiome in response to immunotherapy in Thai patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Sitthideatphaiboon P, Somlaw N, Zungsontiporn N, Ouwongprayoon P, Sukswai N, Korphaisarn K, Poungvarin N, Aporntewan C, Hirankarn N, Vinayanuwattikun C, Chanida V. Sitthideatphaiboon P, et al. Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 13;14(1):27791. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-79339-6. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39537963 Free PMC article. - Iparomlimab (QL1604) in patients with microsatellite instability-high (MSI-H) or mismatch repair-deficient (dMMR) unresectable or metastatic solid tumors: a pivotal, single-arm, multicenter, phase II trial.
Bi F, Dong J, Jin C, Niu Z, Yang W, He Y, Yu D, Sun M, Wang T, Yin X, Zhang R, Chen K, Wang K, Wang Z, Li W, Zhang Z, Zhang H, Guo Q, Wang X, Han L, Zhang X, Shen W, Zhang L, Ying J, Wu M, Hu W, Li Z, Li X, Feng W, Zhang B, Li L, Kang X, Guo W. Bi F, et al. J Hematol Oncol. 2024 Nov 11;17(1):109. doi: 10.1186/s13045-024-01627-5. J Hematol Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39529169 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
- International Agency for Research on Cancer. GLOBOCAN 2012: estimated cancer incidence, mortality and prevalence worldwide in 2012 http://globocan.iarc.fr/Pages/fact_sheets_population.aspx (accessed January 13, 2017).
- NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. colon cancer V1.2017. (https://www.nccn.org/). - PubMed
- National Cancer Institute. Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program. Cancer stat facts: colon and rectum cancer http://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/colorect.html (accessed January 13, 2017).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical