A study of Sirt1 regulation and the effect of resveratrol on synoviocyte invasion and associated joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis - PubMed (original) (raw)
A study of Sirt1 regulation and the effect of resveratrol on synoviocyte invasion and associated joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis
Liang Hao et al. Mol Med Rep. 2017 Oct.
Abstract
The aim of the current study was to investigate the role and mechanism of sirtuin 1 (Sirt1) in the regulation of synovial cell invasion and joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). The Sirt1 protein and mRNA levels in fibroblast‑like synoviocytes (FLS) isolated from RA synovial tissues were compared with normal tissues by western blot and reverse transcription‑polymerase chain reaction. RA FLS were then treated with the Sirt1 agonist resveratrol (1, 3 and 10 µg/ml) for 48 h, and their invasiveness and expression of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) 1 and MMP13 protein and mRNA were measured. Furthermore, a collagen‑induced arthritis (CIA) rat model was established and the rats were divided into a model group, and low‑ and high‑dose resveratrol (2.5 and 10 mg/kg/day) groups to receive an intraperitoneal injection of resveratrol for 42 consecutive days. The joint morphology, arthritis index (AI), and MMP1 and MMP13 expression in synovial tissues was monitored. The Sirt1 protein and mRNA levels in RA FLS were significantly lower compared with normal FLS (P<0.01). The resveratrol treatment significantly inhibited the invasive ability of RA FLS (P<0.01) and reduced MMP1 and MMP13 expression (P<0.01). The AI in low‑ and high‑dose groups was significantly lower compared with the model group from day 28 (P<0.01). Resveratrol also reduced the swelling and damage and decreased MMP1 and MMP13 expression levels in CIA rats (P<0.01). The resveratrol‑induced upregulation of Sirt1 in RA FLS may significantly inhibit the invasion of these cells and reduce the degree of joint damage, which may be mediated through the inhibition of MMP1 and MMP13 expression. The present results suggested a regulatory role for Sirt1 in RA pathogenesis, and demonstrated the beneficial effects of resveratrol, which may have potential as an alternative therapeutic strategy for the treatment of patients with RA.
Figures
Figure 1.
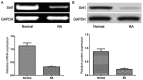
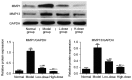
Comparison of Sirt1 mRNA and protein expression in normal fibroblast-like synoviocytes and from patients with RA. (A) Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction and (B) western blot analyses. *P<0.01. Sirt1, sirtuin 1; RA, rheumatoid arthritis.
Figure 2.
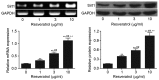
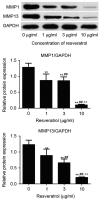
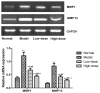
Detection of Sirt1 protein and mRNA expression in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes treated with 1, 3 and 10 µg/ml resveratrol by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction and western blot analyses. **P<0.01 vs. 0 µg/ml control group; ##P<0.01 vs. 1 µg/ml resveratrol group; ++P<0.01 vs. 3 µg/ml resveratrol group. Sirt1, sirtuin 1.
Figure 3.
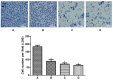
Effect of resveratrol on rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocyte invasiveness. Crystal violet staining of invaded cells in a Transwell assay from (A) control cells without resveratrol treatment, (B) 1 µg/ml resveratrol, (C) 3 µg/ml resveratrol and (D) 10 µg/ml resveratrol groups. *P<0.01. Scale bar, 100 µm.
Figure 4.
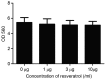
MTT assay comparing the effect of resveratrol on rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocyte cell viability.
Figure 5.
Western blot analyses comparing the expression of MMP proteins in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes treated with resveratrol. **P<0.01 vs. 0 µg/ml group; ##P<0.01 vs. 1 µg/ml resveratrol group; ++P<0.01 vs. 3 µg/ml resveratrol group. MMP, matrix metalloproteinase.
Figure 6.
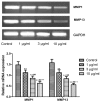
Polymerase chain reaction detected the mRNA expression of MMPs in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes treated with resveratrol. **P<0.01 vs. 0 µg/ml group; ##P<0.01 vs. 1 µg/ml resveratrol group; ++P<0.01 vs. 3 µg/ml resveratrol group. MMP, matrix metalloproteinase.
Figure 7.
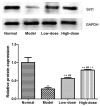
Effect of resveratrol on Sirt1 expression in synovial tissue of collagen-induced arthritis rats. **P<0.01 vs. normal group; ##P<0.01 vs. model group; ++P<0.01 vs. low-dose group. Sirt1, sirtuin 1.
Figure 8.
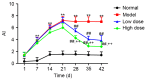
Effect of resveratrol on the AI in collagen-induced arthritis rats. **P<0.01 vs. normal group; ##P<0.01 vs. model group; ++P<0.01 vs. low-dose group. AI, arthritis index.
Figure 9.
Effect of resveratrol on MMPs expression in synovial tissue of collagen-induced arthritis rats. **P<0.01 vs. normal group; ##P<0.01 vs. model group; ++P<0.01 vs. low-dose group. MMP, matrix metalloproteinase.
Figure 10.
Effect of resveratrol on the mRNA expression levels of MMPs in synovial tissue of collagen-induced arthritis rats. **P<0.01 vs. normal group; ##P<0.01 vs. model group; ++P<0.01 vs. low-dose group. MMP, matrix metalloproteinase.
Similar articles
- SIRT1 inhibits rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocyte aggressiveness and inflammatory response via suppressing NF-κB pathway.
Li G, Xia Z, Liu Y, Meng F, Wu X, Fang Y, Zhang C, Liu D. Li G, et al. Biosci Rep. 2018 Jun 21;38(3):BSR20180541. doi: 10.1042/BSR20180541. Print 2018 Jun 29. Biosci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29784872 Free PMC article. - Histone demethylase JMJD3 regulates fibroblast-like synoviocyte-mediated proliferation and joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis.
Jia W, Wu W, Yang D, Xiao C, Su Z, Huang Z, Li Z, Qin M, Huang M, Liu S, Long F, Mao J, Liu X, Zhu YZ. Jia W, et al. FASEB J. 2018 Jul;32(7):4031-4042. doi: 10.1096/fj.201701483R. Epub 2018 Feb 26. FASEB J. 2018. PMID: 29481307 - A novel function of artesunate on inhibiting migration and invasion of fibroblast-like synoviocytes from rheumatoid arthritis patients.
Ma JD, Jing J, Wang JW, Yan T, Li QH, Mo YQ, Zheng DH, Gao JL, Nguyen KA, Dai L. Ma JD, et al. Arthritis Res Ther. 2019 Jun 24;21(1):153. doi: 10.1186/s13075-019-1935-6. Arthritis Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 31234900 Free PMC article. - Destructive Roles of Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes in Chronic Inflammation and Joint Damage in Rheumatoid Arthritis.
Masoumi M, Bashiri H, Khorramdelazad H, Barzaman K, Hashemi N, Sereshki HA, Sahebkar A, Karami J. Masoumi M, et al. Inflammation. 2021 Apr;44(2):466-479. doi: 10.1007/s10753-020-01371-1. Epub 2020 Oct 28. Inflammation. 2021. PMID: 33113036 Review. - Role of glucose metabolism in aggressive phenotype of fibroblast-like synoviocytes: Latest evidence and therapeutic approaches in rheumatoid arthritis.
Masoumi M, Mehrabzadeh M, Mahmoudzehi S, Mousavi MJ, Jamalzehi S, Sahebkar A, Karami J. Masoumi M, et al. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020 Dec;89(Pt A):107064. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107064. Epub 2020 Oct 8. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 33039953 Review.
Cited by
- A Review of Proposed Mechanisms in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Therapeutic Strategies for the Disease.
Mohite R, Doshi G. Mohite R, et al. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2024;24(3):291-301. doi: 10.2174/0118715303250834230923234802. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2024. PMID: 37861027 Review. - Recent Advances on the Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Properties of Red Grape Polyphenols: In Vitro and In Vivo Studies.
Magrone T, Magrone M, Russo MA, Jirillo E. Magrone T, et al. Antioxidants (Basel). 2019 Dec 31;9(1):35. doi: 10.3390/antiox9010035. Antioxidants (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31906123 Free PMC article. Review. - AMPK/SIRT1 Deficiency Drives Adjuvant-Induced Arthritis in Rats by Promoting Glycolysis-Mediated Monocytes Inflammatory Polarization.
Wang DD, He CY, Wu YJ, Xu L, Shi C, Olatunji OJ, Zuo J, Ji CL. Wang DD, et al. J Inflamm Res. 2022 Aug 15;15:4663-4675. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S378090. eCollection 2022. J Inflamm Res. 2022. PMID: 35996683 Free PMC article. - SIRT1 is transcriptionally repressed by YY1 and suppresses ferroptosis in rheumatoid arthritis.
Zhan Y, Yang Z, Zhan F, Huang Y, Lin S. Zhan Y, et al. Adv Rheumatol. 2023 Mar 7;63(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s42358-023-00289-0. Adv Rheumatol. 2023. PMID: 36882816 - The role of resveratrol on rheumatoid arthritis: From bench to bedside.
Sheng S, Wang X, Liu X, Hu X, Shao Y, Wang G, Mao D, Li C, Chen B, Chen X. Sheng S, et al. Front Pharmacol. 2022 Aug 22;13:829677. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.829677. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36105210 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Chi L, Zhou B, Gao W, et al. Research advance on the common drugs for the rheumatoid arthritis treatment. Traditional Chin Med. 2014;39:2851–2858. - PubMed
- Miller MC, Manning HB, Jain A, Troeberg L, Dudhia J, Essex D, Sandison A, Seiki M, Nanchahal J, Nagase H, Itoh Y. Membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase is a crucial promoter of synovial invasion in human rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;60:686–697. doi: 10.1002/art.24331. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical