Rheological studies on the effect of different thickeners in texture-modified chicken rendang for individuals with dysphagia - PubMed (original) (raw)
Rheological studies on the effect of different thickeners in texture-modified chicken rendang for individuals with dysphagia
Nuraihan Abu Zarim et al. J Food Sci Technol. 2018 Nov.
Abstract
Texture-modified food has become an important strategy in managing dysphagia. Pureed food is proven to be the safest texture due to its high viscosity which can slow down the rate of the food bolus during swallowing. In this study, texture-modified chicken rendang was developed according to Texture C (smooth puree) as described by the Australian standard for texture-modified food. Samples were added with five different thickeners (sago starch, tapioca starch, modified corn starch, xanthan gum and carboxymethyl cellulose gum) at three different concentrations (10, 20 and 30% w/w). Their rheological effects were analyzed through dynamic and steady shear test. Results obtained reveals that samples contained xanthan gum have higher structure rigidity and shear thinning behaviour, while carboxymethyl cellulose gum provides the highest viscosity as well as yield stress than other samples. In terms of concentration, a strong dependence of structural rigidity and viscosity of all prepared samples with amount of thickeners added was observed. Overall, based on its rheological properties, the addition of carboxymethyl cellulose gum at 30% concentration was found to be the most suitable thickener, to be incorporated in the texture-modified chicken rendang. Selecting a suitable food thickener in developing food for individual with dysphagia plays an important role to ensure the right texture and consistency for their safe consumption.
Keywords: Dysphagia; Gum; Rheological test; Starch; Texture-modified food; Thickener.
Figures
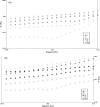
Fig. 1
a Oscillatory rheograms of control and thickened samples for storage modulus (G′) at 30% thickener’s concentration. b Oscillatory rheograms of control and thickened samples for loss modulus (G″) at 30% thickener’s concentration. Control = sample without starch, S = sago starch, T = tapioca starch, MC = modified corn starch, XG = xanthan gum, CMC = carboxymethyl cellulose gum
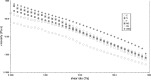
Fig. 2
Steady state flow curves of control and thickened samples at 30% thickener’s concentration. Control = sample without starch, S = sago starch, T = tapioca starch, MC = modified corn starch, XG = xanthan gum, CMC = carboxymethyl cellulose gum
Similar articles
- Rheological Behaviors of Thickened Infant Formula Prepared with Xanthan Gum-Based Food Thickeners for Dysphagic Infants.
Yoon SN, Yoo B. Yoon SN, et al. Dysphagia. 2017 Jun;32(3):454-462. doi: 10.1007/s00455-017-9786-2. Epub 2017 Mar 7. Dysphagia. 2017. PMID: 28271295 - Rheological characteristics of cold thickened beverages containing xanthan gum-based food thickeners used for dysphagia diets.
Cho HM, Yoo B. Cho HM, et al. J Acad Nutr Diet. 2015 Jan;115(1):106-11. doi: 10.1016/j.jand.2014.08.028. Epub 2014 Nov 4. J Acad Nutr Diet. 2015. PMID: 25441963 - Influence of thickening agents on rheological properties and sensory attributes of dysphagic diet.
de O S Schmidt H, Komeroski MR, Steemburgo T, de Oliveira VR. de O S Schmidt H, et al. J Texture Stud. 2021 Dec;52(5-6):587-602. doi: 10.1111/jtxs.12596. Epub 2021 Apr 7. J Texture Stud. 2021. PMID: 33760237 Review. - Rheological Issues on Oropharyngeal Dysphagia.
Gallegos C, Turcanu M, Assegehegn G, Brito-de la Fuente E. Gallegos C, et al. Dysphagia. 2023 Apr;38(2):558-585. doi: 10.1007/s00455-021-10337-w. Epub 2021 Jul 3. Dysphagia. 2023. PMID: 34216239 Review.
Cited by
- Rheological and Nutritional Assessment of Dysphagia-Oriented New Food Preparations.
Cuomo F, Angelicola M, De Arcangelis E, Lopez F, Messia MC, Marconi E. Cuomo F, et al. Foods. 2021 Mar 19;10(3):663. doi: 10.3390/foods10030663. Foods. 2021. PMID: 33808873 Free PMC article. - Preparation and Performance of Thickened Liquids for Patients with Konjac Glucomannan-Mediated Dysphagia.
Zhang W, Ren X, Zhang L, Chen J. Zhang W, et al. Molecules. 2022 Mar 28;27(7):2194. doi: 10.3390/molecules27072194. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35408593 Free PMC article. - Characterizing the Dynamic Textural Properties of Hydrocolloids in Pureed Foods-A Comparison Between TDS and TCATA.
Sharma M, Duizer L. Sharma M, et al. Foods. 2019 May 30;8(6):184. doi: 10.3390/foods8060184. Foods. 2019. PMID: 31151243 Free PMC article. - Exploring Tools for Designing Dysphagia-Friendly Foods: A Review.
Giura L, Urtasun L, Belarra A, Ansorena D, Astiasarán I. Giura L, et al. Foods. 2021 Jun 10;10(6):1334. doi: 10.3390/foods10061334. Foods. 2021. PMID: 34200551 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Ahmed J, Ramaswamy HS. Dynamic and steady shear rheology of fruit puree based baby foods. J Food Sci Technol Mysore. 2007;44:579.
- Behzadfar E, Abdolrasouli MH, Sharif F, Nazockdast H. Effect of solid loading and aggregate size on the rheological behaviour of PDMS/calcium carbonate suspensions. Braz J Chem Eng. 2009;26:713–721. doi: 10.1590/S0104-66322009000400010. - DOI
- Cardello AV, Maller O, Masor HB, Dubose C, Edelman B. Role of consumer expectancies in the acceptance of novel foods. J Food Sci. 1985;50:1707–1718. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2621.1985.tb10571.x. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources