Herbal Medicine Formulas for Parkinson's Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trials - PubMed (original) (raw)
Herbal Medicine Formulas for Parkinson's Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trials
Chun-Shuo Shan et al. Front Aging Neurosci. 2018.
Abstract
Background: Parkinson's disease (PD) is a debitlitating, chronic, progressive neurodegenerative disorder without modifying therapy. Here, we aimed to evaluate the available evidence of herbal medicine (HM) formulas for patients with PD according to randomized double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trials. Methods: HM formulas for PD were searched in eight main databases from their inception to February 2018. The methodological quality was assessed using Cochrane Collaboration risk of bias tool. Meta-analysis was performed using RevMan 5.3 software. Results: Fourteen trials with Seventeen comparisons comprising 1,311 patients were identified. Compared with placebo groups, HM paratherapy (n = 16 comparisons) showed significant better effects in the assessments of total Unified Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale (UPDRS) (WMD: -5.43, 95% CI:-8.01 to -2.86; P < 0.0001), UPDRS I (WMD: -0.30, 95% CI: -0.54 to -0.06; _P_ = 0.02), UPDRS II (WMD: -2.21, 95% CI: -3.19 to -1.22; _P_ < 0.0001), UPDRS III (WMD: -3.26, 95% CI:-4.36 to -2.16; _P_ < 0.00001), Parkinson's Disease Quality of Life Questionnaire (_p_ < 0.01) and Parkinson's Disease Questionnaire-39 (WMD: -7.65, 95% CI: -11.46 to -3.83; _p_ < 0.0001), Non-motor Symptoms Questionnaire (_p_ < 0.01) and Non-Motor Symptoms Scale (WMD: -9.19, 95% CI: -13.11 to -5.28; _P_ < 0.00001), Parkinson's Disease Sleep Scale (WMD: 10.69, 95% CI: 8.86 to 12.53; _P_ < 0.00001), and Hamilton depression rating scale (WMD: -5.87, 95% CI: -7.06 to -4.68; _P_ < 0.00001). The efficiency of HM monotherapy (_n_ = 1 comparison) was not superior to the placebo according to UPDRS II, UPDRS III and total UPDRS score in PD patients who never received levodopa treatment, all _P_ > 0.05. HM formulas paratherapy were generally safe and well tolerated for PD patients (RR: 0.41, 95% CI: 0.21 to 0.80; P = 0.009). Conclusion: The findings of present study supported the complementary use of HM paratherapy for PD patients, whereas the question on the efficacy of HM monotherapy in alleviating PD symptoms is still open.
Keywords: Parkinson's disease; meta-analysis; randomized double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial; systematic review; traditional Chinese medicine.
Figures
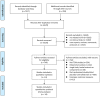
Figure 1
Flow diagram of the search process.
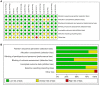
Figure 2
Risk of bias of the included studies. (A) Risk of bias summary: judgements about each risk of bias item for each included study. (B) Risk of bias graph: judgements about each risk of bias item presented as percentages across all included studies. +, low risk of bias; -, high risk of bias; ?, unclear risk of bias.
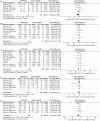
Figure 3
Forest plot of HM plus WCM vs. placebo plus WCM in terms of (A) UPDRS I, (B) UPDRS II, (C) UPDRS III, (D) UPDRS IV, and (E) Total UPDRS Score. (HM, herbal medicine; WCM, western conventional medicine; UPDRS, Unified Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale).
Figure 4
Forest plot of HM plus WCM vs. placebo plus WCM in terms of (A) PDQ-39, (B) NMSS, (C) PDSS, and (D) HAMD. (HM, herbal medicine; WCM, western conventional medicine; PDQ-39, Parkinson's Disease Questionnaire-39; NMSS, Non-Motor Symptoms Scale; PDSS, Parkinson's Disease Sleep Scale; HAMD, Hamilton depression rating scale).
Figure 5
Forest plot of HM plus WCM vs. placebo plus WCM in terms of adverse events.
Similar articles
- Efficacy of herbal medicine treatment based on syndrome differentiation for Parkinson's disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized placebo-controlled clinical trials.
Jun P, Zhao H, Jung IC, Kwon O, Han CH, Won J, Jang JH. Jun P, et al. Front Pharmacol. 2023 Feb 27;14:1108407. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1108407. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36925641 Free PMC article. - Comparison of the Efficacy of Different Drugs on Non-Motor Symptoms of Parkinson's Disease: a Network Meta-Analysis.
Li BD, Cui JJ, Song J, Qi C, Ma PF, Wang YR, Bai J. Li BD, et al. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;45(1):119-130. doi: 10.1159/000486252. Epub 2018 Jan 15. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29339630 - Pingchan Granule for Motor Symptoms and Non-Motor Symptoms of Parkinson's Disease: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study.
Gu SC, Ye Q, Wang CD, Zhao SR, Zhou J, Gao C, Zhang Y, Liu ZG, Yuan CX. Gu SC, et al. Front Pharmacol. 2022 Feb 25;13:739194. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.739194. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35281890 Free PMC article. - Effectiveness of traditional Chinese medicine as an adjunct therapy for Parkinson's disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Zhang G, Xiong N, Zhang Z, Liu L, Huang J, Yang J, Wu J, Lin Z, Wang T. Zhang G, et al. PLoS One. 2015 Mar 10;10(3):e0118498. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0118498. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25756963 Free PMC article. Review. - Combination Therapy with Zonisamide and Antiparkinson Drugs for Parkinson's Disease: A Meta-Analysis.
Matsunaga S, Kishi T, Iwata N. Matsunaga S, et al. J Alzheimers Dis. 2017;56(4):1229-1239. doi: 10.3233/JAD-161068. J Alzheimers Dis. 2017. PMID: 28157097 Review.
Cited by
- East Wind, West Wind: Toward the modernization of traditional Chinese medicine.
Yagüe E, Sun H, Hu Y. Yagüe E, et al. Front Neurosci. 2022 Nov 10;16:1057817. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.1057817. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36440293 Free PMC article. Review. - Natural Health Products for Symptomatic Relief of Parkinson's Disease: Prevalence, Interest, and Awareness.
Diadhiou S, Maas BR, Schootemeijer S, Bloem BR, de Vries NM, Calon F, Darweesh SKL, de Rus Jacquet A. Diadhiou S, et al. J Parkinsons Dis. 2024;14(6):1257-1264. doi: 10.3233/JPD-240102. J Parkinsons Dis. 2024. PMID: 38943398 Free PMC article. - Chinese herbal medicine treatment based on subgroup differentiation as adjunct therapy for Parkinson's disease: study protocol of a pilot add-on, randomised, controlled, pragmatic clinical trial.
Yuen SCS, Chua KK, Zhong LLD, Chan KW, Chan CKH, Chan KL, Lin Z, Mok V, Lau AY, Li M. Yuen SCS, et al. Chin Med. 2022 Jan 24;17(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s13020-022-00572-0. Chin Med. 2022. PMID: 35073963 Free PMC article. - Natural Products in Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Great Promise but an Ethical Challenge.
Di Paolo M, Papi L, Gori F, Turillazzi E. Di Paolo M, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Oct 18;20(20):5170. doi: 10.3390/ijms20205170. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31635296 Free PMC article. Review. - Nanophytomedicines as Therapeutic Agents for Parkinson's Disease.
Burns J, Buck AC, D' Souza S, Dube A, Bardien S. Burns J, et al. ACS Omega. 2023 Nov 2;8(45):42045-42061. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c04862. eCollection 2023 Nov 14. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 38024675 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources