Pleiotropic Effects of GLP-1 and Analogs on Cell Signaling, Metabolism, and Function - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Pleiotropic Effects of GLP-1 and Analogs on Cell Signaling, Metabolism, and Function
Jordan Rowlands et al. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018.
Abstract
The incretin hormone Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) is best known for its "incretin effect" in restoring glucose homeostasis in diabetics, however, it is now apparent that it has a broader range of physiological effects in the body. Both in vitro and in vivo studies have demonstrated that GLP-1 mimetics alleviate endoplasmic reticulum stress, regulate autophagy, promote metabolic reprogramming, stimulate anti-inflammatory signaling, alter gene expression, and influence neuroprotective pathways. A substantial body of evidence has accumulated with respect to how GLP-1 and its analogs act to restore and maintain normal cellular functions. These findings have prompted several clinical trials which have reported GLP-1 analogs improve cardiac function, restore lung function and reduce mortality in patients with obstructive lung disease, influence blood pressure and lipid storage, and even prevent synaptic loss and neurodegeneration. Mechanistically, GLP-1 elicits its effects via acute elevation in cAMP levels, and subsequent protein kinase(s) activation, pathways well-defined in pancreatic β-cells which stimulate insulin secretion in conjunction with elevated Ca2+ and ATP. More recently, new studies have shed light on additional downstream pathways stimulated by chronic GLP-1 exposure, findings which have direct relevance to our understanding of the potential therapeutic effects of longer lasting analogs recently developed for clinical use. In this review, we provide a comprehensive description of the diverse roles for GLP-1 across multiple tissues, describe downstream pathways stimulated by acute and chronic exposure, and discuss novel pleiotropic applications of GLP-1 mimetics in the treatment of human disease.
Keywords: GLP-1; cell function and integrity; diabetes; metabolism; signaling.
Figures
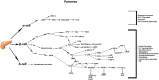
Figure 1
Commonly accepted GLP-1 signaling in the pancreatic tissue. Summary of the most commonly known signaling cascades activated by GLP-1 in the three different endocrine cell types α, β, δ, and their overall impact on diverse cellular processes.
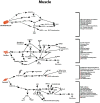
Figure 2
GLP-1 signaling across different muscle types. Multiple signal transduction pathways and their net impact arising from GLP-1R stimulation in skeletal, cardiac, and both multi and single unit smooth muscle.
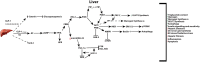
Figure 3
Active GLP-1 and its truncated products signaling in the liver. Active GLP-1 and its cAMP dependent pathways (solid arrows), as well as hypothesized (dashed arrows) truncated product induced signaling and their respective net effects.
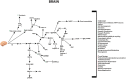
Figure 4
Pleiotropic effects of GLP-1 signaling in the brain. GLP-1 and its analogs activate diverse signaling pathways in the brain, leading to a plethora of neuroprotective outcomes.
Similar articles
- Multifaceted Roles of GLP-1 and Its Analogs: A Review on Molecular Mechanisms with a Cardiotherapeutic Perspective.
Pandey S, Mangmool S, Parichatikanond W. Pandey S, et al. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Jun 3;16(6):836. doi: 10.3390/ph16060836. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37375783 Free PMC article. Review. - beta-cell failure in diabetes and preservation by clinical treatment.
Wajchenberg BL. Wajchenberg BL. Endocr Rev. 2007 Apr;28(2):187-218. doi: 10.1210/10.1210/er.2006-0038. Epub 2007 Mar 12. Endocr Rev. 2007. PMID: 17353295 Review. - Anti-diabetic actions of glucagon-like peptide-1 on pancreatic beta-cells.
Lee YS, Jun HS. Lee YS, et al. Metabolism. 2014 Jan;63(1):9-19. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2013.09.010. Epub 2013 Oct 17. Metabolism. 2014. PMID: 24140094 Review. - Central effects of GLP-1: new opportunities for treatments of neurodegenerative diseases.
Hölscher C. Hölscher C. J Endocrinol. 2014 Mar 7;221(1):T31-41. doi: 10.1530/JOE-13-0221. Print 2014 Apr. J Endocrinol. 2014. PMID: 23999914 Review. - Harnessing the therapeutic potential of glucagon-like peptide-1: a critical review.
Baggio LL, Drucker DJ. Baggio LL, et al. Treat Endocrinol. 2002;1(2):117-25. doi: 10.2165/00024677-200201020-00005. Treat Endocrinol. 2002. PMID: 15765627 Review.
Cited by
- Neuroprotective efficacy of 4-Hydroxyisoleucine in experimentally induced intracerebral hemorrhage.
Mehmood Siddiqui E, Mehan S, Upadhayay S, Khan A, Halawi M, Ahmed Halawi A, Alsaffar RM. Mehmood Siddiqui E, et al. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2021 Nov;28(11):6417-6431. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.07.010. Epub 2021 Jul 10. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34764759 Free PMC article. - Alterations in pancreatic islet cell function in response to small bowel resection.
Courtney CM, Shyr ZA, Yan Z, Onufer EJ, Steinberger AE, Tecos ME, Barron LK, Guo J, Remedi MS, Warner BW. Courtney CM, et al. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2020 Jul 1;319(1):G36-G42. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00282.2019. Epub 2020 May 28. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32463335 Free PMC article. - Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) signalling in the brain: From neural circuits and metabolism to therapeutics.
Kabahizi A, Wallace B, Lieu L, Chau D, Dong Y, Hwang ES, Williams KW. Kabahizi A, et al. Br J Pharmacol. 2022 Feb;179(4):600-624. doi: 10.1111/bph.15682. Epub 2021 Nov 4. Br J Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34519026 Free PMC article. Review. - Semaglutide Alleviates Ovary Inflammation via the AMPK/SIRT1/NF‑κB Signaling Pathway in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Mice.
Liu M, Guo S, Li X, Tian Y, Yu Y, Tang L, Sun Q, Zhang T, Fan M, Zhang L, Xu Y, An J, Gao X, Han L, Zhang L. Liu M, et al. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024 Sep 4;18:3925-3938. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S484531. eCollection 2024. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024. PMID: 39247793 Free PMC article. - NLRP3 Inflammasome and Gut Dysbiosis Linking Diabetes Mellitus and Inflammatory Bowel Disease.
Malicevic U, Rai V, Skrbic R, Agrawal DK. Malicevic U, et al. Arch Intern Med Res. 2024;7(3):200-218. doi: 10.26502/aimr.0178. Epub 2024 Aug 31. Arch Intern Med Res. 2024. PMID: 39328924 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous