Trends of Human Plague, Madagascar, 1998-2016 - PubMed (original) (raw)
Trends of Human Plague, Madagascar, 1998-2016
Voahangy Andrianaivoarimanana et al. Emerg Infect Dis. 2019 Feb.
Abstract
Madagascar is more seriously affected by plague, a zoonosis caused by Yersinia pestis, than any other country. The Plague National Control Program was established in 1993 and includes human surveillance. During 1998-2016, a total of 13,234 suspected cases were recorded, mainly from the central highlands; 27% were confirmed cases, and 17% were presumptive cases. Patients with bubonic plague (median age 13 years) represented 93% of confirmed and presumptive cases, and patients with pneumonic plague (median age 29 years) represented 7%. Deaths were associated with delay of consultation, pneumonic form, contact with other cases, occurrence after 2009, and not reporting dead rats. A seasonal pattern was observed with recrudescence during September-March. Annual cases peaked in 2004 and decreased to the lowest incidence in 2016. This overall reduction occurred primarily for suspected cases and might be caused by improved adherence to case criteria during widespread implementation of the F1 rapid diagnostic test in 2002.
Keywords: Madagascar; Yersinia pestis; bacteria; bubonic plague; case-fatality rate; fleas; human plague; plague; pneumonic plague; rats; trends; zoonoses.
Figures
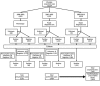
Figure 1
Diagnostic flowchart for suspected cases of plague, Madagascar, 1998–2016.
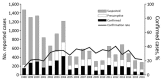
Figure 2
Classification of reported plague cases and confirmation rate, Madagascar, 1998–2016.
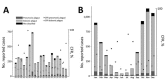
Figure 3
Yearly (A) and monthly (B) distributions of bubonic and pneumonic plague and their CFR, Madagascar, 1998–2016. CFR, case-fatality rate.
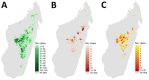
Figure 4
Geographic distributions of bubonic plague (A), pneumonic plague (B), and infection clusters (C), Madagascar, 1998–2016.
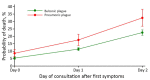
Figure 5
Predictive mortality rate according to clinical form and day of consultation for cases of plague, Madagascar, 1998–2016. Error bars indicate 95% CIs.
Similar articles
- Short- and long-term humoral immune response against Yersinia pestis in plague patients, Madagascar.
Andrianaivoarimanana V, Iharisoa AL, Rahalison L, Ralimanantsoa ML, Ratsitorahina M, Rakotonanahary RJL, Carniel E, Demeure C, Rajerison M. Andrianaivoarimanana V, et al. BMC Infect Dis. 2020 Nov 10;20(1):822. doi: 10.1186/s12879-020-05565-8. BMC Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 33172393 Free PMC article. - Epidemiological characteristics of an urban plague epidemic in Madagascar, August-November, 2017: an outbreak report.
Randremanana R, Andrianaivoarimanana V, Nikolay B, Ramasindrazana B, Paireau J, Ten Bosch QA, Rakotondramanga JM, Rahajandraibe S, Rahelinirina S, Rakotomanana F, Rakotoarimanana FM, Randriamampionona LB, Razafimbia V, De Dieu Randria MJ, Raberahona M, Mikaty G, Le Guern AS, Rakotonjanabelo LA, Ndiaye CF, Rasolofo V, Bertherat E, Ratsitorahina M, Cauchemez S, Baril L, Spiegel A, Rajerison M. Randremanana R, et al. Lancet Infect Dis. 2019 May;19(5):537-545. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(18)30730-8. Epub 2019 Mar 28. Lancet Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 30930106 Free PMC article. - [The plague in Madagascar: epidemiologic data from 1989 to 1995 and the national control program].
Champetier de Ribes G, Rasoamanana B, Randriambelosoa J, Rakoto LJ, Rabescn D, Chanteau S. Champetier de Ribes G, et al. Sante. 1997 Jan-Feb;7(1):53-60. Sante. 1997. PMID: 9172878 French. - The rise of pneumonic plague in Madagascar: current plague outbreak breaks usual seasonal mould.
Rabaan AA, Al-Ahmed SH, Alsuliman SA, Aldrazi FA, Alfouzan WA, Haque S. Rabaan AA, et al. J Med Microbiol. 2019 Mar;68(3):292-302. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.000915. Epub 2019 Jan 11. J Med Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30632956 Review. - Review of genotyping methods for Yersinia pestis in Madagascar.
Randriantseheno LN, Andrianaivoarimanana V, Pizarro-Cerdá J, Wagner DM, Rajerison M. Randriantseheno LN, et al. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2024 Jun 27;18(6):e0012252. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0012252. eCollection 2024 Jun. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2024. PMID: 38935608 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Status and analysis of undetected plague cases in Yunnan Province, China.
Su C, Duan B, Duan Q, He Z, Sha H, Liang Y, Pu E, Qin S, Duan R, Lyu D, Li W, Tang D, Zhang P, Xiao M, Xia L, Jing H, Wang X, Gao Z, Kan B. Su C, et al. Front Public Health. 2024 Sep 4;12:1408025. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1408025. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39296840 Free PMC article. - Factors influencing the re-emergence of plague in Madagascar.
Alderson J, Quastel M, Wilson E, Bellamy D. Alderson J, et al. Emerg Top Life Sci. 2020 Dec 11;4(4):411-421. doi: 10.1042/ETLS20200334. Emerg Top Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 33258957 Free PMC article. Review. - Characterization of two affinity matured Anti-Yersinia pestis F1 human antibodies with medical countermeasure potential.
Velappan N, Biryukov SS, Rill NO, Klimko CP, Rosario-Acevedo R, Shoe JL, Hunter M, Dankmeyer JL, Fetterer DP, Bedinger D, Phipps ME, Watt AJ, Abergel RJ, Dichosa A, Kozimor SA, Cote CK, Lillo AM. Velappan N, et al. PLoS One. 2024 Jul 2;19(7):e0305034. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0305034. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38954719 Free PMC article. - Comparative sequence analysis elucidates the evolutionary patterns of Yersinia pestis in New Mexico over thirty-two years.
Warren ME, Pickett BE, Adams BJ, Villalva C, Applegate A, Robison RA. Warren ME, et al. PeerJ. 2023 Sep 26;11:e16007. doi: 10.7717/peerj.16007. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 37780382 Free PMC article. - Phylogenetic analysis of the origin and spread of plague in Madagascar.
Esquivel Gomez LR, Savin C, Andrianaivoarimanana V, Rahajandraibe S, Randriantseheno LN, Zhou Z, Kocher A, Didelot X, Rajerison M, Kühnert D. Esquivel Gomez LR, et al. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2023 May 1;17(5):e0010362. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0010362. eCollection 2023 May. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2023. PMID: 37126517 Free PMC article.
References
- Bertherat E. Plague around the world, 2010–2015. Wkly Epidemiol Rec. 2016;91:89–93. - PubMed
- Brygoo ER. [Epidemiology of the plague at Madagascar] [in French]. Med Trop (Mars). 1966;26:26–, 79.. - PubMed
- Migliani R, Chanteau S, Rahalison L, Ratsitorahina M, Boutin JP, Ratsifasoamanana L, et al. Epidemiological trends for human plague in Madagascar during the second half of the 20th century: a survey of 20,900 notified cases. Trop Med Int Health. 2006;11:1228–37. 10.1111/j.1365-3156.2006.01677.x - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical