Multifunctional Hydroxyapatite Coated with Arthemisia absinthium Composites - PubMed (original) (raw)
doi: 10.3390/molecules25020413.
Simona Liliana Iconaru 2, Andreea Groza 3, Carmen Cimpeanu 4, Gabriel Predoi 1, Liliana Ghegoiu 2, Monica Luminita Badea 2 5, Mariana Carmen Chifiriuc 6 7, Luminita Marutescu 6 7, Roxana Trusca 8, Ciprian Florin Furnaris 1, Claudiu Stefan Turculet 9, Dorin Valter Enache 10, Daniela Predoi 2
Affiliations
- PMID: 31963829
- PMCID: PMC7024177
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25020413
Multifunctional Hydroxyapatite Coated with Arthemisia absinthium Composites
Mariana Stefania Raita et al. Molecules. 2020.
Abstract
There is significant research showing that essential oils extracted from the plants have antibacterial effects. The purpose of this study was to develop a biocomposite based on hydroxyapatite coated with Artemisia absinthium essential oil and to highlight its antibacterial activity. Therefore, present studies are aimed at developing new materials combining hydroxyapatite with Artemisia absinthium essential oil, in order to avoid postoperative infections. The purpose of this work is to highlight the antimicrobial properties of the Artemisia absinthium essential oil-hydroxyapatite composites obtained by a simple method and at low costs. The structural properties and antimicrobial efficiency of the Artemisia absinthium essential oil-hydroxyapatite composite have been studied. The samples based on Artemisia absinthium essential oil analyzed in this study showed that wormwood essential oil presented the highest efficacy against the fungal strain of C. parapsilosis. It has been shown that wormwood essential oil has a strong antimicrobial effect against the microbial strains tested in this study. Furthermore, the antimicrobial properties of the biocomposites based on hydroxyapatite and essential oil are due to the presence of the essential oil in the samples.
Keywords: Arthemisia absinthium; antimicrobial properties; hydroxyapatite.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
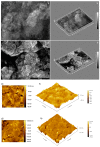
Figure 1
SEM images of HAp nanoparticles (a); 3D surface plot of SEM images of HAp (b); SEM images of HApWW sample (c); 3D surface plot of SEM images of HApWW sample (d) and AFM 2D and 3D surface topographies of HAp pellet (e,f) and HApWW pellet (g,h).
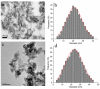
Figure 2
TEM image of HAp (a) and HApWW (c) nanoparticles. Distribution of HAp (b) and HApWW (d) nanoparticles obtained from TEM images.
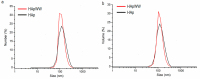
Figure 3
Dynamic light scattering (DLS) measurements of size dispersion of HAp (black) and HApWW (red) represent data weighted by number (a) and volume (b) of particles.
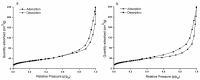
Figure 4
The nitrogen adsorption/desorption isotherms of HAp (a) and HApWW (b) samples.
Figure 5
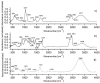
FTIR spectra of the HAp solution (a), WW EO (b) and HApWW (c) samples.
Similar articles
- Chemical composition of the essential oils of serbian wild-growing Artemisia absinthium and Artemisia vulgaris.
Blagojević P, Radulović N, Palić R, Stojanović G. Blagojević P, et al. J Agric Food Chem. 2006 Jun 28;54(13):4780-9. doi: 10.1021/jf060123o. J Agric Food Chem. 2006. PMID: 16787028 - Chemical composition of the essential oil of Artemisia absinthium growing wild in Iran.
Rezaeinodehi A, Khangholi S. Rezaeinodehi A, et al. Pak J Biol Sci. 2008 Mar 15;11(6):946-9. doi: 10.3923/pjbs.2008.946.949. Pak J Biol Sci. 2008. PMID: 18814663 - Antimicrobial, antioxidative, and insect repellent effects of Artemisia absinthium essential oil.
Mihajilov-Krstev T, Jovanović B, Jović J, Ilić B, Miladinović D, Matejić J, Rajković J, Dorđević L, Cvetković V, Zlatković B. Mihajilov-Krstev T, et al. Planta Med. 2014 Dec;80(18):1698-705. doi: 10.1055/s-0034-1383182. Epub 2014 Oct 15. Planta Med. 2014. PMID: 25317772 - Bioactive Compounds, Pharmacological Actions, and Pharmacokinetics of Wormwood (Artemisia absinthium).
Batiha GE, Olatunde A, El-Mleeh A, Hetta HF, Al-Rejaie S, Alghamdi S, Zahoor M, Magdy Beshbishy A, Murata T, Zaragoza-Bastida A, Rivero-Perez N. Batiha GE, et al. Antibiotics (Basel). 2020 Jun 23;9(6):353. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics9060353. Antibiotics (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32585887 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Enhanced Antibacterial Property of Sulfate-Doped Ag3PO4 Nanoparticles Supported on PAN Electrospun Nanofibers.
Panthi G, Hassan MM, Kuk YS, Kim JY, Chung HJ, Hong ST, Park M. Panthi G, et al. Molecules. 2020 Mar 19;25(6):1411. doi: 10.3390/molecules25061411. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32204541 Free PMC article. - MAPLE Coatings Embedded with Essential Oil-Conjugated Magnetite for Anti-Biofilm Applications.
Gherasim O, Popescu RC, Grumezescu V, Mogoșanu GD, Mogoantă L, Iordache F, Holban AM, Vasile BȘ, Bîrcă AC, Oprea OC, Grumezescu AM, Andronescu E. Gherasim O, et al. Materials (Basel). 2021 Mar 25;14(7):1612. doi: 10.3390/ma14071612. Materials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33806228 Free PMC article. - Enhancing bioactivity and mechanical performances of hydroxyapatite-calcium sulfate bone cements for bone repair: in vivo histological evaluation in rabbit femurs.
Jaita P, Chokethawai K, Randorn C, Boonsri K, Pringproa K, Thongkorn K, Watcharapasorn A, Jarupoom P. Jaita P, et al. RSC Adv. 2024 Jul 24;14(32):23286-23302. doi: 10.1039/d4ra03686g. eCollection 2024 Jul 19. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 39049882 Free PMC article. - Loaded n-Hydroxyapatite/SSG 3D Scaffolds as a Drug Delivery System of Nigella sativa Fractions for the Management of Local Antibacterial Infections.
Dalli M, El Guerraf A, Azizi SE, Benataya K, Azghar A, Mi-Kyung J, Maleb A, Bonglee K, Gseyra N. Dalli M, et al. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022 Mar 3;12(5):856. doi: 10.3390/nano12050856. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35269342 Free PMC article. - Antibacterial Activity of Biocellulose with Oregano Essential Oil against Cronobacter Strains.
Nagmetova G, Berthold-Pluta A, Garbowska M, Kurmanbayev A, Stasiak-Różańska L. Nagmetova G, et al. Polymers (Basel). 2020 Jul 24;12(8):1647. doi: 10.3390/polym12081647. Polymers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32722062 Free PMC article.
References
- Raho G.B., Abouni B. Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus most common source of infection. In: Méndez-Vilas A., editor. The Battle against Microbial Pathogens: Basic Science, Technological Advances and Educational Programs. Formatex Research Center; Badajoz, Spain: 2015.
- Tiemersma E.W., Bronzwaers S.L., Lyytikäinen O., Degener J.E., Schrijnemakers P., Bruinsma N., Monen J., Witte W., Grundman H., European Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance System Participants European antimicrobial resistance surveillance system participants: Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Europe. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2004;10:1627–1633. doi: 10.3201/eid1009.040069. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources