Roles and Functions of Exosomal Non-coding RNAs in Vascular Aging - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
. 2020 Feb 1;11(1):164-178.
doi: 10.14336/AD.2019.0402. eCollection 2020 Feb.
Affiliations
- PMID: 32010490
- PMCID: PMC6961769
- DOI: 10.14336/AD.2019.0402
Review
Roles and Functions of Exosomal Non-coding RNAs in Vascular Aging
Yu-Qing Ni et al. Aging Dis. 2020.
Abstract
Aging is a progressive loss of physiological integrity and functionality process which increases susceptibility and mortality to diseases. Vascular aging is a specific type of organic aging. The structure and function changes of endothelial cells (ECs) and vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) are the main cause of vascular aging, which could influence the threshold, process, and severity of vascular related diseases. Accumulating evidences demonstrate that exosomes serve as novel intercellular information communicator between cell to cell by delivering variety biologically active cargos, especially exosomal non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs), which are associated with most of aging-related biological and functional disorders. In this review, we will summerize the emerging roles and mechanisms of exosomal ncRNAs in vascular aging and vascular aging related diseases, focusing on the role of exosomal miRNAs and lncRNAs in regulating the functions of ECs and VSMCs. Moreover, the relationship between the ECs and VSMCs linked by exosomes, the potential diagnostic and therapeutic application of exosomes in vascular aging and the clinical evaluation and treatment of vascular aging and vascular aging related diseases will also be discussed.
Keywords: endothelial cells; exosomes; vascular aging; vascular diseases; vascular smooth muscle cells.
Copyright: © 2019 Ni et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest Not applicable. The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
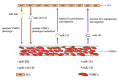
Figure 1.
The communication between ECs and VSMCs via exosomal ncRNAs. The blue and brown arrows indicate that exosomal miR206 and miR-143/145 secreted by ECs regulate the functions of VSMCs. The green and purple arrows indicate that exosomal miR-155 and miR-143 secreted by VSMCs regulate the functions of ECs.
Similar articles
- Exosomal Notch3 from high glucose-stimulated endothelial cells regulates vascular smooth muscle cells calcification/aging.
Lin X, Li S, Wang YJ, Wang Y, Zhong JY, He JY, Cui XJ, Zhan JK, Liu YS. Lin X, et al. Life Sci. 2019 Sep 1;232:116582. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.116582. Epub 2019 Jun 17. Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 31220525 - Function, Role, and Clinical Application of MicroRNAs in Vascular Aging.
Lin X, Zhan JK, Wang YJ, Tan P, Chen YY, Deng HQ, Liu YS. Lin X, et al. Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:6021394. doi: 10.1155/2016/6021394. Epub 2016 Dec 21. Biomed Res Int. 2016. PMID: 28097140 Free PMC article. Review. - The Potential Roles of Exosomal Non-Coding RNAs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.
Wang W, Hao LP, Song H, Chu XY, Wang R. Wang W, et al. Front Oncol. 2022 Feb 24;12:790916. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.790916. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35280805 Free PMC article. Review. - Roles and mechanisms of exosomal non-coding RNAs in human health and diseases.
Li C, Ni YQ, Xu H, Xiang QY, Zhao Y, Zhan JK, He JY, Li S, Liu YS. Li C, et al. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021 Nov 10;6(1):383. doi: 10.1038/s41392-021-00779-x. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021. PMID: 34753929 Free PMC article. Review. - Intracellular and exosomal microRNAome profiling of human vascular smooth muscle cells during replicative senescence.
Nguyen DDN, Zain SM, Kamarulzaman MH, Low TY, Chilian WM, Pan Y, Ting KN, Hamid A, Abdul Kadir A, Pung YF. Nguyen DDN, et al. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2021 Oct 1;321(4):H770-H783. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00058.2021. Epub 2021 Sep 10. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34506226
Cited by
- Berberine Improves Cognitive Impairment by Simultaneously Impacting Cerebral Blood Flow and β-Amyloid Accumulation in an APP/tau/PS1 Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease.
Ye C, Liang Y, Chen Y, Xiong Y, She Y, Zhong X, Chen H, Huang M. Ye C, et al. Cells. 2021 May 11;10(5):1161. doi: 10.3390/cells10051161. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34064687 Free PMC article. - Single-sEV profiling identifies the TACSTD2 + sEV subpopulation as a factor of tumor susceptibility in the elderly.
Ning N, Lu J, Li Q, Li M, Cai Y, Wang H, Li J. Ning N, et al. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024 May 3;22(1):222. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02456-x. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024. PMID: 38698420 Free PMC article. - BMF-AS1/BMF Promotes Diabetic Vascular Calcification and Aging both In Vitro and In Vivo.
Lin X, Xiang QY, Li S, Song WL, Wang YJ, Ni YQ, Zhao Y, Li C, Wang Y, Li HH, Liang Z, Zhan JK, Liu YS. Lin X, et al. Aging Dis. 2023 Feb 1;14(1):170-183. doi: 10.14336/AD.2022.0427. eCollection 2023 Feb 1. Aging Dis. 2023. PMID: 36818559 Free PMC article. - The Role of SGLT2 Inhibitors in Vascular Aging.
Liu L, Ni YQ, Zhan JK, Liu YS. Liu L, et al. Aging Dis. 2021 Aug 1;12(5):1323-1336. doi: 10.14336/AD.2020.1229. eCollection 2021 Aug. Aging Dis. 2021. PMID: 34341711 Free PMC article. Review. - Aging Hallmarks and the Role of Oxidative Stress.
Maldonado E, Morales-Pison S, Urbina F, Solari A. Maldonado E, et al. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Mar 6;12(3):651. doi: 10.3390/antiox12030651. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36978899 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Lai RC, Chen TS, Lim SK (2011). Mesenchymal stem cell exosome: a novel stem cell-based therapy for cardiovascular disease. Regen Med, 6: 481-92. - PubMed
- Liao XB, Zhang ZY, Yuan K, Liu Y, Feng X, Cui RR, et al. (2013). MiR-133a modulates osteogenic differentiation of vascular smooth muscle cells. Endocrinology, 154: 3344-52. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources