Effect of Cordyceps militaris Hot Water Extract on Immunomodulation-associated Gene Expression in Broilers, Gallus gallus - PubMed (original) (raw)
Effect of Cordyceps militaris Hot Water Extract on Immunomodulation-associated Gene Expression in Broilers, Gallus gallus
Yeong-Hsiang Cheng et al. J Poult Sci. 2019.
Abstract
Cordyceps militaris is a well-known Chinese medicinal fungus that has been used as a nutraceutical food in several Asian countries. Cordycepin (3'-deoxyadenosine), a secondary metabolite produced from Cordyceps militaris, has been demonstrated to exert a wide spectrum of pharmacological activities, such as anti-microbial and antitumor activities. However, the effect of cordycepin on immunomodulation in broilers is poorly investigated. In the current study, we investigated the effect of cordycepin (9.69, 19.38, and 38.76 mg) from Cordyceps militaris hot water extract (CMHW) on growth performance and immunocompetence in broilers. Results showed that CMHW significantly decreased inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) mRNA levels in the bursa of Fabricius after 4 weeks of feeding (P<0.05). CMHW treatment reduced cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) mRNA levels in the spleen and bursa of Fabricius after 4 weeks of feeding (P<0.05). Supplementation of CMHW for 3 days after vaccination reduced iNOS mRNA level in the spleen of 14 and 28 day-old broilers (P<0.05). Prior to vaccination, CMHW pretreatment significantly down-regulated COX-2 mRNA levels in the spleen and bursa of Fabricius of 14-day-old broilers (P<0.05). Furthermore, CMHW significantly reduced lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced iNOS and COX-2 mRNA levels in the spleen and bursa of Fabricius (P<0.05). CMHW treatment attenuated LPS-induced IFN-γ expression in the spleen and bursa of Fabricius, whereas CMHW induced IL-4 expression in these organs in response to LPS challenge (P<0.05). Taken together, these observations demonstrate that CMHW exerts an immunomodulatory role in broilers. CMHW is a potential novel feed additive with applications in inflammation-related diseases and bacterial infection in broilers.
Keywords: Cordyceps militaris; broiler; immunomodulation; lipopolysaccharide.
2019, Japan Poultry Science Association.
Figures
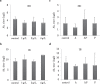
Fig. 1.
Effects of CMHW supplementation on antibody titer in broilers. (a) Effect of different concentrations of CMHW (1, 2, and 4 g/L in drinking water) on antibody titers against Newcastle disease (ND) in 14-day-old broilers. (b) Effect of different concentrations of CMHW (1, 2, and 4 g/L in drinking water) on antibody titers against infectious bronchitis (IB) in 14-day-old broilers. (c) Effect of different supplementation period (A, anterior only; AP: anterior and posterior; P, posterior only) of CMHW (2 g/L in drinking water) on antibody titers against ND in 35-day-old broilers. (d) Effect of different supplementation period (A, anterior only; AP: anterior and posterior; P, posterior only) of CMHW (2 g/L in drinking water) on antibody titers against IB in 35-day-old broilers. Values represent mean±SD (_n_=3).
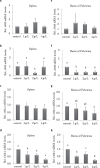
Fig. 2.
Effects of different concentrations of CMHW on inflammation-related gene expression in broilers. Effect of different concentrations of CMHW (1, 2, and 4 g/L in drinking water) on iNOS mRNA level in the spleen of 14-day-old (a) and 28-day-old broilers (b). COX-2 mRNA level in the spleen of 14-day-old (c) and 28-day-old broilers (d). Effect of different concentrations of CMHW (1, 2, and 4 g/L in drinking water) on iNOS mRNA level in the bursa of Fabricius of 14-day-old (e) and 28-day-old broilers (f). COX-2 mRNA level in the bursa of Fabricius of 14-day-old (g) and 28-day-old broilers (h). Values represent mean±SD (_n_=6). Means with different letter superscripts are significantly different (P<0.05)
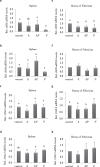
Fig. 3.
Effects of CMHW supplementation on inflammation-associated gene expression in broilers during vaccination. Effect of different supplementation period (A, anterior only; AP, anterior and posterior; P, posterior only) of CMHW (2 g/L in drinking water) on iNOS mRNA level in the spleen of 21-day-old (a) and 35-day-old broilers (b). COX-2 mRNA level in the spleen of 21-day-old (c) and 35-day-old broilers (d). Effect of different supplementation period (A, anterior only; AP, anterior and posterior; P, posterior only) of CMHW (2 g/L in drinking water) on iNOS mRNA expression in the bursa of Fabricius of 21-day-old (e) and 35-day-old broilers (f). COX-2 mRNA level in the bursa of Fabricius of 21-day-old (g) and 35-day-old broilers (h). Values represent mean±SD (_n_=6). Means with different letter superscripts are significantly different (P<0.05)
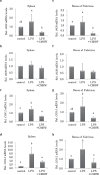
Fig. 4.
Effects of CMHW supplementation on inflammation-related gene expression in LPS-challenged broilers. Effect of CMHW supplementation on iNOS mRNA level in the spleen of broilers 3 h (a) and 24 h (b) post-injection of LPS. COX-2 mRNA level in the spleen of broilers 3 h (c) and 24 h (d) post-injection of LPS. Effect of CMHW supplementation on iNOS mRNA expression in the bursa of Fabricius of broilers 3 h (e) and 24 h (f) post-injection of LPS. COX-2 mRNA level in the bursa of Fabricius of broilers 3 h (g) and 24 h (h) post-injection of LPS. Values are expressed as mean±SD (_n_=6). Means with different letter superscripts are significantly different (P<0.05)
Fig. 5.
Effects of CMHW supplementation on type 1 helper T-lymphocytes (Th1) /type 2 helper T-lymphocytes (Th2) cytokine expression in LPS-challenged broilers. Effect of CMHW supplementation on IFN-γ mRNA level in the spleen of broilers 3 h (a) and 24 h (b) post-injection of LPS, and IL-4 mRNA level in the spleen of broilers 3 h (c) and 24 h (d) post-injection of LPS. Effect of CMHW supplementation on IFN-γ mRNA level in the bursa of Fabricius of broilers 3 h (e) and 24 h (f) post-injection of LPS. IL-4 mRNA level in the bursa of Fabricius of broilers 3 h (g) and 24 h (h) post-injection of LPS. Values represent mean±SD (_n_=6). Means with different letter superscripts are significantly different (P<0.05).
Similar articles
- Cordycepin-enriched Cordyceps militaris induces immunomodulation and tumor growth delay in mouse-derived breast cancer.
Jeong MH, Lee CM, Lee SW, Seo SY, Seo MJ, Kang BW, Jeong YK, Choi YJ, Yang KM, Jo WS. Jeong MH, et al. Oncol Rep. 2013 Oct;30(4):1996-2002. doi: 10.3892/or.2013.2660. Epub 2013 Aug 6. Oncol Rep. 2013. PMID: 23921598 - Chai Hu oral liquid enhances the immune functions of both spleen and bursa of Fabricius in heat-stressed broilers through strengthening TLR4-TBK1 signaling pathway.
Tang LP, Liu YL, Ding KN, Hou XJ, Qin JJ, Zhang YA, Liu HX, Shen XL, He YM. Tang LP, et al. Poult Sci. 2021 Sep;100(9):101302. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2021.101302. Epub 2021 Jul 18. Poult Sci. 2021. PMID: 34289428 Free PMC article. - Cordycepin inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation by the suppression of NF-kappaB through Akt and p38 inhibition in RAW 264.7 macrophage cells.
Kim HG, Shrestha B, Lim SY, Yoon DH, Chang WC, Shin DJ, Han SK, Park SM, Park JH, Park HI, Sung JM, Jang Y, Chung N, Hwang KC, Kim TW. Kim HG, et al. Eur J Pharmacol. 2006 Sep 18;545(2-3):192-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2006.06.047. Epub 2006 Jun 28. Eur J Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16899239 - Trends in the Immunomodulatory Effects of Cordyceps militaris: Total Extracts, Polysaccharides and Cordycepin.
Lee CT, Huang KS, Shaw JF, Chen JR, Kuo WS, Shen G, Grumezescu AM, Holban AM, Wang YT, Wang JS, Hsiang YP, Lin YM, Hsu HH, Yang CH. Lee CT, et al. Front Pharmacol. 2020 Nov 30;11:575704. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.575704. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 33328984 Free PMC article. Review. - [Advances in biosynthesis of cordycepin from Cordyceps militaris].
Zhao X, Li Q, Liu W, Guan H, Li C, Wang J, Wang L. Zhao X, et al. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2020 Jul 25;36(7):1293-1304. doi: 10.13345/j.cjb.190500. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2020. PMID: 32748587 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
- Cordycepin for Health and Wellbeing: A Potent Bioactive Metabolite of an Entomopathogenic Cordyceps Medicinal Fungus and Its Nutraceutical and Therapeutic Potential.
Ashraf SA, Elkhalifa AEO, Siddiqui AJ, Patel M, Awadelkareem AM, Snoussi M, Ashraf MS, Adnan M, Hadi S. Ashraf SA, et al. Molecules. 2020 Jun 12;25(12):2735. doi: 10.3390/molecules25122735. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32545666 Free PMC article. Review. - Antimicrobial, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and cytotoxic activities of Cordyceps militaris spent substrate.
Zhang D, Tang Q, He X, Wang Y, Zhu G, Yu L. Zhang D, et al. PLoS One. 2023 Sep 8;18(9):e0291363. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0291363. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37682981 Free PMC article. - Cordyceps militaris as a Bio Functional Food Source: Pharmacological Potential, Anti-Inflammatory Actions and Related Molecular Mechanisms.
Phull AR, Ahmed M, Park HJ. Phull AR, et al. Microorganisms. 2022 Feb 10;10(2):405. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10020405. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 35208860 Free PMC article. Review. - Benefits of Mushroom-Based Supplements on Growth Performance, Immunocompetence, and Meat Quality in Poultry.
Suberu SA, Isikhuemhen OS, Ogundare TE, Ekunseitan DA, Fasina YO. Suberu SA, et al. Animals (Basel). 2024 May 21;14(11):1517. doi: 10.3390/ani14111517. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38891564 Free PMC article. Review. - Effects of Acremonium terricola Culture on the Growth, Slaughter Yield, Immune Organ, Serum Biochemical Indexes, and Antioxidant Indexes of Geese.
Chen J, Guo Y, Lu Y, He Z, Zhu Y, Liu S, Xie K. Chen J, et al. Animals (Basel). 2022 May 2;12(9):1164. doi: 10.3390/ani12091164. Animals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35565590 Free PMC article.
References
- Abudabos AM, Al-Batshan HA, Murshed MA. Effects of prebiotics and probiotics on the performance and bacterial colonization of broiler chickens. South African Journal of Animal Science, 45: 419-428. 2015. a.
- Abudabos AM, Alyemni AH, Dafalla YM, Khan RU. The effect of phytogenic feed additives to substitute in-feed antibiotics on growth traits and blood biochemical parameters in broiler chicks challenged with Salmonella typhimurium. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 23: 24151-24157. 2015. b. - PubMed
- Ahn YJ, Park SJ, Lee SG, Shin SC, Choi DH. Cordycepin: selective growth inhibitor derived from liquid culture of Cordyceps militaris against Clostridium spp. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 48: 2744-2748. 2000. - PubMed
- Cheng YH, Wen CM, Dybus A, Proskura WS. Fermentation products of Cordyceps militaris enhance performance and modulate immune response of weaned piglets. South African Journal of Animal Science, 46: 121-128. 2016.
- Choi YH, Kim GY, Lee HH. Anti-inflammatory effects of cordycepin in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages through Toll-like receptor 4-mediated suppression of mitogen-activated protein kinases and NF-κB signaling pathways. Drug Design, Development and Therapy, 16: 1941-1953. 2014. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials