Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study - PubMed (original) (raw)
. 2020 Mar 28;395(10229):1054-1062.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3. Epub 2020 Mar 11.
Ting Yu 2, Ronghui Du 3, Guohui Fan 4, Ying Liu 2, Zhibo Liu 1, Jie Xiang 5, Yeming Wang 6, Bin Song 2, Xiaoying Gu 4, Lulu Guan 3, Yuan Wei 2, Hui Li 1, Xudong Wu 7, Jiuyang Xu 8, Shengjin Tu 2, Yi Zhang 1, Hua Chen 9, Bin Cao 10
Affiliations
- PMID: 32171076
- PMCID: PMC7270627
- DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3
Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study
Fei Zhou et al. Lancet. 2020.
Erratum in
- Department of Error.
[No authors listed] [No authors listed] Lancet. 2020 Mar 28;395(10229):1038. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30606-1. Epub 2020 Mar 12. Lancet. 2020. PMID: 32171424 Free PMC article. No abstract available. - Department of Error.
[No authors listed] [No authors listed] Lancet. 2020 Mar 28;395(10229):1038. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30638-3. Epub 2020 Mar 17. Lancet. 2020. PMID: 32192581 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Since December, 2019, Wuhan, China, has experienced an outbreak of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of patients with COVID-19 have been reported but risk factors for mortality and a detailed clinical course of illness, including viral shedding, have not been well described.
Methods: In this retrospective, multicentre cohort study, we included all adult inpatients (≥18 years old) with laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 from Jinyintan Hospital and Wuhan Pulmonary Hospital (Wuhan, China) who had been discharged or had died by Jan 31, 2020. Demographic, clinical, treatment, and laboratory data, including serial samples for viral RNA detection, were extracted from electronic medical records and compared between survivors and non-survivors. We used univariable and multivariable logistic regression methods to explore the risk factors associated with in-hospital death.
Findings: 191 patients (135 from Jinyintan Hospital and 56 from Wuhan Pulmonary Hospital) were included in this study, of whom 137 were discharged and 54 died in hospital. 91 (48%) patients had a comorbidity, with hypertension being the most common (58 [30%] patients), followed by diabetes (36 [19%] patients) and coronary heart disease (15 [8%] patients). Multivariable regression showed increasing odds of in-hospital death associated with older age (odds ratio 1·10, 95% CI 1·03-1·17, per year increase; p=0·0043), higher Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score (5·65, 2·61-12·23; p<0·0001), and d-dimer greater than 1 μg/mL (18·42, 2·64-128·55; p=0·0033) on admission. Median duration of viral shedding was 20·0 days (IQR 17·0-24·0) in survivors, but SARS-CoV-2 was detectable until death in non-survivors. The longest observed duration of viral shedding in survivors was 37 days.
Interpretation: The potential risk factors of older age, high SOFA score, and d-dimer greater than 1 μg/mL could help clinicians to identify patients with poor prognosis at an early stage. Prolonged viral shedding provides the rationale for a strategy of isolation of infected patients and optimal antiviral interventions in the future.
Funding: Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences; National Science Grant for Distinguished Young Scholars; National Key Research and Development Program of China; The Beijing Science and Technology Project; and Major Projects of National Science and Technology on New Drug Creation and Development.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
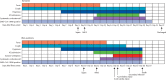
Figure 1
Clinical courses of major symptoms and outcomes and duration of viral shedding from illness onset in patients hospitalised with COVID-19 Figure shows median duration of symptoms and onset of complications and outcomes. ICU=intensive care unit. SARS-CoV-2=severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. ARDS=acute respiratory distress syndrome. COVID-19=coronavirus disease 2019.
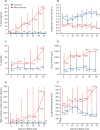
Figure 2
Temporal changes in laboratory markers from illness onset in patients hospitalised with COVID-19 Figure shows temporal changes in d-dimer (A), lymphocytes (B), IL-6 (C), serum ferritin (D), high-sensitivity cardiac troponin I (E), and lactate dehydrogenase (F). Differences between survivors and non-survivors were significant for all timepoints shown, except for day 4 after illness onset for d-dimer, IL-6, and high-sensitivity cardiac troponin I. For serum ferritin (D), the median values after day 16 exceeded the upper limit of detection, as indicated by the dashed line. COVID-19=coronavirus disease 2019. IL-6=interleukin-6.
Comment in
- Clinical course and mortality risk of severe COVID-19.
Weiss P, Murdoch DR. Weiss P, et al. Lancet. 2020 Mar 28;395(10229):1014-1015. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30633-4. Epub 2020 Mar 17. Lancet. 2020. PMID: 32197108 Free PMC article. No abstract available. - Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and covid-19.
Little P. Little P. BMJ. 2020 Mar 27;368:m1185. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m1185. BMJ. 2020. PMID: 32220865 No abstract available. - COVID-19 and rheumatology: first steps towards a different future?
McInnes IB. McInnes IB. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020 May;79(5):551-552. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-217494. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020. PMID: 32299844 No abstract available. - SARS-CoV-2 shedding and infectivity.
Atkinson B, Petersen E. Atkinson B, et al. Lancet. 2020 Apr 25;395(10233):1339-1340. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30868-0. Epub 2020 Apr 15. Lancet. 2020. PMID: 32304647 Free PMC article. No abstract available. - Bacterial and fungal infections in COVID-19 patients: A matter of concern.
Zhou P, Liu Z, Chen Y, Xiao Y, Huang X, Fan XG. Zhou P, et al. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2020 Sep;41(9):1124-1125. doi: 10.1017/ice.2020.156. Epub 2020 Apr 22. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2020. PMID: 32317036 Free PMC article. No abstract available. - Coronavirus disease 2019 and obstructive sleep apnea syndrome.
Pazarlı AC, Ekiz T, İlik F. Pazarlı AC, et al. Sleep Breath. 2021 Mar;25(1):371. doi: 10.1007/s11325-020-02087-0. Epub 2020 Apr 28. Sleep Breath. 2021. PMID: 32342265 Free PMC article. No abstract available. - Is there a role for lung perfusion [99mTc]-MAA SPECT/CT to rule out pulmonary embolism in COVID-19 patients with contraindications for iodine contrast?
Burger IA, Niemann T, Patriki D, Fontana F, Beer JH. Burger IA, et al. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2020 Aug;47(9):2062-2063. doi: 10.1007/s00259-020-04837-4. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2020. PMID: 32350559 Free PMC article. No abstract available. - Anticoagulation in COVID-19.
Atallah B, Mallah SI, AlMahmeed W. Atallah B, et al. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Pharmacother. 2020 Jul 1;6(4):260-261. doi: 10.1093/ehjcvp/pvaa036. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 32352517 Free PMC article. No abstract available. - Prevalence and fatality rates of COVID-19: What are the reasons for the wide variations worldwide?
Al-Tawfiq JA, Leonardi R, Fasoli G, Rigamonti D. Al-Tawfiq JA, et al. Travel Med Infect Dis. 2020 May-Jun;35:101711. doi: 10.1016/j.tmaid.2020.101711. Epub 2020 Apr 29. Travel Med Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32360326 Free PMC article. No abstract available. - Primary Care Providers: Discuss COVID-19-Related Goals of Care with Your Vulnerable Patients Now.
Kutscher E, Kladney M. Kutscher E, et al. J Gen Intern Med. 2020 Jul;35(7):2195-2196. doi: 10.1007/s11606-020-05862-7. Epub 2020 May 6. J Gen Intern Med. 2020. PMID: 32378009 Free PMC article. No abstract available. - Inflammatory Bowel Diseases and Biological Treatment in SARS-CoV-2 Era. Why Not?
Grassia R, Soro S, Conti CB. Grassia R, et al. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2020 Jun 18;26(7):e71. doi: 10.1093/ibd/izaa110. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2020. PMID: 32386056 Free PMC article. No abstract available. - SARS-CoV-2 and influenza virus co-infection.
Cuadrado-Payán E, Montagud-Marrahi E, Torres-Elorza M, Bodro M, Blasco M, Poch E, Soriano A, Piñeiro GJ. Cuadrado-Payán E, et al. Lancet. 2020 May 16;395(10236):e84. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31052-7. Epub 2020 May 5. Lancet. 2020. PMID: 32423586 Free PMC article. No abstract available. - ACE2, TMPRSS2, and furin gene expression in the airways of people with asthma-implications for COVID-19.
Bradding P, Richardson M, Hinks TSC, Howarth PH, Choy DF, Arron JR, Wenzel SE, Siddiqui S. Bradding P, et al. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2020 Jul;146(1):208-211. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2020.05.013. Epub 2020 May 22. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32450087 Free PMC article. No abstract available. - Markers of liver injury and clinical outcomes in COVID-19 patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Kunutsor SK, Laukkanen JA. Kunutsor SK, et al. J Infect. 2021 Jan;82(1):159-198. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2020.05.045. Epub 2020 May 28. J Infect. 2021. PMID: 32474033 Free PMC article. No abstract available. - Elevated Cardiac Troponin I Is Associated with Poor Outcomes in COVID-19 Patients at an Academic Medical Center in Midwestern USA.
Franks CE, Scott MG, Farnsworth CW. Franks CE, et al. J Appl Lab Med. 2020 Sep 1;5(5):1137-1139. doi: 10.1093/jalm/jfaa092. J Appl Lab Med. 2020. PMID: 32484893 Free PMC article. No abstract available. - Allocation criteria for an initial shortage of a future SARS-CoV-2 vaccine and necessary measures for global immunity.
Henn W. Henn W. Vaccine. 2020 Jul 22;38(34):5396-5397. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2020.06.058. Epub 2020 Jun 23. Vaccine. 2020. PMID: 32600909 Free PMC article. No abstract available. - The challenge of COVID-19 has accelerated the use of new data-sharing technologies.
Ramnath VR, Kairaitis K, Malhotra A. Ramnath VR, et al. Respirology. 2020 Aug;25(8):800-801. doi: 10.1111/resp.13894. Epub 2020 Jul 1. Respirology. 2020. PMID: 32613654 Free PMC article. No abstract available. - SARS-CoV-2 Receptor ACE2 (Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2) Is Upregulated in Colonic Organoids From Hypertensive Rats.
Li J, Stevens BR, Richards EM, Raizada MK. Li J, et al. Hypertension. 2020 Sep;76(3):e26-e28. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.120.15725. Epub 2020 Jul 9. Hypertension. 2020. PMID: 32643416 Free PMC article. No abstract available. - Is there really room for anti-rheumatic drugs in the treatment of COVID-19?
Favalli EG, Ingegnoli F, Biggioggero M, Caporali R. Favalli EG, et al. Scand J Rheumatol. 2020 Sep;49(5):412-413. doi: 10.1080/03009742.2020.1765413. Epub 2020 Jul 28. Scand J Rheumatol. 2020. PMID: 32720847 No abstract available. - The Unrecognized Threat of Secondary Bacterial Infections with COVID-19.
Vaillancourt M, Jorth P. Vaillancourt M, et al. mBio. 2020 Aug 7;11(4):e01806-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01806-20. mBio. 2020. PMID: 32769090 Free PMC article. - [Antibiotic use in hospitals in cases of COVID-19].
Borén HK, Thaulow CM, Quist-Paulsen E, Wæhre T, Akselsen PE, Tonby K. Borén HK, et al. Tidsskr Nor Laegeforen. 2020 Jun 19;140(11). doi: 10.4045/tidsskr.20.0443. Print 2020 Aug 18. Tidsskr Nor Laegeforen. 2020. PMID: 32815355 Norwegian. No abstract available. - d-Dimer and COVID-19.
Oudkerk M, Büller HR, Kuijpers D, Oudkerk SF, van Beek EJR. Oudkerk M, et al. Radiology. 2020 Dec;297(3):E343-E344. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2020203481. Epub 2020 Oct 13. Radiology. 2020. PMID: 33048037 Free PMC article. No abstract available. - Deep vein thrombosis in SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia-affected patients within standard care units: Exploring a submerged portion of the iceberg.
Pizzolo F, Rigoni AM, De Marchi S, Friso S, Tinazzi E, Sartori G, Stefanoni F, Nalin F, Montagnana M, Pilotto S, Milella M, Azzini AM, Tacconelli E, Marchi G, Girelli D, Olivieri O, Martinelli N. Pizzolo F, et al. Thromb Res. 2020 Oct;194:216-219. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2020.08.008. Epub 2020 Aug 6. Thromb Res. 2020. PMID: 33074107 Free PMC article. - Scientific effort in combating COVID-19 in obstetrics and gynecology.
Martinez-Portilla RJ, Gil MM, Poon LC. Martinez-Portilla RJ, et al. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2021 Feb;57(2):189-194. doi: 10.1002/uog.23584. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2021. PMID: 33428290 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
- Clinical characteristics and risk factors for severity of COVID-19 outside Wuhan: a double-center retrospective cohort study of 213 cases in Hunan, China.
Hu X, Hu C, Yang Y, Chen J, Zhong P, Wen Y, Chen X. Hu X, et al. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2020 Jan-Dec;14:1753466620963035. doi: 10.1177/1753466620963035. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2020. PMID: 33138694 Free PMC article. - Clinical course and outcome of 107 patients infected with the novel coronavirus, SARS-CoV-2, discharged from two hospitals in Wuhan, China.
Wang D, Yin Y, Hu C, Liu X, Zhang X, Zhou S, Jian M, Xu H, Prowle J, Hu B, Li Y, Peng Z. Wang D, et al. Crit Care. 2020 Apr 30;24(1):188. doi: 10.1186/s13054-020-02895-6. Crit Care. 2020. PMID: 32354360 Free PMC article. - Clinical characteristics of 113 deceased patients with coronavirus disease 2019: retrospective study.
Chen T, Wu D, Chen H, Yan W, Yang D, Chen G, Ma K, Xu D, Yu H, Wang H, Wang T, Guo W, Chen J, Ding C, Zhang X, Huang J, Han M, Li S, Luo X, Zhao J, Ning Q. Chen T, et al. BMJ. 2020 Mar 26;368:m1091. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m1091. BMJ. 2020. PMID: 32217556 Free PMC article. - Liver diseases in COVID-19: Etiology, treatment and prognosis.
Wu J, Song S, Cao HC, Li LJ. Wu J, et al. World J Gastroenterol. 2020 May 21;26(19):2286-2293. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i19.2286. World J Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 32476793 Free PMC article. Review. - Assessment of risk, severity, mortality, glycemic control and antidiabetic agents in patients with diabetes and COVID-19: A narrative review.
Singh AK, Khunti K. Singh AK, et al. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2020 Jul;165:108266. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108266. Epub 2020 Jun 11. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2020. PMID: 32533989 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Role of Biomarkers Diagnostic Tools in Patients with COVID-19: Stratification Made Easy.
Salman AA, Abdallah HM, Eldahdouh S, Elkhadry SW, Awad SM, Gaballah GMK, Awaad EK, Saad MG, Taha AE, Gaballa NK. Salman AA, et al. Int J Gen Med. 2024 Oct 25;17:4895-4906. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S488968. eCollection 2024. Int J Gen Med. 2024. PMID: 39473634 Free PMC article. - Hyperexpression of PTAFR and PF4 as Possible Platelet Risk Biomarkers in Patients With COVID-19.
DE Oliveira Sales L, DA Silva JBS, DE Pinho Pessoa FMC, Dias Nogueira BM, DE Oliveira LLB, Khayat AS, DE Moraes Filho MO, DE Moraes MEA, Montenegro RC, Moreira-Nunes CA. DE Oliveira Sales L, et al. In Vivo. 2024 Nov-Dec;38(6):2853-2863. doi: 10.21873/invivo.13766. In Vivo. 2024. PMID: 39477442 Free PMC article. - Investigating the impact of severe maternal SARS-CoV-2 infection on infant DNA methylation and neurodevelopment.
Hill RA, Gibbons A, Suwakulsiri W, Taseska A, Darke H, Malhotra A, Yee H, Fahey M, Hunt RW, Lim I, Palmer K, Sundram S. Hill RA, et al. Mol Psychiatry. 2024 Oct 30. doi: 10.1038/s41380-024-02808-x. Online ahead of print. Mol Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 39478169 - Longitudinal Analysis of COVID-19 Patients Shows Age-Associated T Cell Changes Independent of Ongoing Ill-Health.
Townsend L, Dyer AH, Naughton A, Kiersey R, Holden D, Gardiner M, Dowds J, O'Brien K, Bannan C, Nadarajan P, Dunne J, Martin-Loeches I, Fallon PG, Bergin C, O'Farrelly C, Cheallaigh CN, Bourke NM, Conlon N. Townsend L, et al. Front Immunol. 2021 May 7;12:676932. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.676932. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34025675 Free PMC article. - COVID-19: A Multimodality Review of Radiologic Techniques, Clinical Utility, and Imaging Features.
Manna S, Wruble J, Maron SZ, Toussie D, Voutsinas N, Finkelstein M, Cedillo MA, Diamond J, Eber C, Jacobi A, Chung M, Bernheim A. Manna S, et al. Radiol Cardiothorac Imaging. 2020 Jun 1;2(3):e200210. doi: 10.1148/ryct.2020200210. eCollection 2020 Jun. Radiol Cardiothorac Imaging. 2020. PMID: 33778588 Free PMC article.
References
- Gorbalenya AE, Baker SC, Baric RS, et al. Severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus: the species and its viruses—a statement of the Coronavirus Study Group. bioRxiv. 2020 doi: 10.1101/2020.02.07.937862. published online Feb 11. (preprint). - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous