Changes in blood coagulation in patients with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a meta-analysis - PubMed (original) (raw)
Meta-Analysis
. 2020 Jun;189(6):1050-1052.
doi: 10.1111/bjh.16725. Epub 2020 May 14.
Affiliations
- PMID: 32304581
- PMCID: PMC7264726
- DOI: 10.1111/bjh.16725
Meta-Analysis
Changes in blood coagulation in patients with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a meta-analysis
Mi Xiong et al. Br J Haematol. 2020 Jun.
No abstract available
Keywords: COVID-19; coagulation; coronavirus; laboratory; meta-analysis.
Figures
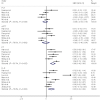
Fig 1
Forest plot of PLT, APTT, PT and D‐D levels in severe COVID‐19 patients versus mild COVID‐19 patients.
Comment in
- D-dimer is associated with the risk of mortality in Coronavirus Disease 2019 patients.
Shi L, Wang Y, Wang YD, Duan GC, Yang HY. Shi L, et al. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020 Aug;24(16):8576-8579. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202008_22655. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32894563
Similar articles
- The association between COVID-19 and asthma: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Wang Y, Ao G, Qi X, Xie B. Wang Y, et al. Clin Exp Allergy. 2020 Nov;50(11):1274-1277. doi: 10.1111/cea.13733. Epub 2020 Sep 24. Clin Exp Allergy. 2020. PMID: 32930476 No abstract available. - COVID-19 cytokine storm: the interplay between inflammation and coagulation.
Jose RJ, Manuel A. Jose RJ, et al. Lancet Respir Med. 2020 Jun;8(6):e46-e47. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30216-2. Epub 2020 Apr 27. Lancet Respir Med. 2020. PMID: 32353251 Free PMC article. No abstract available. - Fungal antigenemia in patients with severe Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): The facts and challenges.
Lei Y, Song Y, Shu Y, Zhao Y, Huo X, Wang H, Zeng Y, Yu X, Li X, Ye G, Fang B, Han S, Li R, Liu L. Lei Y, et al. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2020 Aug;53(4):657-659. doi: 10.1016/j.jmii.2020.05.010. Epub 2020 May 25. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2020. PMID: 32482367 Free PMC article. No abstract available. - COVID-19 and coagulative axis: review of emerging aspects in a novel disease.
Boccia M, Aronne L, Celia B, Mazzeo G, Ceparano M, D'Agnano V, Parrella R, Valente T, Bianco A, Perrotta F. Boccia M, et al. Monaldi Arch Chest Dis. 2020 May 19;90(2). doi: 10.4081/monaldi.2020.1300. Monaldi Arch Chest Dis. 2020. PMID: 32425013 Review. - Vitamin-D and COVID-19: do deficient risk a poorer outcome?
Mitchell F. Mitchell F. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020 Jul;8(7):570. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30183-2. Epub 2020 May 20. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020. PMID: 32445630 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
- Cutaneous, skin histopathological manifestations and relationship to COVID-19 infection patients.
Li H, Zhao Y, Zhou L, Hu J. Li H, et al. Dermatol Ther. 2020 Nov;33(6):e14157. doi: 10.1111/dth.14157. Epub 2020 Sep 7. Dermatol Ther. 2020. PMID: 32770717 Free PMC article. - Targeting spike protein-induced TLR/NET axis by COVID-19 therapeutic NRICM102 ameliorates pulmonary embolism and fibrosis.
Wei WC, Liaw CC, Tsai KC, Chiou CT, Tseng YH, Chiou WF, Lin YC, Tsai CI, Lin CS, Lin CS, Liou KT, Yu IS, Shen YC, Su YC. Wei WC, et al. Pharmacol Res. 2022 Oct;184:106424. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106424. Epub 2022 Sep 5. Pharmacol Res. 2022. PMID: 36064077 Free PMC article. - Cytokine Storm in COVID-19-Immunopathological Mechanisms, Clinical Considerations, and Therapeutic Approaches: The REPROGRAM Consortium Position Paper.
Bhaskar S, Sinha A, Banach M, Mittoo S, Weissert R, Kass JS, Rajagopal S, Pai AR, Kutty S. Bhaskar S, et al. Front Immunol. 2020 Jul 10;11:1648. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01648. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32754159 Free PMC article. - Covid-19-Associated Coagulopathy: Biomarkers of Thrombin Generation and Fibrinolysis Leading the Outcome.
Ranucci M, Sitzia C, Baryshnikova E, Di Dedda U, Cardani R, Martelli F, Corsi Romanelli M. Ranucci M, et al. J Clin Med. 2020 Oct 28;9(11):3487. doi: 10.3390/jcm9113487. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 33126772 Free PMC article. - Prognostic factors for severity and mortality in patients infected with COVID-19: A systematic review.
Izcovich A, Ragusa MA, Tortosa F, Lavena Marzio MA, Agnoletti C, Bengolea A, Ceirano A, Espinosa F, Saavedra E, Sanguine V, Tassara A, Cid C, Catalano HN, Agarwal A, Foroutan F, Rada G. Izcovich A, et al. PLoS One. 2020 Nov 17;15(11):e0241955. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0241955. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33201896 Free PMC article.
References
- Liu M, He P, Liu HG, Wang XJ, Li FJ, Chen S, et al. Clinical characteristics of 30 medical workers infected with new coronavirus pneumonia. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2020;43:E016. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources