Angiopoietin-2 as a marker of endothelial activation is a good predictor factor for intensive care unit admission of COVID-19 patients - PubMed (original) (raw)
Observational Study
. 2020 Nov;23(4):611-620.
doi: 10.1007/s10456-020-09730-0. Epub 2020 May 27.
Coralie L Guerin 3 4, Richard Chocron 5 6, Nader Yatim 7 8, Jeremy Boussier 7 8, Nicolas Gendron 3 9, Lina Khider 10, Jérôme Hadjadj 8 11, Guillaume Goudot 10, Benjamin Debuc 12, Philippe Juvin 13, Caroline Hauw-Berlemont 14, Jean-Loup Augy 14, Nicolas Peron 14, Emmanuel Messas 5 15, Benjamin Planquette 3 16, Olivier Sanchez 3 16, Bruno Charbit 17, Pascale Gaussem 3 18, Darragh Duffy 7 8, Benjamin Terrier 19 20, Tristan Mirault 5 15, Jean-Luc Diehl 3 21
Affiliations
- PMID: 32458111
- PMCID: PMC7250589
- DOI: 10.1007/s10456-020-09730-0
Observational Study
Angiopoietin-2 as a marker of endothelial activation is a good predictor factor for intensive care unit admission of COVID-19 patients
David M Smadja et al. Angiogenesis. 2020 Nov.
Abstract
Background: Coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19), a respiratory disease has been associated with ischemic complications, coagulation disorders, and an endotheliitis.
Objectives: To explore endothelial damage and activation-related biomarkers in COVID-19 patients with criteria of hospitalization for referral to intensive care unit (ICU) and/or respiratory worsening.
Methods: Analysis of endothelial and angiogenic soluble markers in plasma from patients at admission.
Results: Study enrolled 40 consecutive COVID-19 patients admitted to emergency department that fulfilled criteria for hospitalization. Half of them were admitted in conventional wards without any ICU transfer during hospitalization; whereas the 20 others were directly transferred to ICU. Patients transferred in ICU were more likely to have lymphopenia, decreased SpO2 and increased D-dimer, CRP and creatinine levels. In those patients, soluble E-selectin and angiopoietin-2 were significantly increased (p value at 0.009 and 0.003, respectively). Increase in SELE gene expression (gene coding for E-selectin protein) was confirmed in an independent cohort of 32 patients using a whole blood gene expression profile analysis. In plasma, we found a strong association between angiopoetin-2 and CRP, creatinine and D-dimers (with p value at 0.001, 0.001 and 0.003, respectively). ROC curve analysis identified an Angiopoietin-2 cut-off of 5000 pg/mL as the best predictor for ICU outcome (Se = 80.1%, Sp = 70%, PPV = 72.7%, NPV = 77%), further confirmed in multivariate analysis after adjustment for creatinine, CRP or D-dimers.
Conclusion: Angiopoietin-2 is a relevant predictive factor for ICU direct admission in COVID-19 patients. This result showing an endothelial activation reinforces the hypothesis of a COVID-19-associated microvascular dysfunction.
Keywords: Angiogenesis; Angiopoietin-2; Biomarker; COVID-19; E-selectin; Endothelial.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare nothing to disclose.
Figures
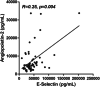
Fig. 1
Correlations between plasma angiopoietin-2 and sE-selectin levels in COVID-19 patients. R for Kendall rank correlation coefficient
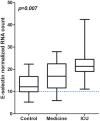
Fig. 2
E-selectin gene expression profile according to admission of patients in medical ward or ICU versus controls. ICU for intensive care unit; RNA for Ribonucleic Acid; Difference between groups evaluated with Kruskal–Wallis test
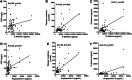
Fig. 3
Correlations between E-selectin and angiopoietin-2 and biological parameters of thrombo-inflammation. a–c correlations between sE-selectin and CRP, plasma creatinine and D-dimers. d–f: correlations between angiopoietin-2 and CRP, plasma creatinine and D-dimers. R for Kendall rank correlation coefficient
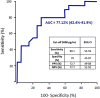
Fig. 4
ROC curve for angiopoietin-2 cut-off in direct ICU admission. Angiopoietin-2 level above 5000 pg/mL was identified using Youden index method as a potential criteria for COVID-19 transfer in ICU (AUC 77.12, 95% CI 62.4–91.9). AUC for area under the curve; CI for confidence interval; PPV for positive predictive value; NPV for negative predictive value. R for Kendall rank correlation coefficient; CRP for C-reactive protein
Similar articles
- Predictive value of National Early Warning Score 2 (NEWS2) for intensive care unit admission in patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Gidari A, De Socio GV, Sabbatini S, Francisci D. Gidari A, et al. Infect Dis (Lond). 2020 Oct;52(10):698-704. doi: 10.1080/23744235.2020.1784457. Epub 2020 Jun 25. Infect Dis (Lond). 2020. PMID: 32584161 - Iron metabolism and lymphocyte characterisation during Covid-19 infection in ICU patients: an observational cohort study.
Bolondi G, Russo E, Gamberini E, Circelli A, Meca MCC, Brogi E, Viola L, Bissoni L, Poletti V, Agnoletti V. Bolondi G, et al. World J Emerg Surg. 2020 Jun 30;15(1):41. doi: 10.1186/s13017-020-00323-2. World J Emerg Surg. 2020. PMID: 32605582 Free PMC article. - Predictors of Intensive Care Unit admission in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).
Carlino MV, Valenti N, Cesaro F, Costanzo A, Cristiano G, Guarino M, Sforza A. Carlino MV, et al. Monaldi Arch Chest Dis. 2020 Jul 15;90(3). doi: 10.4081/monaldi.2020.1410. Monaldi Arch Chest Dis. 2020. PMID: 32672430 - Importance of hyperglycemia in COVID-19 intensive-care patients: Mechanism and treatment strategy.
Mirzaei F, Khodadadi I, Vafaei SA, Abbasi-Oshaghi E, Tayebinia H, Farahani F. Mirzaei F, et al. Prim Care Diabetes. 2021 Jun;15(3):409-416. doi: 10.1016/j.pcd.2021.01.002. Epub 2021 Jan 9. Prim Care Diabetes. 2021. PMID: 33436320 Free PMC article. Review. - COVID-19 and Laboratory Markers from Romanian Patients-A Narrative Review.
Musat O, Sorop VB, Sorop MI, Lazar V, Marti DT, Susan M, Avram CR, Oprisoni A, Vulcanescu DD, Horhat FG, Bagiu IC, Horhat DI, Diaconu MM. Musat O, et al. Life (Basel). 2023 Aug 30;13(9):1837. doi: 10.3390/life13091837. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37763241 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- A systematic review and meta-analysis of regional risk factors for critical outcomes of COVID-19 during early phase of the pandemic.
Kim HJ, Hwang H, Hong H, Yim JJ, Lee J. Kim HJ, et al. Sci Rep. 2021 May 7;11(1):9784. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-89182-8. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33963250 Free PMC article. - COVID-19 risk stratification algorithms based on sTREM-1 and IL-6 in emergency department.
Van Singer M, Brahier T, Ngai M, Wright J, Weckman AM, Erice C, Meuwly JY, Hugli O, Kain KC, Boillat-Blanco N. Van Singer M, et al. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2021 Jan;147(1):99-106.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2020.10.001. Epub 2020 Oct 9. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33045281 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - D-dimer, BNP/NT-pro-BNP, and creatinine are reliable decision-making biomarkers in life-sustaining therapies withholding and withdrawing during COVID-19 outbreak.
Smadja DM, Fellous BA, Bonnet G, Hauw-Berlemont C, Sutter W, Beauvais A, Fauvel C, Philippe A, Weizman O, Mika D, Juvin P, Waldmann V, Diehl JL, Cohen A, Chocron R. Smadja DM, et al. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Sep 6;9:935333. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.935333. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 36148049 Free PMC article. - Immunological analysis of the murine anti-CD3-induced cytokine release syndrome model and therapeutic efficacy of anti-cytokine antibodies.
Nouveau L, Buatois V, Cons L, Chatel L, Pontini G, Pleche N, Ferlin WG. Nouveau L, et al. Eur J Immunol. 2021 Aug;51(8):2074-2085. doi: 10.1002/eji.202149181. Epub 2021 May 19. Eur J Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33945643 Free PMC article. - Cardiac Pericytes: Underappreciated Targets of SARS-CoV-2.
Das M, Chung MK. Das M, et al. JACC Basic Transl Sci. 2023 Feb;8(2):121-123. doi: 10.1016/j.jacbts.2023.01.010. Epub 2023 Feb 27. JACC Basic Transl Sci. 2023. PMID: 36875780 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous