Shenhuang granule in the treatment of severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): study protocol for an open-label randomized controlled clinical trial - PubMed (original) (raw)
Shenhuang granule in the treatment of severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): study protocol for an open-label randomized controlled clinical trial
Bangjiang Fang et al. Trials. 2020.
Abstract
Background: Currently, coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is continuously and rapidly circulating, causing heavy damage on public health. No effective antiviral treatment has been proved thus far. Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) has been widely applied in the treatment of a variety of infection diseases in China, hoping to produce clinical effects and reduce the use of antibiotics and glucocorticoid. The aim of this study is to evaluate the efficacy and safety of Shenhuang granule in treatment of severe COVID-19.
Methods/design: This multicenter, open-label randomized controlled trial is conducted in 160 participants with severe COVID-19. The participants will be randomly (1:1) divided into treatment group or control group. All participants are given standard therapy at the same time. The experiment will receive Shenhuang granule treatment twice a day for 14 days. The clinical indicators of patients will be assessed at baseline and at 3, 5, 7, and 14 days after treatment initiation. The primary outcome is 14-day clinical outcome. Adverse events will be monitored throughout the trial.
Discussion: This will be the first randomized controlled trial, which evaluate the effect of Shenhuang granule in patients with severe COVID-19 in China. The results of this trial may not only provide evidence-based recommendations to clinicians to treat severe COVID-19, but also enrich the theory and practice of TCM in treating infectious diseases.
Trial registration: Chinese Clinical Trial Registry, ChiCTR2000029777. Registered on 13 February 2020.
Keywords: Randomized controlled trial; Severe COVID-19; Shenhuang granule; “Truncation and Reversion” strategy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
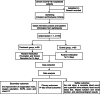
Fig. 1
Flow chart of the study design. COVID-19, coronavirus disease 2019; SOFA score, Sequential Organ Failure Assessment score; CT, computed tomography
Similar articles
- Baidu Jieduan granules, traditional Chinese medicine, in the treatment of moderate coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19): study protocol for an open-label, randomized controlled clinical trial.
Zhang W, Xie Q, Xu X, Sun S, Fan T, Wu X, Qu Y, Che J, Huang T, Li H, Zheng Y, Jiang C, Fang B, Zhou S. Zhang W, et al. Trials. 2021 Jul 22;22(1):476. doi: 10.1186/s13063-021-05418-y. Trials. 2021. PMID: 34294144 Free PMC article. - Traditional Chinese medicine shenhuang granule in patients with severe/critical COVID-19: A randomized controlled multicenter trial.
Zhou S, Feng J, Xie Q, Huang T, Xu X, Zhou D, Zhang W, Sun S, Liu X, Wu X, Che J, Fan T, Zou D, Wang J, Zhan D, Peng D, Feng Y, Yu G, Yuan Z, Fang B. Zhou S, et al. Phytomedicine. 2021 Aug;89:153612. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153612. Epub 2021 May 28. Phytomedicine. 2021. PMID: 34126419 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - Efficacy of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Maxingshigan-Weijing in the management of COVID-19 patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome: A structured summary of a study protocol for a randomized controlled trial.
Zeng C, Yuan Z, Pan X, Zhang J, Zhu J, Zhou F, Shan Z, Yuan Y, Ye R, Cheng J. Zeng C, et al. Trials. 2020 Dec 23;21(1):1029. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-04970-3. Trials. 2020. PMID: 33357239 Free PMC article. - Ivermectin for preventing and treating COVID-19.
Popp M, Reis S, Schießer S, Hausinger RI, Stegemann M, Metzendorf MI, Kranke P, Meybohm P, Skoetz N, Weibel S. Popp M, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jun 21;6(6):CD015017. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015017.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35726131 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Herbal Remedies, Nutraceuticals, and Dietary Supplements for COVID-19 Management: An Update.
Chavda VP, Patel AB, Vihol D, Vaghasiya DD, Ahmed KMSB, Trivedi KU, Dave DJ. Chavda VP, et al. Clin Complement Med Pharmacol. 2022 Mar;2(1):100021. doi: 10.1016/j.ccmp.2022.100021. Epub 2022 Feb 5. Clin Complement Med Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36620357 Free PMC article. Review. - Third dose of anti-SARS-CoV-2 inactivated vaccine for patients with RA: Focusing on immunogenicity and effects of RA drugs.
Zhao T, Wang B, Shen J, Wei Y, Zhu Y, Tian X, Wen G, Xu B, Fu C, Xie Z, Xi Y, Li Z, Peng J, Wu Y, Tang X, Wan C, Pan L, Zhu W, Li Z, Qin D. Zhao T, et al. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Aug 31;9:978272. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.978272. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36117981 Free PMC article. - Pharmacological Efficacy of Ginseng against Respiratory Tract Infections.
Alsayari A, Muhsinah AB, Almaghaslah D, Annadurai S, Wahab S. Alsayari A, et al. Molecules. 2021 Jul 5;26(13):4095. doi: 10.3390/molecules26134095. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34279434 Free PMC article. Review. - Clinical Effect of Traditional Chinese Medicine Shenhuang Granule in Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19: A Single-Centered, Retrospective, Observational Study.
Feng J, Fang B, Zhou D, Wang J, Zou D, Yu G, Fen Y, Peng D, Hu J, Zhan D. Feng J, et al. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021 Mar 28;31(3):380-386. doi: 10.4014/jmb.2009.09029. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 33746189 Free PMC article. - Current updates on the European and WHO registered clinical trials of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).
Verma HK, Merchant N, Verma MK, Kuru Cİ, Singh AN, Ulucan F, Verma P, Bhattacharya A, Bhaskar LVKS. Verma HK, et al. Biomed J. 2020 Oct;43(5):424-433. doi: 10.1016/j.bj.2020.07.008. Epub 2020 Jul 24. Biomed J. 2020. PMID: 32792167 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- “Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) Situation Report – 99”. World Health Organization, 28 April 2020. https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situatio.... Accessed 4 June 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- SJZLJZ.N01/Emergency Committee of the World Federation of Chinese Medicine Societies and Shanghai Society of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia Emergency Tackling Key Project
- 2018YFC1705900/National Key Research and Development Program of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical