MicroRNAs Modulate Drug Resistance-Related Mechanisms in Hepatocellular Carcinoma - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
MicroRNAs Modulate Drug Resistance-Related Mechanisms in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Yuehui Liang et al. Front Oncol. 2020.
Abstract
Primary liver cancer [hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)] is one of the most common malignant tumors worldwide, causing serious health threats because of its high morbidity and mortality, rapid growth, and strong invasiveness. Patients with HCC frequently develop resistance to the current chemotherapeutic drugs, and this is largely attributed to the high-level heterogeneity of the tumor tissue. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a group of master regulators for multiple physiological and pathological processes and play important roles in the tumorigenesis. More recent studies have indicated that miRNAs also play a non-negligible role in the development of drug resistance in liver cancer. In this review, we summarize the data from the latest studies on the mechanisms of drug resistance in liver cancer, including autophagy, membrane transporters, epithelial-mesenchymal transitions (EMTs), tumor microenvironment, and genes and proteins that are associated with apoptosis. The data herein will provide valuable information for the development of novel approaches to tackle drug resistance in the management of liver cancer.
Keywords: autophagy; drug resistance; hepatocellular carcinoma; microRNAs; tumor microenvironment.
Copyright © 2020 Liang, Liang, Qiao and Xiao.
Figures
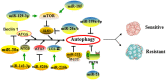
Figure 1
Role of microRNAs (miRNAs) in the regulation of autophagy-related drug resistance. MiRNAs exert important roles in drug resistance through positive or negative regulation of key molecules or pathways of autophagy.
Figure 2
A schematic diagram illustrating the mechanisms of how microRNAs (miRNAs) regulate membrane transporter in the development of drug resistance. MiRNAs may affect the entrance of chemotherapy drugs into cells by negatively regulating membrane transport receptor.
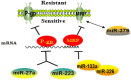
Figure 3
Role of microRNAs (miRNA)-regulated epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) in the development of resistance. Epithelial cells are more sensitive to chemotherapeutic drugs, whereas mesenchymal cells are resistant to the drugs and more aggressive. MiRNAs mainly affect drug resistance through negative regulation of key molecules in the EMT process.
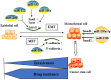
Figure 4
Role of cancer stem cells (CSCs), hypoxia, and the Warburg effect regulated by MICRORNAS (miRNAs) in the development of drug resistance. MiRNAs mainly affect drug resistance through negative regulation of key molecules in the above process.
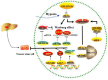
Figure 5
Key mechanisms related to drug resistance in hepatoma cells. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) can affect the outcome of chemotherapy, mainly acting on key molecules or signaling pathways related to the above mechanisms.
Similar articles
- MicroRNAs contribute to ATP-binding cassette transporter- and autophagy-mediated chemoresistance in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Espelt MV, Bacigalupo ML, Carabias P, Troncoso MF. Espelt MV, et al. World J Hepatol. 2019 Apr 27;11(4):344-358. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v11.i4.344. World J Hepatol. 2019. PMID: 31114639 Free PMC article. Review. - Role of exosomal microRNAs in cancer therapy and drug resistance mechanisms: focus on hepatocellular carcinoma.
Zelli V, Compagnoni C, Capelli R, Corrente A, Di Vito Nolfi M, Zazzeroni F, Alesse E, Tessitore A. Zelli V, et al. Front Oncol. 2022 Jul 15;12:940056. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.940056. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35912267 Free PMC article. Review. - The emerging role of microRNAs and long noncoding RNAs in drug resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Wei L, Wang X, Lv L, Liu J, Xing H, Song Y, Xie M, Lei T, Zhang N, Yang M. Wei L, et al. Mol Cancer. 2019 Oct 25;18(1):147. doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-1086-z. Mol Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31651347 Free PMC article. Review. - Small but Heavy Role: MicroRNAs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression.
Chen E, Xu X, Liu R, Liu T. Chen E, et al. Biomed Res Int. 2018 May 22;2018:6784607. doi: 10.1155/2018/6784607. eCollection 2018. Biomed Res Int. 2018. PMID: 29951542 Free PMC article. Review. - MicroRNA-125b attenuates epithelial-mesenchymal transitions and targets stem-like liver cancer cells through small mothers against decapentaplegic 2 and 4.
Zhou JN, Zeng Q, Wang HY, Zhang B, Li ST, Nan X, Cao N, Fu CJ, Yan XL, Jia YL, Wang JX, Zhao AH, Li ZW, Li YH, Xie XY, Zhang XM, Dong Y, Xu YC, He LJ, Yue W, Pei XT. Zhou JN, et al. Hepatology. 2015 Sep;62(3):801-15. doi: 10.1002/hep.27887. Epub 2015 Jul 3. Hepatology. 2015. PMID: 25953743
Cited by
- TIMELESS promotes reprogramming of glucose metabolism in oral squamous cell carcinoma.
Chen Y, Han Z, Zhang L, Gao C, Wei J, Yang X, Han Y, Li Y, Zhang C, Wei Y, Dong J, Xun W, Sun W, Zhang T, Zhang H, Chen J, Yuan P. Chen Y, et al. J Transl Med. 2024 Jan 4;22(1):21. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04791-3. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38178094 Free PMC article. - MiRNA-124-3p.1 sensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma cells to sorafenib by regulating FOXO3a by targeting AKT2 and SIRT1.
Dong ZB, Wu HM, He YC, Huang ZT, Weng YH, Li H, Liang C, Yu WM, Chen W. Dong ZB, et al. Cell Death Dis. 2022 Jan 10;13(1):35. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-04491-0. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 35013144 Free PMC article. - The Role of microRNAs in Hepatocellular Cancer: A Narrative Review Focused on Tumor Microenvironment and Drug Resistance.
Tavakoli Pirzaman A, Alishah A, Babajani B, Ebrahimi P, Sheikhi SA, Moosaei F, Salarfar A, Doostmohamadian S, Kazemi S. Tavakoli Pirzaman A, et al. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2024 Jan-Dec;23:15330338241239188. doi: 10.1177/15330338241239188. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2024. PMID: 38634139 Free PMC article. Review. - Master regulator genes and their impact on major diseases.
Cai W, Zhou W, Han Z, Lei J, Zhuang J, Zhu P, Wu X, Yuan W. Cai W, et al. PeerJ. 2020 Oct 6;8:e9952. doi: 10.7717/peerj.9952. eCollection 2020. PeerJ. 2020. PMID: 33083114 Free PMC article. - Functionalized Carbon Nanotubes for Delivery of Ferulic Acid and Diosgenin Anticancer Natural Agents.
AbouAitah K, Abdelaziz AM, Higazy IM, Swiderska-Sroda A, Hassan AME, Shaker OG, Szałaj U, Stobinski L, Malolepszy A, Lojkowski W. AbouAitah K, et al. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2024 Feb 19;7(2):791-811. doi: 10.1021/acsabm.3c00700. Epub 2024 Jan 22. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2024. PMID: 38253026 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources