Effect of Vitamin E on Serum Levels of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor and Angiopoietin-1 in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Pilot Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial - PubMed (original) (raw)
Effect of Vitamin E on Serum Levels of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor and Angiopoietin-1 in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Pilot Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial
S Habnam Shirazi et al. Int J Fertil Steril. 2021 Jan.
Abstract
Background: Angiogenesis disturbances are common in women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Vitamin E has antiangiogenic properties. Data on the effects of vitamin E on angiogenesis in PCOS is limited, so the current study was conducted to evaluate its effects on angiogenic indices in PCOS patients.
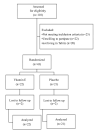
Materials and methods: This randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial was performed on 43 women aged 20-40 years, diagnosed with PCOS (Rotterdam criteria). It was performed at the referral clinic affiliated to Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Tabriz, Iran, from April 2017 to September 2017. Patients were randomly assigned into two groups to receive either 400 IU/day vitamin E -as alpha tocopheryl acetate- (n=22) or placebo (n=21), for 8 weeks. Anthropometric, and angiogenic parameters including body weight, fat mass and fat free mass, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF), angiopoietin-1 (Ang-1), and angiopoietin- 2 (Ang-2) were measured by standard methods at the beginning and at the end of study. Statistical Package for Social Science version 25 was used for statistical analysis and P<0.05 were considered significant.
Results: After adjusting for potential confounders, we observed that vitamin E supplementation significantly reduced body weight, fat mass, Ang-1, Ang-1/Ang-2 ratio and VEGF (P<0.01). We did not observe any considerable effect for vitamin E on Ang-2 level or bFGF.
Conclusion: Vitamin E supplementation for 8 weeks in the PCOS women had beneficial effects on body weight, Ang- 1, Ang-1/Ang-2 ratio, and VEGF level (Registration number: IRCT201610193140N18).
Keywords: Angiopoietins; Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor; Polycystic Ovary Syndrome; Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor; Vitamin E.
Copyright© by Royan Institute. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Fig.1
Flowchart of the study.
Similar articles
- The effect of vitamin D supplementation in combination with low-calorie diet on anthropometric indices and androgen hormones in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial.
Jafari-Sfidvajani S, Ahangari R, Hozoori M, Mozaffari-Khosravi H, Fallahzadeh H, Nadjarzadeh A. Jafari-Sfidvajani S, et al. J Endocrinol Invest. 2018 May;41(5):597-607. doi: 10.1007/s40618-017-0785-9. Epub 2017 Nov 6. J Endocrinol Invest. 2018. PMID: 29110281 Clinical Trial. - Vitamin D Decreases Serum VEGF Correlating with Clinical Improvement in Vitamin D-Deficient Women with PCOS: A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial.
Irani M, Seifer DB, Grazi RV, Irani S, Rosenwaks Z, Tal R. Irani M, et al. Nutrients. 2017 Mar 28;9(4):334. doi: 10.3390/nu9040334. Nutrients. 2017. PMID: 28350328 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. - The Effects of Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Vitamin E Co-Supplementation on Indices of Insulin Resistance and Hormonal Parameters in Patients with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial.
Ebrahimi FA, Samimi M, Foroozanfard F, Jamilian M, Akbari H, Rahmani E, Ahmadi S, Taghizadeh M, Memarzadeh MR, Asemi Z. Ebrahimi FA, et al. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2017 Jun;125(6):353-359. doi: 10.1055/s-0042-117773. Epub 2017 Apr 13. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2017. PMID: 28407657 Clinical Trial. - Alteration in angiogenic potential of granulosa-lutein cells and follicular fluid contributes to luteal defects in polycystic ovary syndrome.
Patil K, Hinduja I, Mukherjee S. Patil K, et al. Hum Reprod. 2021 Mar 18;36(4):1052-1064. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deaa351. Hum Reprod. 2021. PMID: 33377483 - The influences of vitamin D and omega-3 co-supplementation on clinical, metabolic and genetic parameters in women with polycystic ovary syndrome.
Jamilian M, Samimi M, Mirhosseini N, Afshar Ebrahimi F, Aghadavod E, Talaee R, Jafarnejad S, Hashemi Dizaji S, Asemi Z. Jamilian M, et al. J Affect Disord. 2018 Oct 1;238:32-38. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2018.05.027. Epub 2018 May 26. J Affect Disord. 2018. PMID: 29859385 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
- The Importance of Natural Antioxidants in Female Reproduction.
Vašková J, Klepcová Z, Špaková I, Urdzík P, Štofilová J, Bertková I, Kľoc M, Rabajdová M. Vašková J, et al. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Apr 11;12(4):907. doi: 10.3390/antiox12040907. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37107282 Free PMC article. Review. - A meta-analysis of effects of vitamin E supplementation alone and in combination with omega-3 or magnesium on polycystic ovary syndrome.
Heidari H, Hajhashemy Z, Saneei P. Heidari H, et al. Sci Rep. 2022 Nov 19;12(1):19927. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-24467-0. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36402830 Free PMC article. - Clinical and Biochemical Potential of Antioxidants in Treating Polycystic Ovary Syndrome.
Cheng X, He B. Cheng X, et al. Int J Womens Health. 2022 Apr 1;14:467-479. doi: 10.2147/IJWH.S345853. eCollection 2022. Int J Womens Health. 2022. PMID: 35392500 Free PMC article. Review. - Vitamin E beyond Its Antioxidant Label.
Ungurianu A, Zanfirescu A, Nițulescu G, Margină D. Ungurianu A, et al. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Apr 21;10(5):634. doi: 10.3390/antiox10050634. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33919211 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Goodman NF, Cobin RH, Futterweit W, Glueck JS, Legro RS, Carmina E. American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists, American College of Endocrinology, and Androgen Excess and PCOS Society disease state clinical review: guide to the best practices in the evaluation and treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome-part 1. Endocr Pract. 2015;21(11):1291–1300. - PubMed
- Setji TL, Brown AJ. Polycystic ovary syndrome: update on diagnosis and treatment. Am J Med. 2014;127(10):912–919. - PubMed
- Tal R, Seifer DB, Arici A. The emerging role of angiogenic factor dysregulation in the pathogenesis of polycystic ovarian syndrome. Semin Reprod Med. 2015;33(3):195–207. - PubMed
- Abramovich D, Irusta G, Bas D, Cataldi NI, Parborell F, Tesone M. Angiopoietins/TIE2 system and VEGF are involved in ovarian function in a DHEA rat model of polycystic ovary syndrome. Endocrinology. 2012;153(7):3446–3456. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous