Emerging Role of MiR-192-5p in Human Diseases - PubMed (original) (raw)
Review
Emerging Role of MiR-192-5p in Human Diseases
Fu-Jia Ren et al. Front Pharmacol. 2021.
Abstract
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a type of small non-coding RNAs that play an essential role in numerous biological processes by regulating the post-transcriptional expression of target genes. Recent studies have demonstrated that miR-192-5p, a member of the miR-192 family, partakes in several human diseases, especially various cancers, including cancers of the lung, liver, and breast. Importantly, the levels of miR-192-5p are abundant in biofluids, including the serum and urine, and the exosomal levels of miR-192-5p in circulation can aid in the diagnosis and prognosis of various diseases, such as chronic hepatitis B (CHB) infection disease. Notably, recent studies suggest that miR-192-5p is regulated by long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) and circular RNAs (circRNAs). However, there are no comprehensive overviews on the role of miR-192-5p in human diseases. This review discusses the significant studies on the role of miR-192-5p in various human diseases, with special emphasis on the diseases of the respiratory and digestive systems.
Keywords: Cancers; digestive system; human diseases; miR-192-5p; respiratory system.
Copyright © 2021 Ren, Yao, Cai and Fang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
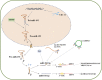
FIGURE 1
The biogenesis and regulation of miR-192-5p. Pre-miR-192 could produce two mature miRNA transcripts, miR-192-5p and miR-192-3p, each of which can regulate gene expression by targeting 3′-UTR of mRNA, such as XIAP, TRIM44, SEMA3A, FABP3, and YY1 for miR-192-5p, and ALDH3A2, SCD and LXR for miR-192-3p. In cell nucleus, KHSRP can promote maturation of pri-miR-192, thereby facilitating the production of miR-192-5p. In cytoplasm, P53 and noncoding RNAs, such as circHIPK3, lnc KCNQ1OT1 and lnc FTX, can inhibit the expression of miR-192-5p.
FIGURE 2
The expression and regulatory mechanism of miR-192-5p in respiratory system. MiR-192-5p is reduced in serum of human asthma, NPC and lung cancer, as well as NPC tissues and lung cancer cell, which can influence diseases progression by targeting CXCR5, XIAP, TRIM44, and PI3K-AKT. Curcumin can promote the expression of miR-192-5p.
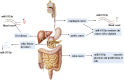
FIGURE 3
The expression and regulatory mechanism of miR-192-5p in digestive system. In different digestive system diseases, the expression of miR-192-5p is flexible. In various liver diseases, miR-192-5p exhibits different expression levels and exerts versatile function. The asterisk (*) represents the controversial role of miR-192-5p.
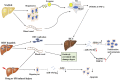
FIGURE 4
The expression and regulatory mechanism of miR-192-5p in different liver diseases. In NAFLD, miR-192-5p is increased in serum exosome, and exosomal miR-192-5p derived from hepatocytes promote the polarization of inflammatory macrophage. In HBV hepatitis, drug or I/R induced liver jury, circulating miR-192-5p is increased, which can target different molecules. In HCC, the expression of miR-192-5p is controversial. Full line represents what actually happens, dotted line represents what might happen. The asterisk (*) represents the controversial role of miR-192-5p.
Similar articles
- MiR-149-5p: An Important miRNA Regulated by Competing Endogenous RNAs in Diverse Human Cancers.
Ren FJ, Yao Y, Cai XY, Cai YT, Su Q, Fang GY. Ren FJ, et al. Front Oncol. 2021 Oct 15;11:743077. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.743077. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34722295 Free PMC article. Review. - Lnc-AL445665.1-4 may be involved in the development of multiple uterine leiomyoma through interacting with miR-146b-5p.
Yang E, Xue L, Li Z, Yi T. Yang E, et al. BMC Cancer. 2019 Jul 18;19(1):709. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-5775-1. BMC Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31319799 Free PMC article. - Regulation of the MIR155 host gene in physiological and pathological processes.
Elton TS, Selemon H, Elton SM, Parinandi NL. Elton TS, et al. Gene. 2013 Dec 10;532(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.12.009. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23246696 Review. - CircMTO1 inhibits liver fibrosis via regulation of miR-17-5p and Smad7.
Wang W, Dong R, Guo Y, He J, Shao C, Yi P, Yu F, Gu D, Zheng J. Wang W, et al. J Cell Mol Med. 2019 Aug;23(8):5486-5496. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14432. Epub 2019 May 31. J Cell Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 31148365 Free PMC article. - NEAT1/hsa-mir-98-5p/MAPK6 axis is involved in non-small-cell lung cancer development.
Wu F, Mo Q, Wan X, Dan J, Hu H. Wu F, et al. J Cell Biochem. 2019 Mar;120(3):2836-2846. doi: 10.1002/jcb.26442. Epub 2018 Dec 14. J Cell Biochem. 2019. PMID: 29095526
Cited by
- Expression and 7-day time course of circulating microRNAs in septic patients treated with nephrotoxic antibiotic agents.
Petejova N, Martinek A, Zadrazil J, Klementa V, Pribylova L, Bris R, Kanova M, Sigutova R, Kacirova I, Svagera Z, Bace E, Stejskal D. Petejova N, et al. BMC Nephrol. 2022 Mar 19;23(1):111. doi: 10.1186/s12882-022-02726-6. BMC Nephrol. 2022. PMID: 35305556 Free PMC article. - Alcohol Promotes Exosome Biogenesis and Release via Modulating Rabs and miR-192 Expression in Human Hepatocytes.
Bala S, Babuta M, Catalano D, Saiju A, Szabo G. Bala S, et al. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Jan 14;9:787356. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.787356. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35096820 Free PMC article. - Serum microRNA Profiles and Pathways in Hepatitis B-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A South African Study.
Sartorius K, Sartorius B, Winkler C, Chuturgoon A, Shen TW, Zhao Y, An P. Sartorius K, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 12;25(2):975. doi: 10.3390/ijms25020975. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38256049 Free PMC article. Review. - Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): Pathogenesis and Noninvasive Diagnosis.
Dorairaj V, Sulaiman SA, Abu N, Abdul Murad NA. Dorairaj V, et al. Biomedicines. 2021 Dec 22;10(1):15. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10010015. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 35052690 Free PMC article. Review. - miRNA biomarkers to predict risk of primary non-function of fatty allografts and drug induced acute liver failures.
Schönberg J, Borlak J. Schönberg J, et al. Mol Cell Biochem. 2024 Oct 18. doi: 10.1007/s11010-024-05129-3. Online ahead of print. Mol Cell Biochem. 2024. PMID: 39424772
References
- Biazzo A., De Paolis M. (2016). Multidisciplinary approach to osteosarcoma. Acta Orthop. Belg. 82, 690–698. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources