The effects of melatonin treatment on oxidative stress induced by ovariohysterectomy in dogs - PubMed (original) (raw)
The effects of melatonin treatment on oxidative stress induced by ovariohysterectomy in dogs
Sina Salavati et al. BMC Vet Res. 2021.
Abstract
Background: As one of the most common surgeries performed in veterinary medicine, ovariohysterectomy (OHE) can induce oxidative stress in dogs. The antioxidant properties of melatonin have been confirmed in various studies. This study aimed to investigate the effects of melatonin administration on oxidative stress in dogs before and after OHE. In this study, 25 mature female intact dogs were selected and randomly divided into five equal groups: Melatonin (melatonin, no surgery), OHE (no melatonin, surgery), OHE + melatonin (melatonin, surgery), anesthesia+melatonin (melatonin, sham surgery), and control (no melatonin, no surgery) groups. Melatonin (0.3 mg/Kg/day, p.o.) was administrated to the dogs in the melatonin, OHE + melatonin, and anesthesia+melatonin groups on days - 1, 0, 1, 2, and 3 (day 0 = OHE). Blood sampling was performed on days - 1, 1, 3, and 5 of the study. Blood samples were immediately transferred to the laboratory and sera were separated and stored at - 20 °C. Superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GPX), catalase (CAT) and malondialdehyde (MDA) concentrations were measured with commercial kits.
Results: The levels of SOD, GPX and CAT were significantly higher in the melatonin and anesthesia+melatonin groups compared to those of the control group at days 3 and 5. The level of antioxidant enzymes significantly decreased in the OHE group compared to that of other groups at days 3 and 5. The administration of melatonin increased the level of antioxidant enzymes in ovariohysterectomized dogs. Ovariohysterectomy significantly increased the concentration of MDA in comparison to that of other groups at day 3. Melatonin administration significantly decreased the level of MDA in melatonin, anesthetized, and ovariohysterectomized dogs at day 3.
Conclusions: Administration of melatonin on day - 1, 0, 1, 2 and 3 modulate the oxidative stress induced by OHE in dogs by increasing antioxidant enzymes concentration and decreasing MDA levels.
Keywords: Antioxidants; Dog; Melatonin; Oxidative stress; Surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
‘The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
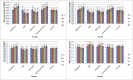
Fig. 1
The mean ± SD concentrations of superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GPX), catalase (CAT), and malondialdehyde (MDA) were compared between days of sampling in each group. Melatonin (0.3 mg/kg p.o.) was administrated on days -1, 0, 1, 2 and 3. Ovariohysterectomy and anesthesia were performed on day 0. Different letters on bars indicate significant differences between days of sampling in each group
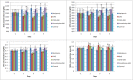
Fig. 2
The mean ± SD concentrations of superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GPX), catalase (CAT), and malondialdehyde (MDA) were compared between the study groups (melatonin, ovariohysterectomy (OHE), OHE+melatonin, anesthesia+melatonin, and control) in each day of sampling. Melatonin (0.3 mg/kg p.o.) was administrated on days -1, 0, 1, 2 and 3. Ovariohysterectomy and anesthesia were performed on day 0. Different letters (a, b, c, d) on bars indicate significant differences (P < 0.05) between groups on each day of sampling
Fig. 3
The schematic design of the study. Blood sampling on days -1, 1, 3, and 5 was performed before oral melatonin administration (0.3 mg/kg) on days -1, 0, 1, 3, and 5 of the study. Ovariohysterectomy (OHE) and anesthesia were performed on day 0
Similar articles
- Effects of ovariohysterectomy on oxidative stress markers in female dogs.
Szczubial M, Kankofer M, Bochniarz M, Dąbrowski R. Szczubial M, et al. Reprod Domest Anim. 2015 Jun;50(3):393-9. doi: 10.1111/rda.12501. Epub 2015 Feb 21. Reprod Domest Anim. 2015. PMID: 25704084 - Synergestic effect of lycopene and melatonin against the genesis of oxidative stress induced by cyclophosphamide in rats.
Al-Malki AL. Al-Malki AL. Toxicol Ind Health. 2014 Jul;30(6):570-5. doi: 10.1177/0748233712459916. Epub 2012 Sep 28. Toxicol Ind Health. 2014. PMID: 23024110 - The protective effect of melatonin on nicotine-induced myocardial injury in newborn rats whose mothers received nicotine.
Baykan A, Narin N, Narin F, Akgün H, Yavaşcan S, Saraymen R. Baykan A, et al. Anadolu Kardiyol Derg. 2008 Aug;8(4):243-8. Anadolu Kardiyol Derg. 2008. PMID: 18676298 - Antioxidative role of melatonin in organophosphate toxicity in rats.
Buyukokuroglu ME, Cemek M, Yurumez Y, Yavuz Y, Aslan A. Buyukokuroglu ME, et al. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2008 Apr;24(2):151-8. doi: 10.1007/s10565-007-9024-z. Epub 2007 Sep 2. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2008. PMID: 17768667 - Antioxidant Actions of Melatonin: A Systematic Review of Animal Studies.
Monteiro KKAC, Shiroma ME, Damous LL, Simões MJ, Simões RDS, Cipolla-Neto J, Baracat EC, Soares-Jr JM. Monteiro KKAC, et al. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Apr 7;13(4):439. doi: 10.3390/antiox13040439. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38671887 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
- Effects of Medetomidine-Butorphanol and Medetomidine-Buprenorphine on Oxidative Stress and Vital Parameters in Dogs Undergoing Ovariohysterectomy.
Burbaitė E, Čechovičienė S, Sarapinienė I, Karvelienė B, Riškevičienė V, Daunoras G, Juodžentė D. Burbaitė E, et al. Animals (Basel). 2024 Apr 30;14(9):1349. doi: 10.3390/ani14091349. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38731353 Free PMC article. - Unveiling Glucosinolate Diversity in Brassica Germplasm and In Silico Analysis for Determining Optimal Antioxidant Potential.
Iwar K, Desta KT, Ochar K, Kim SH. Iwar K, et al. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Mar 19;13(3):376. doi: 10.3390/antiox13030376. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38539909 Free PMC article. - Oxidative stress, hormones, and effects of natural antioxidants on intestinal inflammation in inflammatory bowel disease.
Sahoo DK, Heilmann RM, Paital B, Patel A, Yadav VK, Wong D, Jergens AE. Sahoo DK, et al. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Aug 28;14:1217165. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1217165. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37701897 Free PMC article. Review. - Dietary Strategies for Relieving Stress in Pet Dogs and Cats.
Fan Z, Bian Z, Huang H, Liu T, Ren R, Chen X, Zhang X, Wang Y, Deng B, Zhang L. Fan Z, et al. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Feb 21;12(3):545. doi: 10.3390/antiox12030545. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36978793 Free PMC article. Review.
References
- Serin G, Kiral F, Serin I. Acute effect of ovariohysterectomy on lipid peroxidation and some antioxidant levels in dogs. Bull Vet Inst Pulawy. 2008;52:251–253.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous