Boosting of Antioxidants and Alkaloids in Catharanthus roseus Suspension Cultures Using Silver Nanoparticles with Expression of CrMPK3 and STR Genes - PubMed (original) (raw)
Boosting of Antioxidants and Alkaloids in Catharanthus roseus Suspension Cultures Using Silver Nanoparticles with Expression of CrMPK3 and STR Genes
Ahmed Fouad et al. Plants (Basel). 2021.
Abstract
Global agricultural systems are under unprecedented pressures due to climate change. Advanced nano-engineering can help increase crop yields while ensuring sustainability. Nanotechnology improves agricultural productivity by boosting input efficiency and reducing waste. Alkaloids as one of the numerous secondary metabolites that serve variety of cellular functions essential for physiological processes. This study tests the competence of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) in boosting alkaloids accumulation in Catharanthus roseus suspension cultures in relation to the expression of C. roseus Mitogen Activated Protein Kinase 3 (CrMPK3) and Strictosidine Synthase (STR) genes. Five concentrations (5, 10, 15, 20 and 25 mg·L-1) of AgNPs were utilized in addition to deionized water as control. Results reflected binary positive correlations among AgNPs concentration, oxidative stress indicated with increase in hydrogen peroxide and malondialdehyde contents, activities of ascorbate peroxidase and superoxide dismutase, expression of the regulatory gene CrMPK3 and the alkaloid biosynthetic gene STR as well as alkaloids accumulation. These correlations add to the growing evidence that AgNPs can trigger the accumulation of alkaloids in plant cells through a signaling pathway that involves hydrogen peroxide and MAPKs, leading to up-regulation of the biosynthetic genes, including STR gene.
Keywords: APX; Catharanthus roseus; CrMPK3; H2O2; SOD; STR; alkaloids; malondialdehyde; silver nanoparticles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
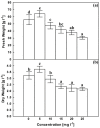
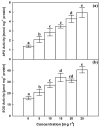
Figure 1
Effects of AgNPs at concentrations of 5, 10, 15, 20 and 25 mg L−1 on fresh weight (a) and dry weight (b) of C. roseus cell suspension cultures. Means ± standard deviations (SDs), n = 3, Values followed by the same small letter within each column are not significantly different at p ≤ 0.05.
Figure 2
Effects of AgNPs at concentrations of 5, 10, 15, 20 and 25 mg L−1 on H2O2 content (a) and MDA content (b) of C. roseus cell suspension cultures. Means ± standard deviations (SDs), n = 3, Values followed by the same small letter within each column are not significantly different at p ≤ 0.05.
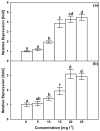
Figure 3
Effects of AgNPs at concentrations of 5, 10, 15, 20 and 25 mg L−1 on relative expression of CrMPK3 gene (a) and STR gene (b) of C. roseus cell suspension cultures. Means ± standard deviations (SDs), n = 3, Values followed by the same small letter within each column are not significantly different at p ≤ 0.05.
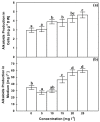
Figure 4
Effects of AgNPs at concentrations of 5, 10, 15, 20 and 25 mg L−1 on alkaloids content in dried cells (a) and growth medium (b) of C. roseus cell suspension cultures. Means ± standard deviations (SDs), n = 3, Values followed by the same small letter within each column are not significantly different at p ≤ 0.05.
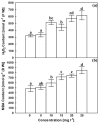
Figure 5
Effects of AgNPs at concentrations of 5, 10, 15, 20 and 25 mg L−1 on APX activity (a) and SOD activity (b) of C. roseus cell suspension cultures. Means ± standard deviations (SDs), n = 3, Values followed by the same small letter within each column are not significantly different at p ≤ 0.05.
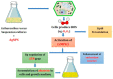
Figure 6
Summary for the action mechanism for AgNPs-mediated alkaloids biosynthesis in Catharanthus roseus.
Similar articles
- Effect of cobalt nanoparticles and cobalt ions on alkaloids production and expression of CrMPK3 gene in Catharanthus roseus suspension cultures.
Fouad AS, Hafez RM. Fouad AS, et al. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2018 Sep 30;64(12):62-69. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2018. PMID: 30301505 - CrMPK3, a mitogen activated protein kinase from Catharanthus roseus and its possible role in stress induced biosynthesis of monoterpenoid indole alkaloids.
Raina SK, Wankhede DP, Jaggi M, Singh P, Jalmi SK, Raghuram B, Sheikh AH, Sinha AK. Raina SK, et al. BMC Plant Biol. 2012 Aug 7;12:134. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-12-134. BMC Plant Biol. 2012. PMID: 22871174 Free PMC article. - Terpenoid indole alkaloid biosynthesis in Catharanthus roseus: effects and prospects of environmental factors in metabolic engineering.
Liu Y, Patra B, Singh SK, Paul P, Zhou Y, Li Y, Wang Y, Pattanaik S, Yuan L. Liu Y, et al. Biotechnol Lett. 2021 Nov;43(11):2085-2103. doi: 10.1007/s10529-021-03179-x. Epub 2021 Sep 25. Biotechnol Lett. 2021. PMID: 34564757 Free PMC article. Review. - [Advance in biosynthesis of terpenoid indole alkaloids and its regulation in Catharanthus roseus].
Kuang XJ, Wang CX, Zou LQ, Zhu XX, Sun C. Kuang XJ, et al. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2016 Nov;41(22):4129-4137. doi: 10.4268/cjcmm20162208. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 28933078 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
- Biosynthesized Ag nanoparticles on urea-based periodic mesoporous organosilica enhance galegine content in Galega.
Varjovi MB, Zakaria RA, Rostamnia S, Gholipour B. Varjovi MB, et al. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023 Mar;107(5-6):1589-1608. doi: 10.1007/s00253-023-12414-6. Epub 2023 Feb 4. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36738339 - Emerging alternatives to traditional anthelmintics: the in vitro antiparasitic activity of silver and selenium nanoparticles, and pomegranate (Punica granatum) peel extract against Haemonchus contortus.
Kaiaty AM, Salib FA, El-Gameel SM, Abdel Massieh ES, Hussien AM, Kamel MS. Kaiaty AM, et al. Trop Anim Health Prod. 2023 Sep 22;55(5):317. doi: 10.1007/s11250-023-03722-0. Trop Anim Health Prod. 2023. PMID: 37737938 Free PMC article. - Salt Priming as a Smart Approach to Mitigate Salt Stress in Faba Bean (Vicia faba L.).
Nasrallah AK, Atia MAM, Abd El-Maksoud RM, Kord MA, Fouad AS. Nasrallah AK, et al. Plants (Basel). 2022 Jun 20;11(12):1610. doi: 10.3390/plants11121610. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35736763 Free PMC article. - Nano-elicitation and hydroponics: a synergism to enhance plant productivity and secondary metabolism.
Jadoon L, Gul A, Fatima H, Babar MM. Jadoon L, et al. Planta. 2024 Mar 4;259(4):80. doi: 10.1007/s00425-024-04353-x. Planta. 2024. PMID: 38436711 Review. - Biogenic Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Catharanthus roseus and Its Cytotoxicity Effect on Vero Cell Lines.
Jamil K, Khattak SH, Farrukh A, Begum S, Riaz MN, Muhammad A, Kamal T, Taj T, Khan I, Riaz S, Batool H, Mandokhail K, Majeed S, Khan Bangash SA, Mushtaq A, Bashir S, Kaleem I, Pervaiz F, Rasool A, Amanat MA, Ali GM. Jamil K, et al. Molecules. 2022 Sep 21;27(19):6191. doi: 10.3390/molecules27196191. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36234756 Free PMC article.
References
- Pan Q., Mustafa N.R., Tang K., Choi Y.H., Verpoorte R. Monoterpenoid Indole Alkaloids Biosynthesis and Its Regulation in Catharanthus roseus: A Literature Review from Genes to Metabolites. Phytochem. Rev. 2016;15:221–250. doi: 10.1007/s11101-015-9406-4. - DOI
- Pan Y.-J., Liu J., Guo X.-R., Zu Y.-G., Tang Z.-H. Gene Transcript Profiles of the TIA Biosynthetic Pathway in Response to Ethylene and Copper Reveal Their Interactive Role in Modulating TIA Biosynthesis in Catharanthus roseus. Protoplasma. 2015;252:813–824. doi: 10.1007/s00709-014-0718-9. - DOI - PubMed
- Ghorbanpour M., Hatami M., Hatami M. Activating Antioxidant Enzymes, Hyoscyamine and Scopolamine Biosynthesis of Hyoscyamus Niger L. Plants with Nano-Sized Titanium Dioxide and Bulk Application. Acta Agric. Slov. 2015;105:23–32. doi: 10.14720/aas.2015.105.1.03. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous