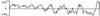A testicular antigen aberrantly expressed in human cancers detected by autologous antibody screening - PubMed (original) (raw)
A testicular antigen aberrantly expressed in human cancers detected by autologous antibody screening
Y T Chen et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997.
Abstract
Serological analysis of recombinant cDNA expression libraries (SEREX) using tumor mRNA and autologous patient serum provides a powerful approach to identify immunogenic tumor antigens. We have applied this methodology to a case of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and identified several candidate tumor targets. One of these, NY-ESO-1, showed restricted mRNA expression in normal tissues, with high-level mRNA expression found only in testis and ovary tissues. Reverse transcription-PCR analysis showed NY-ESO-1 mRNA expression in a variable proportion of a wide array of human cancers, including melanoma, breast cancer, bladder cancer, prostate cancer, and hepatocellular carcinoma. NY-ESO-1 encodes a putative protein of Mr 17,995 having no homology with any known protein. The pattern of NY-ESO-1 expression indicates that it belongs to an expanding family of immunogenic testicular antigens that are aberrantly expressed in human cancers in a lineage-nonspecific fashion. These antigens, initially detected by either cytotoxic T cells (MAGE, BAGE, GAGE-1) or antibodies [HOM-MEL-40(SSX2), NY-ESO-1], represent a pool of antigenic targets for cancer vaccination.
Figures
Figure 1
RT-PCR analysis of NY-ESO-1 (A) and NY-ESO-4 (B) mRNA expression. Total RNA was extracted from the original esophageal cancer (lane 1) and from normal colon (lane 2), kidney (lane 3), testis (lane 4), liver (lane 5), and brain (lane 6). Negative control with no RNA was included (lane 7). NY-ESO-1 PCR primer sequences were: ESO1A, 5′-CACACAGGATCCATGGATGCTGCAGATGCGG-3′ and ESO1B, 5′-CACACAAAGCTTGGCTTAGCGCCTCTGCCCTG.
Figure 2
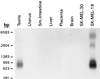
Northern blot analysis of NY-ESO-1, showing NY-ESO-1 mRNA in testis and SK-MEL-19, but not in uterus, small intestine, liver, placenta, brain, and SK-MEL-30. The major mRNA species is 0.8–0.9 kb, with minor higher molecular weight species seen in SK-MEL-19.
Figure 3
Nucleotide and amino acid sequences of NY-ESO-1, indicating potential _N_-myristoylation (Myr) and phosphorylation (P) sites. The potential transmembrane domain at the carboxyl end is italicized. (GenBank database accession number: U87459U87459.)
Figure 4
Hydrophilicity plot of NY-ESO-1, indicating hydrophilic domain (positive value) in the amino terminus, and a long hydrophobic stretch (negative value) close to the carboxyl end of the putative protein sequence.
Similar articles
- Identification of tumor-restricted antigens NY-BR-1, SCP-1, and a new cancer/testis-like antigen NW-BR-3 by serological screening of a testicular library with breast cancer serum.
Jäger D, Unkelbach M, Frei C, Bert F, Scanlan MJ, Jäger E, Old LJ, Chen YT, Knuth A. Jäger D, et al. Cancer Immun. 2002 Jun 28;2:5. Cancer Immun. 2002. PMID: 12747750 - Analysis of cancer/testis antigens in sporadic medullary thyroid carcinoma: expression and humoral response to NY-ESO-1.
Maio M, Coral S, Sigalotti L, Elisei R, Romei C, Rossi G, Cortini E, Colizzi F, Fenzi G, Altomonte M, Pinchera A, Vitale M. Maio M, et al. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003 Feb;88(2):748-54. doi: 10.1210/jc.2002-020830. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003. PMID: 12574209 - Genomic cloning and localization of CTAG, a gene encoding an autoimmunogenic cancer-testis antigen NY-ESO-1, to human chromosome Xq28.
Chen YT, Boyer AD, Viars CS, Tsang S, Old LJ, Arden KC. Chen YT, et al. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1997;79(3-4):237-40. doi: 10.1159/000134734. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1997. PMID: 9605863 - Expression of cancer-testis antigens in esophageal cancer and their progress in immunotherapy.
Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Zhang L. Zhang Y, et al. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2019 Feb;145(2):281-291. doi: 10.1007/s00432-019-02840-3. Epub 2019 Jan 17. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30656409 Free PMC article. Review. - Cancer/testis antigens: an expanding family of targets for cancer immunotherapy.
Scanlan MJ, Gure AO, Jungbluth AA, Old LJ, Chen YT. Scanlan MJ, et al. Immunol Rev. 2002 Oct;188:22-32. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-065x.2002.18803.x. Immunol Rev. 2002. PMID: 12445278 Review.
Cited by
- Unveiling the significance of cancer-testis antigens and their implications for immunotherapy in glioma.
Zhuo S, Yang S, Chen S, Ding Y, Cheng H, Yang L, Wang K, Yang K. Zhuo S, et al. Discov Oncol. 2024 Oct 29;15(1):602. doi: 10.1007/s12672-024-01449-4. Discov Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39472405 Free PMC article. Review. - Unveiling the role of KRAS in Chinese colorectal cancer patients: a positive influence on tumor mutational burden.
Wan X, Zhang X, Xu M, Zheng Z, Zhou Y, Zhong Z. Wan X, et al. Transl Cancer Res. 2024 Sep 30;13(9):4752-4762. doi: 10.21037/tcr-24-600. Epub 2024 Sep 25. Transl Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39430843 Free PMC article. - NY-ESO-1 antigen: A promising frontier in cancer immunotherapy.
Alsalloum A, Shevchenko JA, Sennikov S. Alsalloum A, et al. Clin Transl Med. 2024 Sep;14(9):e70020. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.70020. Clin Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39275923 Free PMC article. Review. - Engineered T cells for Colorectal Cancer.
Rus Bakarurraini NAA, Kamarudin AA, Jamal R, Abu N. Rus Bakarurraini NAA, et al. Immunotherapy. 2024;16(14-15):987-998. doi: 10.1080/1750743X.2024.2391733. Epub 2024 Sep 4. Immunotherapy. 2024. PMID: 39229803 Review. - Expression of the tumor antigens NY-ESO-1, tyrosinase, MAGE-A3, and TPTE in pediatric and adult melanoma: a retrospective case control study.
Forchhammer S, Pop OT, Hahn M, Aebischer V, Seitz CM, Schroeder C, Liebmann A, Abele M, Wild H, Bien E, Kunc M, Schneider DT, Cuk K, Büttel I, Flemmig C, Peters M, Laible M, Brück P, Türeci Ö, Sahin U, Flatz L, Brecht IB. Forchhammer S, et al. Virchows Arch. 2024 Aug;485(2):335-346. doi: 10.1007/s00428-024-03846-0. Epub 2024 Jun 18. Virchows Arch. 2024. PMID: 38890171 Free PMC article.
References
- Boon T, Cerottini J C, Van den Eynde B, van der Bruggen P, Van Pel A. Annu Rev Immunol. 1994;12:337–365. - PubMed
- Robbins P F, El-Gamil M, Kawakami Y, Rosenberg S A. Cancer Res. 1994;54:3124–3126. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases