Orbit – Orbit Image Analysis (original) (raw)
Sophisticated Image Analysis Algorithms
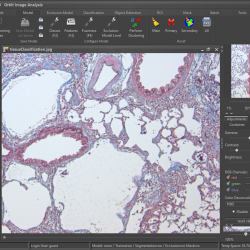
Orbit has many build-in image analysis algorithms. Tissue quantification using machine learning techniques, object / cell segmentation, and object classification are the basic ones. Region of interest (ROI) can be defined by manual annotations or via a trainable exclusion map. Everything can be combined.
WORKS FOR BIG IMAGES, e.g. WHOLE SLIDE SCANS
All algorithms are build to work on really big images, up to gigapixel images, especially whole slide scans.
This is possible due to a tile-based processing pipeline and combination with the use of different resolutions of the image.
Connectivity: OMERO & Spark connectors
You can use your existing image server, e.g. it has been designed to work great with Omero.
Orbit can also run in stand-alone mode and open whole slide images like SVS, NDPI, SCN, ….
A Spark infrastructure can be used as scaleout infrastructure to distribute computation intensive tasks.
Scripting & Extentions & Connectors
Orbit provides a versatile API for developers to create scripts or extentions. For instance, you can easily iterate over all tiles within a defined ROI and apply any algorithm or ImageJ plugin. You write s.th. which works for small in-memory images, Orbit takes care that is works for really big images.
Individual image server and scaleout connectors can also be created by implementing clear interfaces.
Verison 3.64: Omero/websockets support
Startup crash bugfix
OMERO 5.6.x, Deep Learning Segmentation, TMA Grid spot detection, HighDPI, ... check it out!
Our Orbit paper is out!
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1007313
It's completely free, really!
And it will stay for free.
No demo, it's a full version.
Orbit Image Analysis is a free open source software with the focus to quantify big images like whole slide scans.
It can connect to image servers, e.g. Omero.
Analysis can be done on your local computer or via scaleout functionality in a distrubuted computing environment like a Spark cluster.
Sophisticated image analysis algorithms incl. tissue quantification using machine learning, object segmentation and classification are build in. In addition a versatile API allows you to enhance Orbit and to run your own scripts.
- Sophisticated Algorithms
- Connectivity
- Scaleout
- Programming API

Tissue Quantification
Compute the ratio of different tissue classes, e.g. percentage of collagen in a tissue.
Machine learning based tissue quantification allows the domain expert to train the system specific (e.g stained) tissue classes and to quantify it.
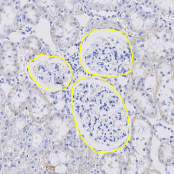
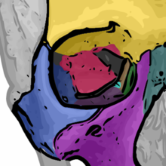
Object segmentation
Segment objects like cells or nerves.
Object detection based on trainable foreground / background classes. Overlapping object, e.g. cell clusters can be devided afterwards. Features of objects (shape factors, area, intensities, …) can be computed and reported or used for object classification.
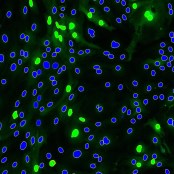
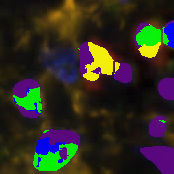
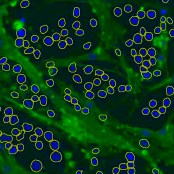
Object Classification
Assign classes to objects based on their features.
Segmented objects can be classified based on their features like size, shape factors or intensities. For instance, it can be distinguished between stained and not stained cells or between round and edgy objects. This classification is based on machine learning; the user can specify classes by selecting examples.

Annotations & ROI
Annotations and trainable exclusion maps for ROI definition.
The ROI (region of interest) can be defined by manual annotations or a trainable exclusion map which defines “the good” area of your tissue. Both methods can be combined.
Orbit version 3.60 released
We are happy to announce that we just released version 3.60 of Orbit Image Analysis, a cross-platform research tool for Whole Slide Image Analysis. For details of research applications, see the recently published article. Downloads for Windows, Mac and Linux can be found here. Version 3.60 includes a new tool for semi-automating annotations of TMA[…]
Darken your GUI with Radiance
The last couple of days I’ve been working on some improvements to the Orbit Image Analysis software. At the moment it’s mostly technical changes to help us be able to switch to using Java 11 (and then the next LTS Java JDKs). A nice side effect of that is being able to use my favourite[…]
Deep learning object detection
Version 3.0 integrates the deep learning framework Tensorflow for object detection. You can use a pre-trained model, like our glomeruli detection model available in our model zoo, or train your own deep learning model based on manually created object annotations. This new feature allows to detect arbitrary complex and heterogeneous objects like glomeruli, vessels, and[…]
Masks
The new Orbit version 2.8 comes with a brand new masking functionality. It allows you to define ‘active region’ classes within a classification model or use a segmentation model to define the segmented objects as ‘active’ and then do another classification or segmentation inside these active regions. This functionality unveils the power of Orbit for[…]
Native NDPI(s) reader
Orbit 2.7 has build-in support for native NDPI(s) reading out of the box (Win and Linux distributions). This leads to a tremendous speed improvement for reading NDPI and NDPIS files from local file system. We want to thank Hamamatsu for the great support and for providing the native library.
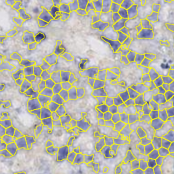
Cell Cluster Segmentation
Segmenting cells in cell clusters is very challenging because they cannot be separated easily from the background – thus classical segmentation algorithms fail. Unfortunately in WSI (whole slide imaging) you will have to deal with these situations – especially if you don’t have a single cell layer, like e.g. in tumor tissue. A collaboration with[…]
Orbit 2.52 with multichannel + Omero 5.3.x support
Today we release Orbit version 2.52 (for Omero 5.2.x) and Orbit 2.53 (for Omero 5.3.x). Both versions are identical except support for different Omero major versions and support multichannel / fluorescence images with unlimited number of channels. In addition, this version provides many bugfixes and speed improvements. Multi series / scenes can be selected in[…]
Bio-Formats 5.3.0
Orbit 2.4.3 makes use of the new Bio-Formats 5.3.0 library which enables CZI files with JPEG-XR compression support. In addition Orbit supports multi image series, e.g. you can open all image series of your VSI images.
Open Local Images
Today the new Orbit version 2.41 is released. The main achievement of this major version is the ability to work with whole slide images images in standalone mode, even without using an image server. In addition, many speed improvements (faster rendering) and bug-fixes are included. Orbit is designed to work with an image server, e.g.[…]
Maven Central artifacts available
Orbit Image Analysis and all its dependencies are now available via Maven Central. If you want to use the Orbit API, just add com.actelion.research orbit-image-analysis 2.30 in your POM or compile ‘com.actelion.research:orbit-image-analysis:2.30’ for Gradle. See the Orbit API page for details.