Wavelength frequency convert lambda Hz sound conversion acoustics acoustic audio radio measure speed of sound and radio typical waves wave length light vacuum equation formula for frequency speed of light color electromagnetic spectrum (original) (raw)
If instead of the speed of light, the speed of sound in air c = 343 m/s at 20°C
has to be used as speed of propagation, the following conversions apply.
Calculator used with kind permission of DoctorProAudio.com
Fill out the gray box above and click on the calculation button of the respective column.
Choose the wanted unit.
The proposed speed of sound c = 343 m/s or 1125.33 ft/s can be changed here.
The 1986 established value is c = 331.3 m/s at a temperature of ϑ = 0° Celsius.
Sometimes when you switch from m to cm to ft and inch the answer is wrong the
first time. Toggle between the changed values. Do a "refresh" and try again.
Formulas and equations for sound: c = λ × f λ = c / f = c × T f = c / λ
| Physical value | symbol | unit | formula |
|---|---|---|---|
| frequency | f = 1/T | Hz = 1/s | f = c / λ |
| wavelength | λ | m | λ = c / f |
| time period or cycle duration | T = 1/f | s | T = λ / c |
| wave speed speed of sound | c | m/s | c = λ × f |

Conversion of period to frequency and back
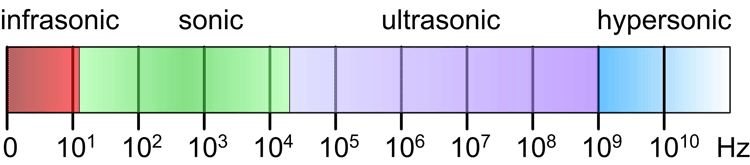
The top open range of the frequency spectrum for sound waves

● 2 − Radio waves and light waves in a vacuum ●
Conversion: frequency f to wavelength λ and wavelength to frequency
c is the speed of light waves and the speed of radio waves in a vacuum.
The speed of light in free space (a vacuum) is the speed at which
electromagnetic waves propagate, including light waves.
If instead of the speed of sound in air, the speed of light c = 299 792 458 m/s
has to be used as speed of propagation, the following conversions apply.
Fill out the gray box above and click on the calculation button of the respective column.
Choose the wanted unit.
The proposed speed of light c = 299 792 458 m/s or 983 571 056 ft/s can be changed here.
Formulas and Equations: c = λ × f λ = c / f = c × T f = c / λ
Wave frequency in Hz = 1/s and wavelength in nm = 10−9 m
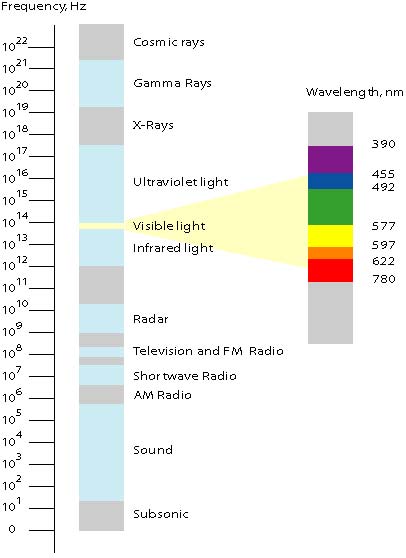
Electromagnetic Spectrum
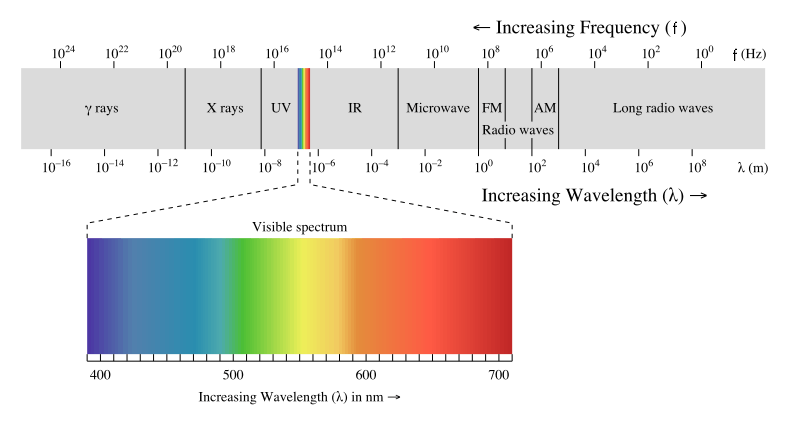
Spectrum of electromagnetic radiation
Radio wave frequency and microwave radiation are both forms of energy called
electromagnetic radiation. Sunshine contains three other forms of electromagnetic
radiation: ultraviolet rays, infrared (heat) waves, and visible light waves. These
electromagnetic waves spread in a vacuum at the speed of light ≈ 300,000 km/s as
electromagnetic radiation.
The propagation speed of electrical signals via optical fiber is about 9/10
the speed of light, that is ≈ 270,000 km/s.
The propagation speed of electrical signals via copper cables is about 2/3
the speed of light, that is ≈ 200,000 km/s.
In theory electrical signals move at the speed of light. Cables only slow them down.
The velocity propagation factor (Velocity of propagation):
VOP = 1 ⁄ √ε -epsilon is the dielectric constant, which is for polyethylene dielectrics
(PVC) nearly 1.4.
Sound is also shown at the spectrum chart, but it is no electromagnetic radiation.
Sound pressure is the deviation from the local ambient pressure (sound pressure
deviation) caused by a sound wave − mainly in air. The speed of sound is 343 m/s
at 20°C in air.
Sometimes the wavelength is still given in units of Ångström (angstrom):
1 Å = 10−10 m = 0.1 nm angegeben.
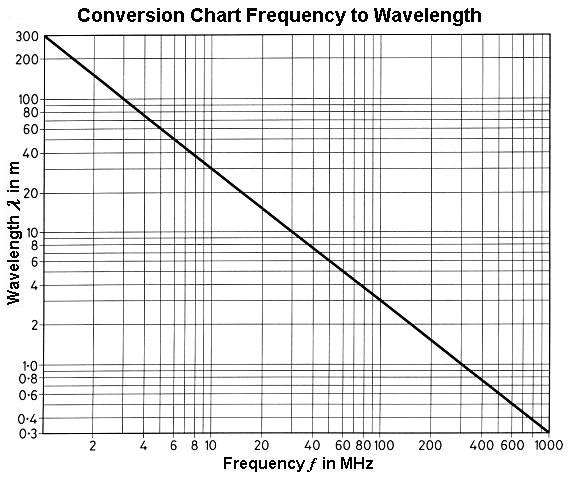
Conversion Chart − Frequency to Wavelength
Radio waves and light waves in a vacuum
Spectrum of Electromagnetic Radiation
| Region | Wavelengthangstroms | Wavelengthcentimeters | FrequencyHz | Energy eV |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Radio | > 109 | > 10 | < 3×109 | < 10−5 |
| Microwave | 109 − 106 | 10 − 0.01 | 3×109 − 3×1012 | 10−5 − 0.01 |
| Infrared | 106 − 7000 | 0.01 − 7×10−5 | 3×1012 − 4.3×1014 | 0.01 − 2 |
| Visible | 7000 − 4000 | 7×10−5 − 4×10−5 | 4.3×1014 − 7.5×1014 | 2 − 3 |
| Ultraviolet | 4000 − 10 | 4×10−5 − 10−7 | 7.5×1014 − 3×1017 | 3 − 103 |
| X-Rays | 10 − 0.1 | 10−7 − 10−9 | 3×1017 − 3×1019 | 103 − 105 |
| Gamma Rays | < 0.1 | <10−9 | > 3×1019 | >105 |
The notation "eV" stands for electron-volts, a common unit of energy measure in atomic physics.
A graphical representation of the electromagnetic spectrum is shown in the figure below.
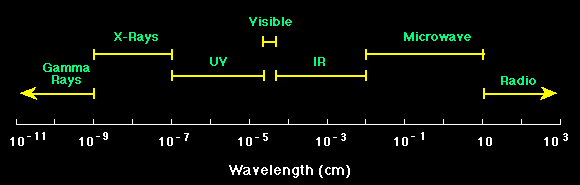 |
|---|
| Electromagnetic spectrum |
Thus we see that visible light and gamma rays and microwaves are really the same.
They are all electromagnetic radiation and they just differ in their wavelengths.
Sometimes the unit Ångström (angstrom) = 10−10 m = 0.1 nm is used for wavelength.
Wavelengths and frequency ranges of colors
| Color | Wavelengthnm | Frequency THz |
|---|---|---|
| red | 780 − 622 | 384 − 482 |
| orange | 622 − 597 | 482 − 503 |
| yellow | 597 − 577 | 503 − 520 |
| green | 577 − 492 | 520 − 610 |
| blue | 492 − 455 | 610 − 659 |
| violet | 455 − 390 | 659 − 769 |
1 terahertz (THz) = 103 GHz = 106 MHz = 1012 Hz,
1 nm = 10−3 μm = 10−6 mm = 10−9 m.
White light is a mixture of the colors of the visible spectra.
The indication of the frequency is less common in the optics.
Sound waves and electromagnetic waves are different. Sound waves
need a medium to travel through, while the electromagnetic waves do
not. The properties of a sound wave depend on the properties of the
medium it travels through.
| Approximate speed of soundin common materials | ||
|---|---|---|
| Medium | Speed of sound m/s ft/s | |
| Air, dry at 20 °C | 343 | 1 125 |
| Helium at 0 °C | 980 | 3 215 |
| Hydrogen at 0 °C | 1 280 | 4 200 |
| Water at 15 °C | 1 500 | 4 920 |
| Lead | 2 160 | 7 090 |
| Concrete | 3 100 | 10 200 |
| Wood (soft − along the fibre) | 3 800 | 12 500 |
| Glass | 5 500 | 18 500 |
| Steel | 5 800 | 19 000 |
Conversion of the radio frequency to wavelength and vice versa
To use the calculator, simply enter a value.
The calculator works in both directions of the ↔ sign.
● Electromagnetic waves need no transport medium.
Conversion of the acoustic frequency to wavelength and vice versa
To use the calculator, simply enter a value.
The calculator works in both directions of the ↔ sign.
● Sound waves or acoustic waves need necessarily a transport medium.