Top 10 Extreme Planet Facts (original) (raw)
Strange, But True - Our Solar System

IAU/Martin Kornmesser
The worlds around our sun run the gamut from small and lifeless chunks of rock to gargantuan globes of gas. Our planet's siblings each have its own extreme features and crazy phenomena. -- Charles Q. Choi
The air of Earth

NASA
It might seem a bit like navel-gazing to point out how special Earth is — after all, we live here. Although Earth is covered in oceans of water, Mars could have once hosted seas as well. But nowhere else in the solar system can one find atmospheres loaded with free oxygen, which ultimately proved vital to one of the other unique features of Earth — us.
The Great Red Spot of Jupiter

NASA/ESA/A. Simon-Miller (NASA Goddard Space Flight Center)
The most extraordinary feature on Jupiter's surface is undoubtedly the Great Red Spot, a giant storm seen for more than 300 years. At its widest diameter, the Great Red Spot is roughly three times as wide as Earth. Every now and again, the spot fades entirely.
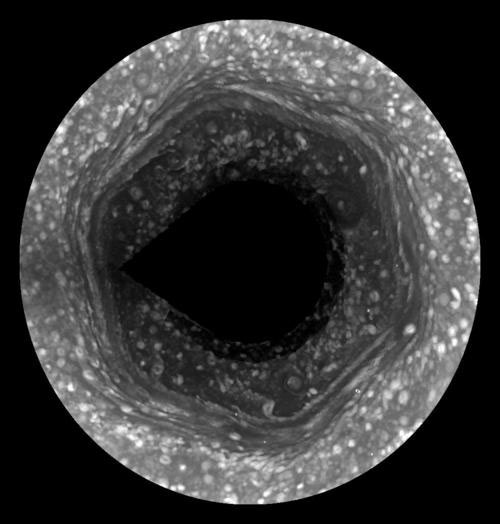
The hexagon of Saturn
NASA/JPL/Space Science Institute
Saturn may be most famous for its spectacular rings, but Jupiter, Uranus and Neptune have rings too. However, nothing like the giant hexagon circling Saturn's north pole has ever been seen on any other planet, with each of its sides nearly 7,500 miles (12,500 kilometers) across — big enough to fit nearly four Earths inside. Thermal images show it reaches some 60 miles (100 kilometers) down into the planet's atmosphere. Scientists have bandied about several other ideas concerning the hexagon's origin. One such idea is that the hexagon arises from a complex interaction between waves undulating through the atmosphere and gas churning up.
The storms of Mars

NASA/JPL-Caltech/Malin Space Science Systems
The dust storms of Mars are the largest in the solar system, capable of blanketing the entire red planet and lasting for months. One theory as to why dust storms can grow so big on Mars starts with airborne dust particles absorbing sunlight, warming the Martian atmosphere in their vicinity. Warm pockets of air flow toward colder regions, generating winds. Strong winds lift more dust off the ground, which in turn heats the atmosphere, raising more wind and kicking up more dust.
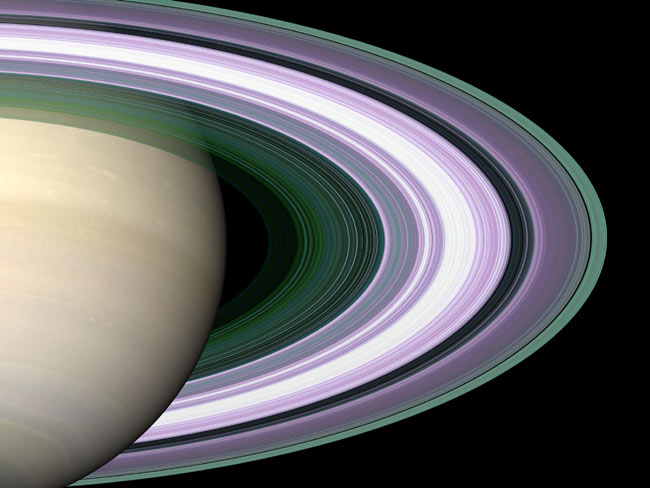
The rings of Saturn
NASA/JPL
Saturn is most famous for its spectacular rings. One ring, too faint to be seen from Earth and discovered just in 2009, measures at least 200 times the diameter of the planet — a billion Earths could fit inside the ring.
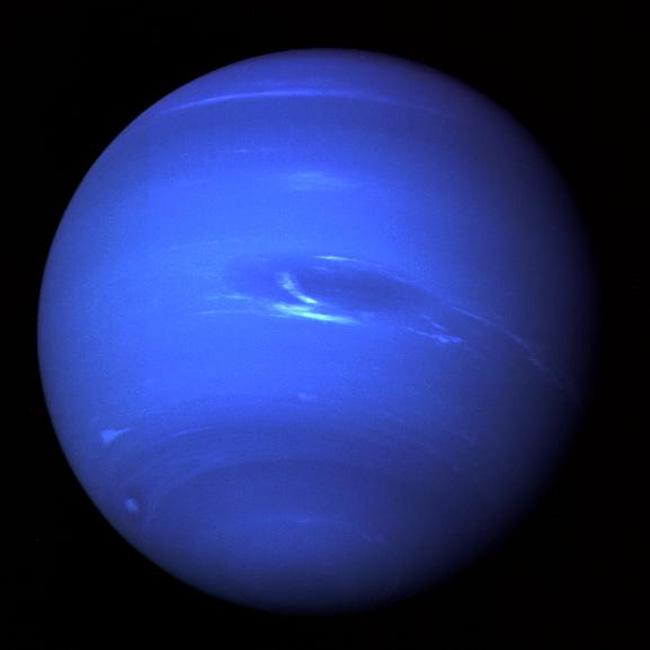
The winds of Neptune

NASA/JPL
On Neptune, one can find jet stream winds traveling at more than 1,500 mph. It remains a mystery as to how it gets the energy to drive the fastest planetary winds seen in the solar system, despite it being so far from the sun — at times farther from the sun than Pluto — and having relatively weak internal heat.
The weird tilt of Uranus
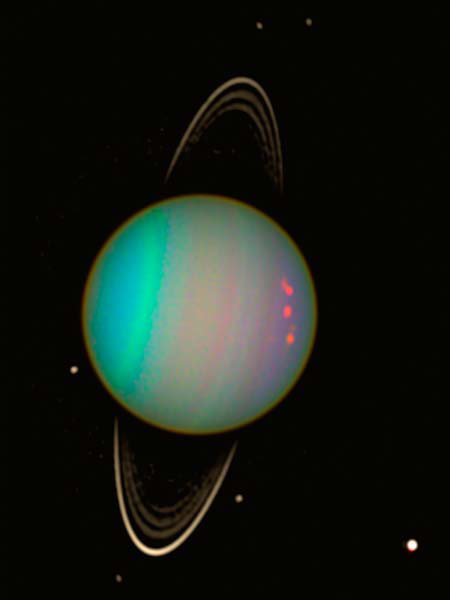

NASA and Erich Karkoschka, U. of Arizona
Unlike other worlds, Uranus is tilted so far that it essentially orbits the sun on its side, with the axis of its spin nearly pointing at the star. Many astronomers believe this unusual orientation might be due to a collision with an Earth-sized planet soon after it was formed.
The highs and lows of Mars
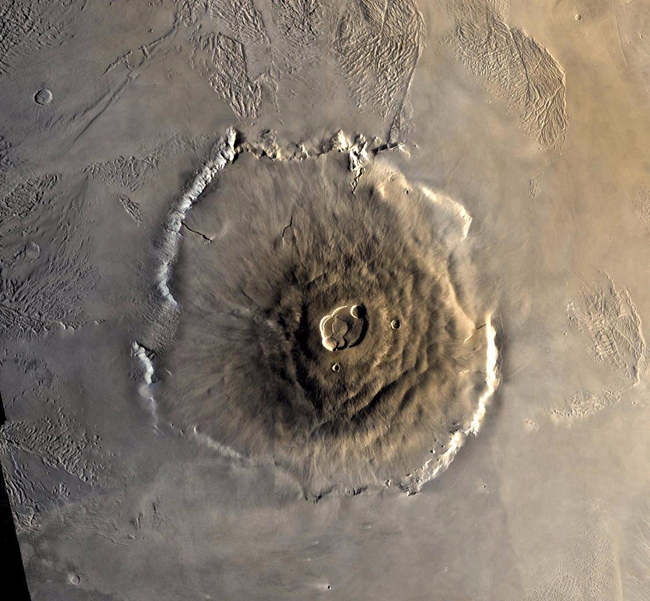

NASA/JPL
The red planet is home to both the highest mountain and the deepest, longest valley in the solar system. Olympus Mons is roughly 17 miles (27 kilometers) high, about three times as tall as Mount Everest, while the Valles Marineris can go as deep as 5 to 6 miles (8 to 10 kilometers) in some places and runs for roughly 2,500 miles (4,000 kilometers), which is close to the width of Australia or the distance from Philadelphia to San Diego.
The wild temperature swings of Mercury
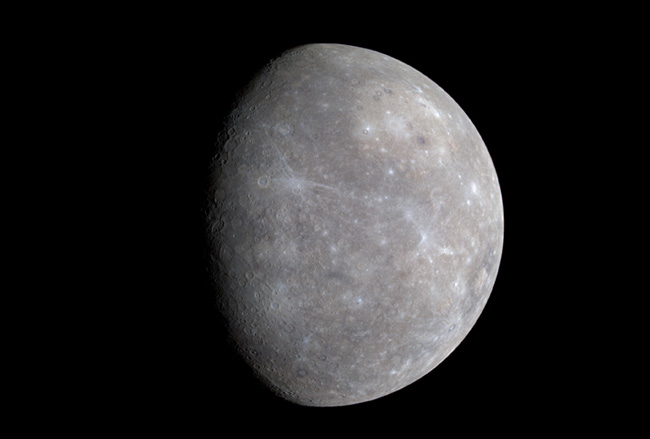

NASA/Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory/Carnegie Institution of Washington
As the planet nearest the sun, the surface of Mercury can reach a scorching 840 degrees F (450 degrees C). However, since this world doesn't have enough atmosphere to entrap any heat, at night temperatures can plummet to -275 degrees F (-170 degrees C), a more than 1,100 degrees F temperature swing that is the greatest in the solar system.
The blistering surface of Venus
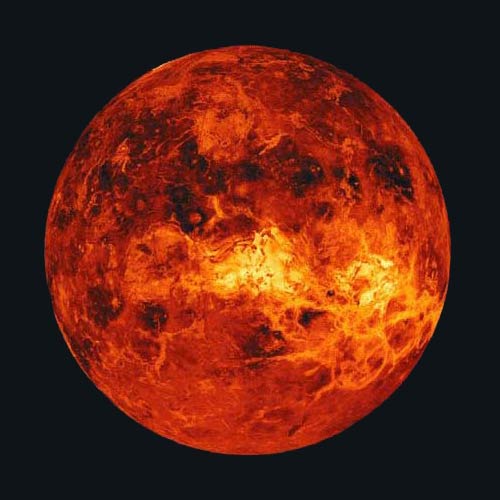

NASA
Although Venus is only the planet second nearest the sun, its dense, toxic atmosphere traps heat in a runaway version of the greenhouse effect that warms up the Earth. As a result, temperatures on Venus reach 870 degrees F (465 degrees C), more than hot enough to melt lead.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: community@space.com.
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
Charles Q. Choi is a contributing writer for Space.com and Live Science. He covers all things human origins and astronomy as well as physics, animals and general science topics. Charles has a Master of Arts degree from the University of Missouri-Columbia, School of Journalism and a Bachelor of Arts degree from the University of South Florida. Charles has visited every continent on Earth, drinking rancid yak butter tea in Lhasa, snorkeling with sea lions in the Galapagos and even climbing an iceberg in Antarctica. Visit him at http://www.sciwriter.us