Friction Coefficient Tables in Air and Vacuum – About Tribology (original) (raw)
HomeWikiFriction Coefficient Tables in Air and Vacuum

- Friction coefficient tables for solid lubricants, metals, plastics and anti-friction materials
- Steel friction coefficient table
- Friction Coefficient of Wood, Leather, and Stone
- Sliding Friction Coefficient Table for Selected Ceramic Materials (Room Temperature in Air)
- Ice friction coefficient
- Friction coefficient table for materials in fretting regime
- Friction coefficient table in fretting regime as a function of humidity
Friction coefficient tables for solid lubricants, metals, plastics and anti-friction materials
Friction coefficient tables for various material pairs in atmosphere and vacuum are provided below. The data was collected from various sources [1,2,3]. See the definition of friction coefficient.
| Material Combination | Friction coefficient in air | Friction coefficient in vacuum |
|---|---|---|
| Fe-Fe | 0.3 | 1.9 |
| Fe-Mg | 1 | 0.6 |
| Fe-Cd | 1.5 | 0.4 |
| Fe-Pb | 0.9 | 0.4 |
| Stainless Steel -Stainless Steel | 0.5 | 2.9 |
| Stainless Steel – Cu | – | 0.3 |
| Stainless Steel-Al | 0.4 | 0.3 |
| Stainless Steel-Mo | – | 0.8 |
| Stainless Steel-Ni | – | 0.8 |
| Stainless Steel-Teflon | – | 0.2 |
| Stainless Steel-Si | – | 0.2 |
| Stainless Steel-Ge | – | 0.2 |
| Stainless Steel-Glass | – | 0.5 |
| Chromium Steel – Chromium Steel | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Cu-Cu | 0.5-1.0 | 4.8-21.0 |
| Cu-Ni | 0.6 | 1.5-2.0 |
| Al-Al | 0.8 | 1.6-2.2 |
| Al-Ni | – | 2.4 |
| Al-Cu | – | 1.5 |
| Al-Ag | – | 2.2 |
| Brass-Brass | 0.4 | 0.7 |
| Ni-Ni | – | 4.9 |
| Ag-Ag | – | 3.9 |
| Cr-Cr | 0.6 | 3 |
| Au-Au | 0.6 | 4.5 |
| Zn-Zn | 1 | 3 |
| Zr-Zr | – | 1.5 |
| Chromium Steel – MoS2 (vacuum deposition) | – | 0.06 |
| Chromium Steel – MoS2 (friction deposition) | – | 0.06 |
| Cu-MoS2 | 0.2 | 0.07 |
| Brass-Steel | 0.35 | – |
| Tire – Asphalt | 0.72 | – |
| Tire – Grass | 0.35 | – |
| Diamond – Diamond | 0.1 | – |
| Glass – Glass | 0.9-1.0 | – |
| Graphite – Steel | 0.1 | – |
| Graphite – Graphite | 0.1 | 0.5-0.8 |
| Ice – Ice | 0.02-0.09 | – |
| Ice – Steel | 0.03 | – |
| Wood – Wood | >0.2 | – |
| Polytetrafluoroethylene – Polytetrafluoroethylene | 0.04 | – |
Steel friction coefficient table
Friction Coefficient of Wood, Leather, and Stone
Sliding Friction Coefficient Table for Selected Ceramic Materials (Room Temperature in Air)
Ice friction coefficient
Depending on pressure, temperature, and the conditions of formation, ice can take on any of at least eight allotropic forms, the largest number for any known substance. These changes impact the ice friction coefficient behavior, as shown in the figure below.
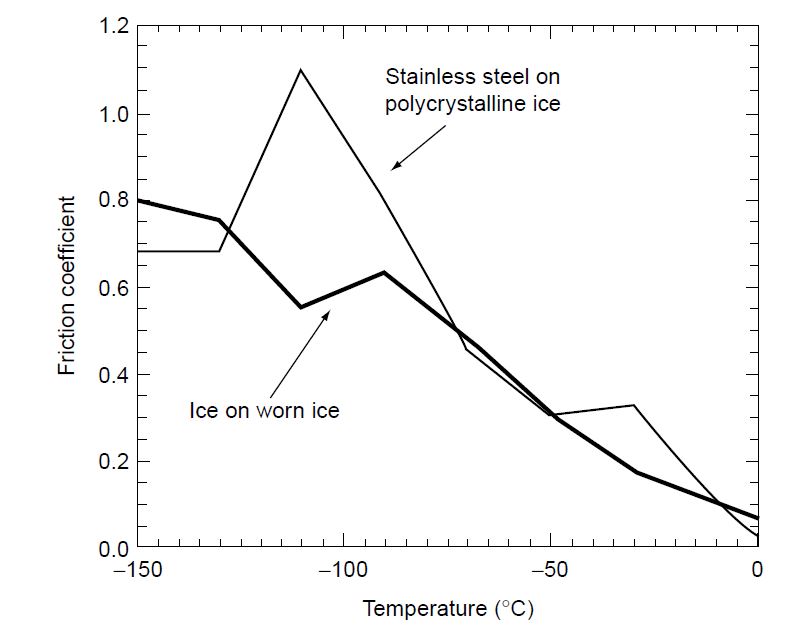
Figure 1. Friction coefficient for stainless steel and ice on polycrystalline ice as a function of temperature, [3].
Friction coefficient table for materials in fretting regime
In fretting, friction coefficients are different for the same pairs of materials due to changes in friction mechanisms. These tables include some data for commonly used materials.
Friction coefficient table in fretting regime as a function of humidity
References
- [1]. Mechanics and Physics of Precise Vacuum Mechanisms, E.A. Deulin, V.P. Mikhailov, Yu.V. Panfilov, R.A. Nevshupa.
- [2]. http://www.engineeringtoolbox.com/friction-coefficients-d\_778.html.
- [3]. Friction Science and Technology: From Concepts to Applications, Peter J. Blau, 2005

Administration of the project

