Mucosal adhesion and anti-inflammatory effects of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG in the human colonic mucosa: A proof-of-concept study (original) (raw)
Basic Study
Copyright ©The Author(s) 2018. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 7, 2018; 24(41): 4652-4662
Published online Nov 7, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i41.4652
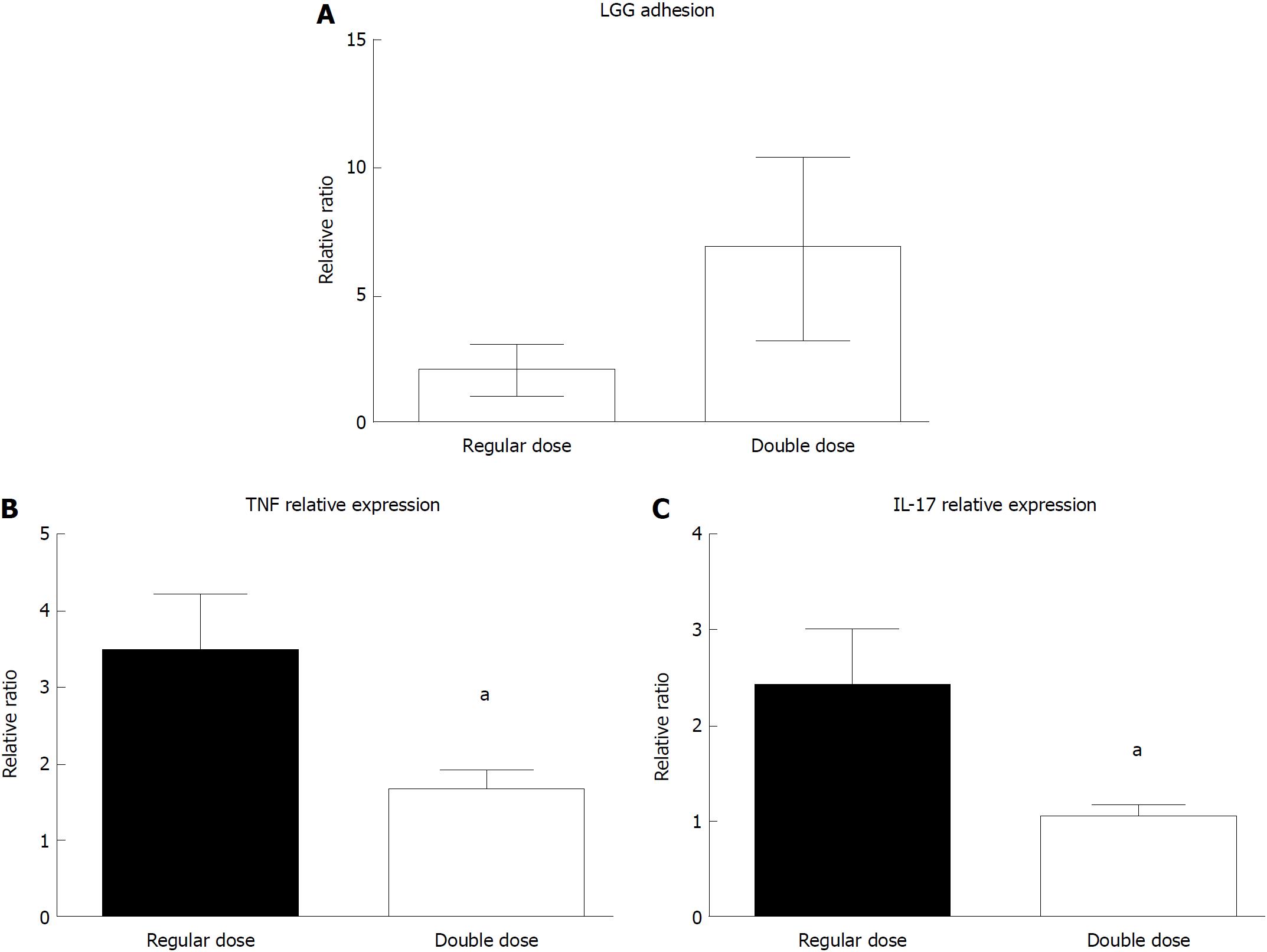
Figure 6 Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG adhesion and mucosal effect in the colon of ulcerative colitis patients. A: Mucosal Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (LGG) quantification in colon biopsies of ulcerative colitis (UC) patients who consumed a regular (12 × 109 UFC/die) or a double (24 × 109 UFC/die) dose of LGG supplement for 7 d (n = 10 per group); B: Tumor necrosis factor alpha mRNA quantification in colon biopsies from UC patients who consumed a regular or a double dose of LGG supplement for 7 d. Mean ± standard error is represented; C: Interleukin-17 mRNA quantification in colon biopsies from UC patients who consumed a regular or a double dose of LGG supplement for 7 d. a_P_ < 0.05. TNFα: Tumor necrosis factor alpha; IL: Interleukin; LGG: Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG; UC: Ulcerative colitis.
- Citation: Pagnini C, Corleto VD, Martorelli M, Lanini C, D’Ambra G, Di Giulio E, Delle Fave G. Mucosal adhesion and anti-inflammatory effects of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG in the human colonic mucosa: A proof-of-concept study. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(41): 4652-4662
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i41/4652.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i41.4652