
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
Nitric acid/UDMH
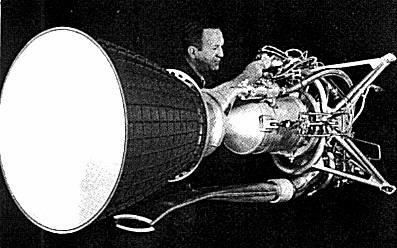
Agena Engine
Credit: Bell
Nitric acid/UDMH propellant. Drawing on the German World War II Wasserfall rocket, nitric acid (HNO3) became the early storable oxidizer of choice for missiles and upper stages of the 1950's. To overcome various problems with its use, it was necessary to combine the nitric acid with N2O4 and passivation compounds. These formulae were considered extremely secret at the time. By the late 1950's it was apparent that N2O4 by itself was a better oxidizer. Therefore nitric acid was almost entirely replaced by pure N2O4 in storable liquid fuel rocket engines developed after 1960. Unsymmetrical Dimethylhydrazine ((CH3)2NNH2) became the storable liquid fuel of choice by the mid-1950's. Development of UDMH in the Soviet Union began in 1949. It is used in virtually all storable liquid rocket engines, normally in combination with N2O4 rather than nitric acid.
Specific impulse: 323 s. Specific impulse sea level: 276 s. Location: 1675.
Optimum Oxidizer to Fuel Ratio: 3. Temperature of Combustion: 3,225 deg K. Ratio of Specific Heats: 1.23. Density: 1.25 g/cc. Characteristic velocity c: 1,675 m/s (5,495 ft/sec). Isp Shifting: 277 sec. Isp Frozen: 268 sec. Mol: 22.00 M (72.00 ft). Oxidizer Density: 1.510 g/cc. Oxidizer Freezing Point: -42 deg C. Oxidizer Boiling Point: 86 deg C. Fuel Density: 0.793 g/cc. Fuel Freezing Point: -57 deg C. Fuel Boiling Point: 63 deg C.
Subtopics
| 11D49 Isayev Nitric acid/UDMH rocket engine. Kosmos-3M stage 2. Engine has one main and four steering nozzles. Thrust 157.5 + 4 x 25 kN. Predecessor was 11D47 in R-14 (derivative) stage 2. First flight 1964. |
| 45LR-35000 Aerojet Nitric acid/UDMH rocket engine for Bomarc missile. Development begun 1953. Pressure-fed, uncooled, ceramic-lined engine. First flight 1959. |
| Able Nitric acid/UDMH propellant rocket stage. Engine for Vanguard was AJ10-37; for later Able models AJ10-41 and AJ10-42. Total of 21 stages built and delivered by Aerojet. |
| Able-Star Nitric acid/UDMH propellant rocket stage. The Air Force requested increases in the propulsion system capabilities of the original Able upper stage design in an effort to meet their ever-expanding mission requirements. As a result, the stainless steel version of the basic Able engine was selected, and it was uprated to increase thrust 34.7 kN to 37.0 kN and to increase the duration 2-1/2 times (easily done with the stainless steel thrust chamber) - and this configuration was called Ablestar. |
 |
Agena A Nitric acid/UDMH propellant rocket stage. The Agena space vehicle was used in large numbers during the 1960s and 1970s as upper stage with SLV-2 Thor, SLV-3 Atlas and SLV-5 Titan boosters to launch a variety of military and civilian payloads into orbit. The Agena itself was actually the first general-purpose satellite, and formed the core for many operational satellites and experimental space vehicles. |
| Agena B Nitric acid/UDMH propellant restartable rocket stage. Often integrated with the functional payload, acting. 94 launches, 1960 to 1967. Launched by Atlas Agena B; Thor Agena B. |
| Agena D Nitric acid/UDMH propellant restartable rocket stage. 205 launches, 1963 to 1987. Often integrated with the functional payload. Launched by Atlas Agena D; Thor Agena D; Titan 3B; Titan 34B. |
| AJ10-101 Aerojet Nitric acid/UDMH rocket engine. Derivative of Vanguard second stage for use with Thor IRBM to produce satellite launch vehicle. First tests February 21, 1958. Flown through 1960. |
| AJ10-104 Aerojet Nitric acid/UDMH rocket engine. Stainless steel version of the basic Able engine, uprated to increase thrust 34.7 kN to 37.0 kN and to increase the duration 2-1/2 times First flight 1960. |
| AJ10-118 Aerojet Nitric acid/UDMH rocket engine. Out of Production. Engine originally developed for the Vanguard launch vehicle, and then for use on the Able and Delta upper stages and as the Apollo Service module engine. Flown 1957-1962. |
| AJ10-118D Aerojet Nitric acid/UDMH rocket engine. Used on Delta B, Delta C, Delta D upper stages. First flight 1962. |
| AJ10-118E Aerojet Nitric acid/UDMH rocket engine. Used on Delta E, Delta G, Delta J, Delta L, Delta M, Delta N upper stages. First flight 1965. |
| AJ10-118F Aerojet Nitric acid/UDMH rocket engine. Used on Delta upper stage for Delta 0100, Delta 1000, N-2 boosters. First flight 1972. |
| AJ10-118G Aerojet Nitric acid/UDMH rocket engine. Delta G. |
| AJ10-118H Aerojet Nitric acid/UDMH rocket engine. Delta H. |
| AJ10-118J Aerojet Nitric acid/UDMH rocket engine. Delta J. |
| AJ10-33 Aerojet Nitric acid/UDMH rocket engine. SMART Sled. Development begun early 1950s. 114,000 lbf thrust, uncooled, ceramic lined, 3 chamber system |
| AJ10-40 Aerojet Nitric acid/UDMH rocket engine. Minor modification of the Vanguard aluminum tube thrust chamber to meet the Able requirements. accomplished in the record time of only three months. |
 |
Bell 8048 Bell Nitric acid/UDMH rocket engine. Out of production. Used on Agena A, derived from Rascal engine. Regeneratively cooled; used drilled holes to create the same effect as more costly stacked spaghetti rubes. First flight 1959. |
| Bell 8081 Bell Nitric acid/UDMH rocket engine. Out of production. Used on Agena B stage atop Thor and Atlas. First flight 1960. |
 |
Bell 8096 Bell Nitric acid/UDMH rocket engine. Out of production. Used in Agena stage on top of Thor, Atlas, and Titan launch vehicles. First flight 1963. |
| Bell 8247 Bell Nitric acid/UDMH rocket engine. Out of Production. Version of Agena engine for the Gemini-Agena Target Vehicle. Minimum capability of five restarts and a demonstrated capability of fifteen restarts. First flight 1963. |
| CZ-1-2 Nitric acid/UDMH propellant rocket stage. Masses, engine performance estimated based on successor improved stage and YF-2 engines in first stage. |
| CZ-YF-2 Nitric acid/UDMH propellant rocket stage. . |
| Delta 104 Nitric acid/UDMH propellant rocket stage. . |
| Delta A Nitric acid/UDMH propellant rocket stage. Able was only the first of many engine and application programs that flowed from the Vanguard experience base. These included Able, Ablestar, Delta, Fat Delta, the Japanese N II, and applications or offshoots such as Hydra, Saint (Satellite Intercept), and other classified programs. |
| Delta D American orbital launch vehicle. Unaugmented Thor with Delta and solid propellant upper stages. |
| Delta E American orbital launch vehicle. Unaugmented Thor with Delta and solid propellant upper stages. |
| Delta F Nitric acid/UDMH propellant rocket stage. . |
| Ghauri stage Nitric acid/UDMH rocket stage. 255.00 kN (57,326 lbf) thrust. Mass 16,000 kg (35,274 lb). |
| Isayev DOS-3/4 Isayev Nitric acid/UDMH rocket engine. DOS-3/4. Out of Production. |
| KDU-414 Isayev Nitric acid/UDMH rocket engine. Molniya 1, Mars 1, Venera 1, Zond 2-3 maneuvering engine. Out of Production. Spacecraft maneuvering engine. |
| Kosmos-1 Nitric acid/UDMH propellant rocket stage. Launch count 411 orbital and ca. 300 suborbital to end 1994. Failures based on proration of failures to orbit. |
| KTDU-35 Isayev Nitric acid/UDMH rocket engine. Out of Production. Soyuz, Salyut 4 maneuvering engine. KTDU-53 version in L-1 circumlunar spacecraft; KTDU-66 in Salyut 1 space station. Thrusts 4.09 kN main + 4.03 kN secondary. First flight 1966. |
| KTDU-417 Isayev Nitric acid/UDMH rocket engine. Luna 15-24 descent stage. Out of Production. Comprised turbopump-fed high-thrust engine with plus KTDU-417-B low-thrust engine. Eleven ignitions for lunar orbit insertion and orbit corrections. |
| KTDU-53 Isayev Nitric acid/UDMH rocket engine. Zond 4-7 maneuvering engine. Out of Production. Spacecraft maneuvering engine, derivative of KTDU-35 without back-up engine. |
| KTDU-66 Isayev Nitric acid/UDMH rocket engine. Out of Production. Maneuvering engine for Salyut 1, derivative of KTDU-35. Longer burn time of 1000 s. Comprised single-chamber main engine plus dual-chamber back-up engine. Thrusts 4.09 + 4.03 kN |
 |
Molniya-1 Russia's first military communications satellite. Built by OKB-1 (#1L-7L); NPO Prikladnoi Mekhaniki (NPO PM) (#8L-35L). Launched 1967 - 1975. Used KAUR-2 bus. |
| Nodong North Korean Nitric acid/UDMH rocket engine. In production. Used in North Korean missiles and Taepodong 1 satellite launcher. Derived from Isayev designs developed for Scud missiles and SLBM's of the Makeyev bureau. First flight 1998. |
| Nodong 1 stage Nitric acid/UDMH rocket stage. 255.00 kN (57,326 lbf) thrust. Mass 15,100 kg (33,290 lb). |
 |
P8E-9 Rocketdyne Nitric acid/UDMH rocket engine. Lance Booster and Sustainer System. Pressure-fed. Sustainer 4400 -14,400 lbf, 227 sec Isp. Thrust and specific impulse values are at sea level. First flight 1972. |
| R-16-1 Nitric acid/UDMH propellant rocket stage. Range 12,000 km. TsNIIMash has 1:10 structural simulation model. Two stage ICBM with nitric acid oxidizer. Developed 1956-1961. Entered service 1961. Chief designer Yangel. Source: Placard, TsNIIMash. |
| R-16-2 Nitric acid/UDMH propellant rocket stage. Range 12,000 km. TsNIIMash has 1:10 structural simulation model. Two stage ICBM with nitric acid oxidizer. Developed 1956-1961. Entered service 1961. Chief designer Yangel. Source: Placard, TsNIIMash. |
 |
R-26-1 Nitric acid/UDMH propellant rocket stage. Orevo has sectioned hardware. TsNIIMash has 1:10 structural simulation model. All figures accurate except empty mass estimated. Source: Placard, TsNIIMash, Orevo. |
| R-26-2 Nitric acid/UDMH propellant rocket stage. Orevo has sectioned hardware. TsNIIMash has 1:10 structural simulation model. All figures accurate except empty mass estimated. Source: Placard, TsNIIMash, Orevo. |
| RD-215 Glushko Nitric acid/UDMH rocket engine. R-14, Kosmos 11K63 stage 1. Out of Production. Original intended use unknown. Two RD-215 clustered to make RD-216. First flight 1966. |
| RD-216 Glushko Nitric acid/UDMH rocket engine. R-14, Kosmos 11K65 stage 1. RD-216 was an assembly of 2 RD-215's with 2 combustion chambers and 2 turbines. Two sets of these were in turn used in the first stage of the R-14. First flight 1964. |
| RD-216M Glushko Nitric acid/UDMH rocket engine. Kosmos-3M stage I. Out of Production. |
| RD-217 Glushko Nitric acid/UDMH rocket engine. R-16 stage 1. Out of Production. Original intended use unknown. Three RD-217 clustered to make RD-218. First flight 1961. |
| RD-218 Glushko Nitric acid/UDMH rocket engine. R-16 stage 1. Consisted of three RD-217; had 6 combustion chambers and 3 turbines; powered the R-16 ICBM. First flight 1960. |
 |
RD-219 Glushko Nitric acid/UDMH rocket engine. R-16 stage 2. Derivative of RD-217 with a truss and piping changes. Despite higher expansion ratio, engine was shorter than first stage version, with relatively low performance. Flown 1960-1972. |
| RD-220 Glushko Nitric acid/UDMH rocket engine. missile stage 1 (stage 2 used RD-221). Developed 1960-. |
| RD-221 Glushko Nitric acid/UDMH rocket engine. missile stage 2 (stage 1 used RD-220). Developed 1960-. |
| RD-222 Glushko Nitric acid/UDMH rocket engine. missile stage 1 (stage 2 used RD-223). Developed 1960-61. Precursor to RD-253. |
| RD-223 Glushko Nitric acid/UDMH rocket engine. missile stage 2 (stage 1 used RD-222). Developed 1960-61. Precursor to RD-253. |
| RD-224 Glushko Nitric acid/UDMH rocket engine. R-26 stage 1. Out of production. RD-224 is a block of 2 RD-225s. An upper stage thrust chamber was developed under designation U102-000. First flight 1961. |
| RD-225 Glushko Nitric acid/UDMH rocket engine. R-26 stage 1. Out of Production. Two clustered together to make RD-224. First flight 1961. |
| RD-68 Yuzhnoye Nitric acid/UDMH rocket engine. R-16 stage 1 attitude control engine. Out of Production. |
| RD-69 Yuzhnoye Nitric acid/UDMH rocket engine. R-16 stage 2 attitude control engine. Out of Production. |
| RD-851 Yuzhnoye Nitric acid/UDMH rocket engine. R-16 (SS-7) stage 1 attitude control engine . Out of Production. Four thrusters are each gimbaled in one single axis. |
| RD-852 Yuzhnoye Nitric acid/UDMH rocket engine. R-16 (SS-7) stage 2 attitude control engine. Out of Production. Four thrusters are each gimbaled in one single axis. |
 |
RD-853 Yuzhnoye Nitric acid/UDMH rocket engine. Stage 2, no application. Developed 1960-63. Designed for second stage, no application. Two thrust levels. Thrust 467.6 kN + 11.8 kN / 7.65 kN. |
 |
RM-100B Rocketdyne Nitric acid/UDMH rocket engine. Satellite Reaction Control. Pressure-fed. |
| S3 Nitric acid/UDMH propellant rocket stage. Launch count 411 orbital and ca. 300 suborbital to end 1994. Failures based on proration of failures to orbit. |
| S5.45 Isayev Nitric acid/UDMH rocket engine. correction engine for Zond-1, Venera-2-8, and others. Out of Production. Pressure-fed engine. Used as correction engine for spacecraft Zond-1, Vernera-8, and others. |
| Shahab 3 stage Nitric acid/UDMH rocket stage. 255.00 kN (57,326 lbf) thrust. Mass 15,100 kg (33,290 lb). |
| Shaheen-2 Sanjiang Nitric acid/UDMH rocket engine. |
 |
Soyuz 7K-L1 Russian manned lunar flyby spacecraft. The Soyuz 7K-L1, a modification of the Soyuz 7K-OK, was designed for manned circumlunar missions. Lunar flyby and return satellite, Russia. Launched 1967 - 1970. |
| Soyuz 7K-L1 PAO Russian manned spacecraft module. 12 launches, 1967.03.10 (Cosmos 146) to 1970.10.20 (Zond 8). Modification of Soyuz 7K-OK basic PAO service module with pump-fed main engines and separate RCS/main engine propellant feed system. Equipment-engine section. |
| Taepo Dong 2-2 Nitric acid/UDMH rocket stage. 570.00 kN (128,141 lbf) thrust. Mass 25,600 kg (56,438 lb). |
| Taepodong 1-2 Nitric acid/UDMH propellant rocket stage. Included 100 kg spin table for spin-up of third stage prior to release. Burn time is 33.7 seconds at full thrust, 142.3 seconds at half thrust. |
| Taepodong 2-1 Nitric acid/UDMH rocket stage. 1000.00 kN (224,809 lbf) thrust. Mass 60,000 kg (132,277 lb). |
| TD-2 CMIK Nitric acid/UDMH rocket engine. Used on Taepodong / Unha first stage. |
| U102-000 Glushko Nitric acid/UDMH rocket engine. R-26 stage 2. Out of production. |
| Von Braun-1 Notional Nitric acid/UDMH rocket engine. Study 1952. Used on Von Braun launch vehicle. |
| Von Braun-2 Notional Nitric acid/UDMH rocket engine. A11, Von Braun studies 1943-1952. |
| Von Braun-3 Notional Nitric acid/UDMH rocket engine. Study 1952. Used on Von Braun launch vehicle. |
| YF-2A Beijing Wan Yuan Nitric acid/UDMH rocket engine. Out of production. Used on CZ-1, CZ-1C, CZ-1D, CZ-1M. First flight 1969. |
| YLR63AJ-3 Aerojet Nitric acid/UDMH rocket engine. F-86. Out of Production. Development begun 1953. Superperformance, modification of YLR45AJ-3 with gas generator turbine drive, 6 restarts. |
Engines: Von Braun-3, YLR63AJ-3, RD-216, RD-217, RD-218, RD-219, RD-852, 11D49, RD-216M, RD-221, RD-222, RD-223, RD-224, Bell 8247, KTDU-53, RM-100B, KTDU-66, Isayev DOS-3/4, 45LR-35000, AJ10-40, AJ10-101, AJ10-104, AJ10-118, AJ10-118D, AJ10-118E, AJ10-118F, AJ10-118G, AJ10-118H, AJ10-118J, AJ10-33, Bell 8081, Bell 8096, Bell 8048, KTDU-417, KDU-414, KTDU-35, Nodong, P8E-9, RD-215, RD-220, RD-225, RD-68, RD-69, RD-851, RD-853, S5.45, Shaheen-2, TD-2, U102-000, Von Braun-1, Von Braun-2, YF-2A. Spacecraft: Molniya-1, Soyuz 7K-L1, Soyuz 7K-L1 PAO. Stages: Von Braun 1956-3, CZ-1-2, S3, R-26-2, R-26-1, CZ-YF-2, Von Braun 1956-2, Von Braun 1956-1, Able, Agena A, Delta 104, Delta A, Agena B, Delta D, R-16-1, R-16-2, Delta E, Agena D, Delta F, Nodong 1 stage, Taepodong 1-1, Ghauri stage, Shahab 3 stage, Taepodong 1-2, Able-Star, Kosmos-1, Shaheen 2-2, Taepodong 2-1, Taepo Dong 2-2.
Back to top of page
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
© 1997-2019 Mark Wade - Contact
© / Conditions for Use

