Volterra Integral Equations - EqWorld (original) (raw)
 |
EqWorld The World of Mathematical Equations |  |
|---|
Home Page Exact Solutions Methods Software Education About This Site Math Forums
Exact Solutions >Integral Equations > Volterra Integral Equations of the First Kind and Related Linear Integral Equations with Variable Limit of Integration
1. Volterra Integral Equations of the First Kind
1-1. Integral equations with kernels involving power-law functions
-
 (x − t) y(t) dt = f(x).
(x − t) y(t) dt = f(x). -
 (Ax + Bt + C) y(t) dt = f(x).
(Ax + Bt + C) y(t) dt = f(x). -
 (x − t)n y(t) dt = f(x),n = 1, 2, ...
(x − t)n y(t) dt = f(x),n = 1, 2, ... -
 (x − t)1/2 y(t) dt = f(x).
(x − t)1/2 y(t) dt = f(x). -
 (x − t)−1/2 y(t) dt = f(x). Abel equation.
(x − t)−1/2 y(t) dt = f(x). Abel equation. -
 (x − t)λ y(t) dt = f(x), 0 < λ < 1.
(x − t)λ y(t) dt = f(x), 0 < λ < 1. -
 (x − t)−λ y(t) dt = f(x), 0 < λ < 1. Generalized Abel equation.
(x − t)−λ y(t) dt = f(x), 0 < λ < 1. Generalized Abel equation.
1-2. Integral equations with kernels involving exponential functions
-
 _e_λ(x_−_t) y(t) dt = f(x).
_e_λ(x_−_t) y(t) dt = f(x). -
 e_λ_x+β_t_ y(t) dt = f(x).
e_λ_x+β_t_ y(t) dt = f(x). -
 [_e_λ(x_−_t) − 1] y(t) dt = f(x).
[_e_λ(x_−_t) − 1] y(t) dt = f(x). -
 [_e_λ(x_−_t) + b] y(t) dt = f(x).
[_e_λ(x_−_t) + b] y(t) dt = f(x). -
 [_e_λ(x_−_t) −_e_μ(x_−_t)] y(t) dt = f(x).
[_e_λ(x_−_t) −_e_μ(x_−_t)] y(t) dt = f(x). -
 (e_λ_x − e_λ_t)−1/2 y(t) dt = f(x).
(e_λ_x − e_λ_t)−1/2 y(t) dt = f(x).
1-3. Integral equations with kernels involving hyperbolic functions
-
 cosh[λ(x − t)] y(t) dt = f(x).
cosh[λ(x − t)] y(t) dt = f(x). -
 {cosh[λ(x − t)] − 1} y(t) dt = f(x).
{cosh[λ(x − t)] − 1} y(t) dt = f(x). -
 {cosh[λ(x − t)] + b} y(t) dt = f(x).
{cosh[λ(x − t)] + b} y(t) dt = f(x). -
 cosh2[λ(x − t)] y(t) dt = f(x).
cosh2[λ(x − t)] y(t) dt = f(x). -
 sinh[λ(x − t)] y(t) dt = f(x).
sinh[λ(x − t)] y(t) dt = f(x). -
 {sinh[λ(x − t)] + b} y(t) dt = f(x).
{sinh[λ(x − t)] + b} y(t) dt = f(x). -
 sinh[λ(x − t)1/2] y(t) dt = f(x).
sinh[λ(x − t)1/2] y(t) dt = f(x).
1-4. Integral equations with kernels involving logarithmic functions
1-5. Integral equations with kernels involving trigonometric functions
-
 cos[λ(x − t)] y(t) dt = f(x).
cos[λ(x − t)] y(t) dt = f(x). -
 {cos[λ(x − t)] − 1} y(t) dt = f(x).
{cos[λ(x − t)] − 1} y(t) dt = f(x). -
 {cos[λ(x − t)] + b} y(t) dt = f(x).
{cos[λ(x − t)] + b} y(t) dt = f(x). -
 sin[λ(x − t)] y(t) dt = f(x).
sin[λ(x − t)] y(t) dt = f(x). -
 sin[λ(x − t)1/2] y(t) dt = f(x).
sin[λ(x − t)1/2] y(t) dt = f(x).
1-6. Integral equations with kernels involving special functions
-
 _J_0(λ(x − t)) y(t) dt = f(x).
_J_0(λ(x − t)) y(t) dt = f(x). -
 _J_0(λ(x − t)1/2) y(t) dt = f(x).
_J_0(λ(x − t)1/2) y(t) dt = f(x). -
 _I_0(λ(x − t)) y(t) dt = f(x).
_I_0(λ(x − t)) y(t) dt = f(x). -
 _I_0(λ(x − t)1/2) y(t) dt = f(x).
_I_0(λ(x − t)1/2) y(t) dt = f(x).
10-7. Integral equations with kernels involving arbitrary functions
-
 [g(x) − g(t)] y(t) dt = f(x).
[g(x) − g(t)] y(t) dt = f(x). -
 [g(x) − g(t) + b] y(t) dt = f(x).
[g(x) − g(t) + b] y(t) dt = f(x). -
 [g(x) + h(t)] y(t) dt = f(x).
[g(x) + h(t)] y(t) dt = f(x). -
 K(x − t) y(t) dt = f(x).
K(x − t) y(t) dt = f(x). -
 [g(x) − g(t)]1/2 y(t) dt = f(x).
[g(x) − g(t)]1/2 y(t) dt = f(x). -
 [g(x) − g(t)]−1/2 y(t) dt = f(x).
[g(x) − g(t)]−1/2 y(t) dt = f(x).
The EqWorld website presents extensive information on solutions to various classes ofordinary differential equations,partial differential equations,integral equations,functional equations, and other mathematical equations.
Copyright © 2004-2017 Andrei D. Polyanin
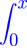 ln(x − t) y(t) dt = f(x).
ln(x − t) y(t) dt = f(x).