An example of K-Means++ initialization (original) (raw)
Note
Go to the endto download the full example code. or to run this example in your browser via JupyterLite or Binder
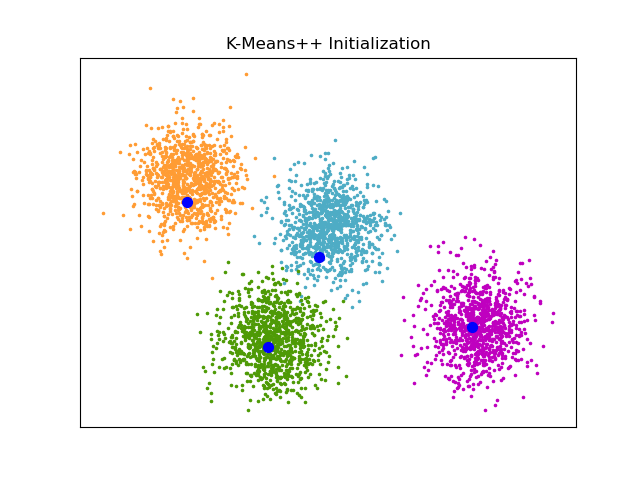
An example to show the output of the sklearn.cluster.kmeans_plusplusfunction for generating initial seeds for clustering.
K-Means++ is used as the default initialization for K-means.
Authors: The scikit-learn developers
SPDX-License-Identifier: BSD-3-Clause
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.cluster import kmeans_plusplus from sklearn.datasets import make_blobs
Generate sample data
n_samples = 4000 n_components = 4
X, y_true = make_blobs( n_samples=n_samples, centers=n_components, cluster_std=0.60, random_state=0 ) X = X[:, ::-1]
Calculate seeds from k-means++
centers_init, indices = kmeans_plusplus(X, n_clusters=4, random_state=0)
Plot init seeds along side sample data
plt.figure(1) colors = ["#4EACC5", "#FF9C34", "#4E9A06", "m"]
for k, col in enumerate(colors): cluster_data = y_true == k plt.scatter(X[cluster_data, 0], X[cluster_data, 1], c=col, marker=".", s=10)
plt.scatter(centers_init[:, 0], centers_init[:, 1], c="b", s=50) plt.title("K-Means++ Initialization") plt.xticks([]) plt.yticks([]) plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.061 seconds)
Related examples