Dual Lander Mission (original) (raw)

Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
Dual Lander Mission
Part of American Mars Expeditions
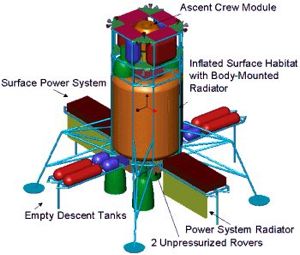
American manned Mars expedition. Study 1999. After some discussion within NASA, in the Combo Lander mission was found to be too lean.
Status: Study 1999.
It was again reformulated as a Design Reference-Mission type with two landers, six crew sent on two different opportunities, and ISRU production on the surface, and split cargo/crew landers to provide more redundancy. Even with the mass-saving advanced technology assumptions of the Combo Lander study, this drove the total mass required in Low Earth Orbit back to 600 metric tons, and the number of heavy lift launch vehicle launches to 12.
Dual Lander Mission Summary:
- Summary: Follow-on of combo lander study - back to 2 landers; no formal report, presentation charts only
- Propulsion: Solar electric/Lox/LH2
- Braking at Mars: aerodynamic
- Mission Type: conjunction
- Split or All-Up: split
- ISRU: ISRU
- Launch Year: 2011
- Crew: 12
- Mars Surface payload-metric tons: 35
- Outbound time-days: 200
- Mars Stay Time-days: 600
- Return Time-days: 210
- Total Mission Time-days: 1010
- Total Payload Required in Low Earth Orbit-metric tons: 600
- Total Propellant Required-metric tons: 110
- Propellant Fraction: 0.18
- Mass per crew-metric tons: 100
- Launch Vehicle Payload to LEO-metric tons: 75
- Number of Launches Required to Assemble Payload in Low Earth Orbit: 12
- Launch Vehicle: Magnum
Family: Mars Expeditions. Country: USA. Agency: NASA. Bibliography: 1989.
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
© 1997-2019 Mark Wade - Contact
© / Conditions for Use