Perseus (original) (raw)
Perseus (abbreviation: Per), the Hero and rescuer of Andromeda from the jaws of Cetus, is a large northern constellation, bordering on Aries to the north and Taurus to the south. The figure of Perseus is thought to hold the head of Medusa in his hand (the star Beta Per representing her evil eye).
As well as a number of interesting stars, most notably Algol, Perseus boasts the Little Dumbbell Nebula, the Double Cluster, and another large, bright open cluster, M34 (NGC 1039), which can be seen with the naked eye on a dark night and can be resolved by a small telescope even at low power (magnitude 5.5; diameter 35 arcminutes; distance 1,400 light-years; RA 02h 42.0m, Dec +42° 47'). See below for details of the constellation's brightest stars.
Perseids
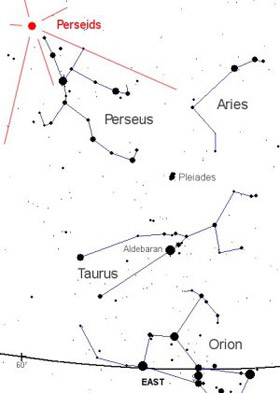 |
|---|
| The radiants of the Perseids, shown in red. |
The Perseids are a major annual meteor shower visible for a week or so before and after peaking on 12 August each year, the date on which Earth crosses the orbit. The maximum hourly rate is about 70 meteors. They appear to radiate from the constellation Perseus, from which they take their name. This shower is associated with Comet Swift-Tuttle (discovered in 1862, reappeared in 1992) and consists of debris left by the comet along its orbit. Typical velocity of a Perseid meteor is about 68 km (42 miles) per second.
Perseus arm
The Perseus arm is one of the spiral arms of our Galaxy, the nearest part of which lies in the direction of Perseus at a distance of about 7,000 light-years. The Perseus arm winds around to the other side of the Galaxy. Recent research suggests that it is much clumpier and less well-defined than previously thought. (Figure 2)
Perseus Cluster
 |
|---|
| Perseus Cluster. Wendelstein Observatory. |
The Perseus Cluster (Abell 426) is a diffuse, irregular cluster of galaxies, containing about 500 members and located about 250 million light-years away, that is dominated by and centered on the Seyfert galaxy NGC 1275 associated with the radio source Perseus A. The mass of cluster has been estimated at 200 trillion solar masses.
Perseus-Pisces Supercluster
The Perseus-Pisces Supercluster is one of the largest known structures in the universe. Even at a distance of 250 million light-years, this chain of galaxy clusters extends more than 40° across the northern winter sky.
| Stars in Perseus brighter than magnitude 4.0 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| star | vis mag | abs mag | spec type | distance (ly) | RA (h m s) | Dec (° ' ") |
| Alpha (Mirfak) | 1.79 | -4.51 | F5Ib | 592 | 03 24 19 | +49 51 40 |
| Beta (Algol) | 2.09v | -0.18 | B8V | 93 | 03 08 10 | +40 57 21 |
| Zeta | 2.84 | -4.56 | B1Ib | 982 | 03 54 08 | +31 53 01 |
| Epsilon | 2.90 | -3.10 | B0.5V+A2V | 538 | 03 57 51 | +40 00 37 |
| Gamma | 2.91 | -1.51 | G8III+A2V | 256 | 03 04 48 | +53 30 23 |
| Delta | 3.01 | -3.04 | B5III | 528 | 03 42 55 | +47 47 15 |
| Rho (Gorgonea Terti) | 3.32v | -1.68 | M3III | 325 | 03 05 11 | +38 50 25 |
| Eta (Miram) | 3.77 | -4.29 | K3Ib | 1,330 | 02 50 42 | +55 53 44 |
| Nu | 3.77 | -2.39 | F5II | 557 | 03 45 12 | +42 34 43 |
| Kappa (Misam) | 3.79 | 1.10 | K0III | 112 | 03 09 30 | +44 51 27 |
| Omicron (Atik) | 3.84 | -4.44 | B1III | 1,480 | 03 44 19 | +32 17 18 |
| Tau (Kerb) | 3.93 | -0.48 | G4II+A4VI | 248 | 02 54 15 | +52 45 45 |
| Xi (Menkib) | 3.98 | -4.70 | O7Iae | 1,770 | 03 58 58 | +35 47 28 |