Hypothyroidism: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia (original) (raw)
Hypothyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormone. This condition is often called underactive thyroid.
The thyroid gland is an important organ of the endocrine system. It is located at the front of the neck, just above where your collarbones meet. The thyroid makes hormones that control the way every cell in the body uses energy. This process is called metabolism.
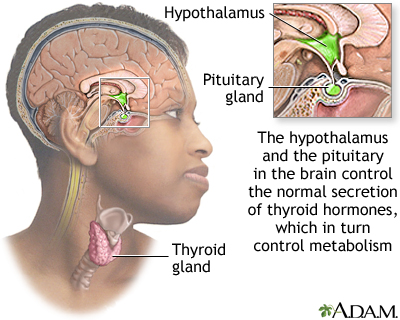
Hypothyroidism is more common in women and people over age 50.
The most common cause of hypothyroidism is thyroiditis. In people with thyroiditis, swelling and inflammation damage the thyroid gland's cells.
Causes of this problem include:
- The immune system attacking the thyroid gland
- Viral infections (common cold) or other respiratory infections
- Pregnancy (often called postpartum thyroiditis)
Other causes of hypothyroidism include:
- Certain medicines, such as lithium and amiodarone, and some types of chemotherapy
- Congenital (birth) defects
- Radiation treatments to the neck or brain to treat different cancers
- Radioactive iodine used to treat an overactive thyroid gland
- Surgical removal of part or all of the thyroid gland
- Sheehan syndrome, a condition that may occur in a woman who bleeds severely during pregnancy or childbirth and causes the destruction of the pituitary gland (which regulates the thyroid gland)
- Pituitary tumor or pituitary surgery
Early symptoms:
- Hard stools or constipation
- Feeling cold (wearing a sweater when others are wearing a t-shirt)
- Fatigue or feeling slowed down
- Heavier and irregular menstrual periods
- Joint or muscle pain
- Paleness or dry skin
- Sadness or depression
- Thin, brittle hair or fingernails
- Weakness
- Weight gain
Late symptoms, if untreated:
- Decreased taste and smell
- Hoarseness
- Puffy face, hands, and feet
- Slow speech
- Thickening of the skin
- Thinning of eyebrows
- Low body temperature
- Slow heart rate
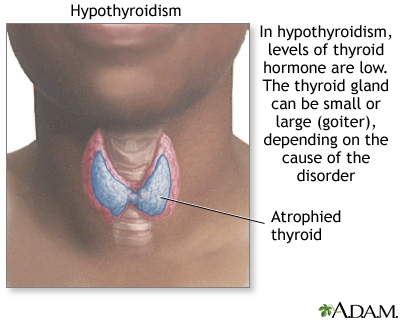
The health care provider will do a physical exam and may find that your thyroid gland is enlarged. Sometimes, the gland is normal size or smaller-than-normal. The exam may also reveal:
- High diastolic blood pressure (second number)
- Thin brittle hair
- Coarse features of the face
- Pale or dry skin, which may be cool to the touch
- Reflexes that have a delayed relaxation phase
- Swelling of the arms and legs
Blood tests are also ordered to measure your thyroid hormones TSH and T4.
- Specialized thyroid tests like thyroid peroxidase antibodies may be needed.
You may also have tests to check:
- Cholesterol levels
- Complete blood count (CBC)
- Liver enzymes
- Prolactin
- Sodium
- Cortisol
Treatment is aimed at replacing the thyroid hormone you are lacking.
Levothyroxine is the most commonly used medicine:
- You will be prescribed the lowest dose possible that relieves your symptoms and brings your blood thyroid hormone levels back to normal.
- If you have heart disease or you are older, your provider may start you on a very small dose.
- Most people with an underactive thyroid will need to take this medicine for life.
- Levothyroxine is usually a pill, but some people with very severe hypothyroidism first need to be treated in the hospital with intravenous levothyroxine (given through a vein).
When starting you on your medicine, your provider may check your hormone levels every 2 to 3 months. After that, your thyroid hormone levels should be monitored at least once every year.
When you are taking thyroid medicine, be aware of the following:
- Do not stop taking the medicine, even when you feel better. Continue taking it exactly as your provider prescribed.
- If you change brands of thyroid medicine, let your provider know. Your levels may need to be checked.
- What you eat can change the way your body absorbs thyroid medicine. Talk with your provider if you are eating a lot of soy products or are on a high-fiber diet.
- Thyroid medicine works best on an empty stomach and when taken 1 hour before any other medicines. Ask your provider if you should take your medicine at bedtime. Taking it at bedtime may allow your body to absorb the medicine better than taking it in the daytime.
- Wait at least 4 hours after taking thyroid hormone before you take fiber supplements, calcium, iron, multivitamins, aluminum hydroxide antacids, colestipol, or medicines that bind bile acids.
While you are taking thyroid replacement therapy, tell your provider if you have any symptoms that suggest your dose is too high, such as:
- Anxiety
- Palpitations
- Rapid weight loss
- Restlessness or shakiness (tremors)
- Sweating
In most cases, thyroid hormone level becomes normal with proper treatment. You will likely take a thyroid hormone medicine for the rest of your life.
Myxedema crisis (also called myxedema coma), the most severe form of hypothyroidism, is rare. It occurs when thyroid hormone levels get very, very low. The severe hypothyroid crisis is often then started by an infection, illness, exposure to cold, or certain medicines (opioids are a common cause) in people with severe hypothyroidism. It can also commonly be caused by failure to take prescribed thyroid hormone consistently or correctly.
Myxedema crisis is a medical emergency that must be treated in the hospital. Some people may need oxygen, breathing assistance (ventilator), fluid replacement, and intensive-care nursing.
Symptoms and signs of myxedema coma include:
- Below normal body temperature
- Decreased breathing
- Low systolic blood pressure
- Low blood sugar
- Unresponsiveness
- Inappropriate or uncharacteristic moods
People with untreated hypothyroidism are at increased risk of:
- Infection
- Infertility, miscarriage, giving birth to a baby with birth defects
- Heart disease because of higher levels of LDL (bad) cholesterol
- Heart failure
Contact your provider if you have symptoms of hypothyroidism.
If you are being treated for hypothyroidism, call your provider if:
- You develop chest pain or rapid heartbeat
- Your symptoms get worse or do not improve with treatment
- You develop new symptoms
Myxedema; Adult hypothyroidism; Underactive thyroid; Goiter - hypothyroidism; Thyroiditis - hypothyroidism; Thyroid hormone - hypothyroidism
Brent GA, Weetman AP. Hypothyroidism and thyroiditis. In: Melmed S, Auchus RJ, Goldfine AB, Koenig RJ, Rosen CJ, eds. Williams Textbook of Endocrinology. 14th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 13.
Garber JR, Cobin RH, Gharib H, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for hypothyroidism in adults: cosponsored by the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and the American Thyroid Association. Endocr Pract. 2012;18(6):988-1028. PMID: 23246686 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23246686/.
Jonklaas J, Bianco AC, Bauer AJ, et al; American Thyroid Association Task Force on Thyroid Hormone Replacement. Guidelines for the treatment of hypothyroidism: prepared by the American Thyroid Association task force on thyroid hormone replacement. Thyroid. 2014;24(12):1670-1751. PMID: 25266247 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25266247/.
Updated by: Sandeep K. Dhaliwal, MD, board-certified in Diabetes, Endocrinology, and Metabolism, Springfield, VA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.