Martin triste - Acridotheres tristis - Common Myna (original) (raw)
- Home
- List
- Passeriformes
- Sturnidae
- Id. Record
- Geographic range
- Pictures
Acridotheres tristis - Martin triste
Systematics
- Order
:
Passeriformes - Family
:
Sturnidés - Genus
:
Acridotheres - Species
:
tristis
Descriptor
Biometrics
- Size
: 25 cm - Wingspan
: - - Weight
: 82 à 143 g
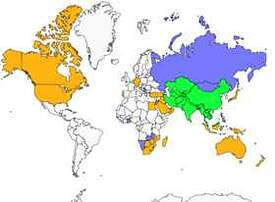
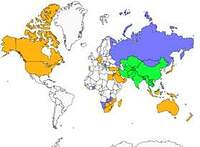
Geographic range
Identification
adult
adult plum. post breeding
Common Myna does not have sexual dimorphism. The back and belly are brown-chocolate. The head and chest are black. The beak and legs are yellow. The eye contour does not have feathers, this yellow skin in an almond shape around the eye forms a continuity with the beak. Undertail and lower belly are white. Tail feathers are black and white. In flight, wide white areas are visible on the wings. The juvenile is lighter, its head and throat are rather brown than black.
Subspecific information 2 subspecies
- Acridotheres tristis tristis (s Kazakhstan, Turkmenistan and e Iran to s China, Indochina, Malay Pen. and s India)
- Acridotheres tristis melanosternus (Sri Lanka)
Foreign names
- Martin triste,
- Miná común,
- mainato-de-mascarilha-amarela,
- Hirtenmaina,
- pásztormejnó,
- Treurmaina,
- Maina comune,
- brun majna,
- Hyrdestær,
- škorec hnedý,
- majna obecná,
- Maina,
- pihamaina,
- Indiese Spreeu,
- minà comú,
- Hjarðmænir,
- majna brunatna,
- parastā maina,
- žalostna majna,
- Майна,
- インドハッカ,
- 家八哥,
- นกเอี้ยงสาริกา,
- 家八哥,
Voice song and cries
adult
The Common Myna chirps, crows and chatters in an unstructured way. Its warbling is muddled and without real melody. Two distinct calls are characteristic of specific actions. At take-off it utters a kwerrh and when alarmed it emits a traaahh. Only during the breeding season do two birds of a pair sync up to make melodious duets. Even though it can sometimes mimic other birds, it is not an expert in this field.
Habitat
adult
The Common Myna is easily spotted in particular in human-populated areas. It looks for human proximity in cities and does not hesitate to penetrate into dwellings. In a natural and remote setting from humans, the Common Myna avoids wooded areas and rarely ventures into the heart of the forest. However, there are some exceptions such as on Mayotte island where it frequents moist forests up to the summits. This is not the case in other islands of the Comoros archipelago.
Behaviour character trait
adult
Common Myna is a gregarious bird and lives in small colonies. At night, they group together into dormitories that can sometimes be very large, up to 1,000 individuals.
adult
It chooses places where it is safe from danger, such as forests of bamboo trees or trees covered in vines. It is a quarrelsome, familiar bird towards humans. Highly opportunistic, they don't disdain waste deposits for food, nor the proximity of pets. It feeds by walking and pecking at the ground. The distance between its feeding site and dormitory can reach 10 km. During the nesting period, Common Myna is very territorial and doesn't hesitate to defend its territory by fiercely fighting. The fights consist mostly of being knocked down to the ground and given violent pecks. Common Myna couples are loyal for life and keep their nesting site. Its aggressiveness is also directed towards indigenous species when looking for natural cavities. Common Myna is flourishing at their detriment.
Flight
adult
In flight, the Common Myna reveals large white patches on its wings.
Dietfeeding habits
adult
The Common Myna is fond of crop-damaging insects, hence its introduction to the islands of the Indian Ocean. However, it has a very eclectic diet. It feeds on all kinds of fruits, insects, invertebrates, eggs, chicks, and even goes as far as to capture small lizards.
Reproduction nesting
adult
The Common Myna is not difficult to build a nest. It is an mixture of twigs and grass in the shape of a cup combined with feathers.
adult
Sometimes even small pieces of plastic or paper are found. It has adapted to its various environments - a cavity is enough: tree, cliff, building, thicket.
The female lays 1 to 4 turquoise-blue eggs which she mainly incubates alone, although couples have been observed to take turns. Incubation takes 13 to 14 days, the two sexes feed at the nest for 25 days, and 3 weeks after fledging. There can be two broods a year for a couple.
Geographic range
immature
The Common Myna is native to Asia. Since the 18th century, it has been introduced to Madagascar and Mauritius to combat a proliferation of locusts in crops. In the Comoros, it was only introduced at the beginning of the twentieth century and later to Mayotte.
The species is present on all the islands of the Society and Hiva Oa (Marquesas). It has been seen recently in Nuku Hiva where an attempt is being made to destroy it. In the Tuamotus, it is present in Hao. In the Austral Islands, it is present in Tubuai and Rurutu. Finally, it is also found in South Africa and Australia.
Threats - protection
juvenile
IUCN conservation status
Extinct
Threatened
Least
concern
Extinc
in the Wild
Near
threatened
Not
evaluated
EX EW CR EN VU NT LC NE
As with many introduced species, the Common Myna has quickly adapted to different environments. This opportunistic and aggressive species is considered to be a nuisance.
Sources of information
IOC World Bird List (v14.1),Gill, F and D Donsker (Eds). 2024-04-18.
Les Oiseaux de Mayotte, Clément Michel, Grissac Philippe, Rolland Robin
Oiseaux des iles de l'océan Indien, Langrand Olivier, ian Sinclair
Avibase, Lepage Denis