XNI Design Details (original) (raw)
The XNI parser pipeline is any combination of components that are either capable of producing XNI events, consuming XNI events, or both. All pipelines consist of a source, zero or more filters, and a target. The source is typically the XML scanner; common filters are DTD and XML Schema validators, a namespace binder, etc; and the target is the parser that consumes the XNI events and produces a common programming interface such as DOM or SAX. The following diagram illustrates the basic pipeline configuration.
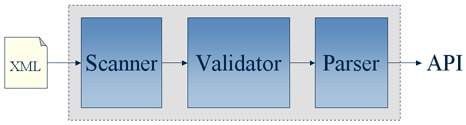
However, this is a simplified view of the pipeline configuration. The Xerces Native Interface actually defines two different pipelines with three interfaces: one for document information and two for DTD information.
The Xerces2 parser, the reference implementation of XNI, contains more components than the basic pipeline configuration diagram shows. The following diagram shows the Xerces2 pipeline configuration. The arrow going from left to right on the top of the image represents the flow of document information and the arrows on the bottom of the image represent the DTD information flowing through the parser pipeline.
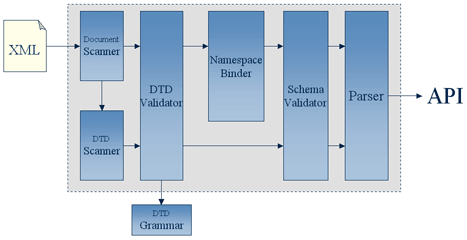
As the diagram shows, the "Document Scanner" is the source for document information and the "DTD Scanner" is the source for DTD information. Both document and DTD information generated by the scanners flow into the "DTD Validator" where structure and content is validated according to the DTD grammar, if present. From here, the validated document information with possible augmentations such as default attribute values and attribute value normalization flows to the "Namespace Binder" which applies the namespace information to elements and attributes. The newly namespace-bound document document information then flows to the "Schema Validator" for validation based on the XML Schema, if present. Finally, the document and DTD information flow to the "Parser" which generates a programming interface such as DOM or SAX.
XNI defines the document information using a number of core interfaces. (These interfaces are described in more detail in theCore API documentation.) But XNI also defines a set of interfaces to build parser configurations that assemble the pipelines in order to parse documents. The next section gives a general overview of the this parser configuration provided by XNI.