How to Deadlift: Proper Form, Benefits, and Variations (original) (raw)
The deadlift is perhaps the most fundamental compound exercise that you can do in the gym. Deadlifts help you build muscle and increase strength that carry over to both other gym exercises as well as your day-to-day life. This guide leaves no stone unturned and dishes out everything you need to know about the deadlift. Strap in — you’re about to get a crash course on becoming a master puller.
Recent Updates: On May 1, 2024, BarBend Senior Writer Jake Dickson reviewed the content in this article and updated certain sections to make the information more accessible to readers of all levels.
About Our Experts
This article was originally written by former BarBend Training Editor Jake Boly, who holds a Masters in Sport Science and is a Certified Strength & Conditioning Specialist (CSCS).
Our deadlift guide was verified by BarBend Senior Writer Jake Dickson. Dickson holds a personal training certificate from the National Academy of Sports Medicine (NASM) as well as a B.S. degree in Exercise Science. You can read more about the guiding principles behind _BarBend_’s training content here.
How To Do the Deadlift
The conventional barbell deadlift teaches you how to properly pick up a heavy weight from the floor. There are many different valuable deadlift variations out there, but if you want to learn how to pull properly, you need to first master the basics.

- Step 1 — Set your feet about hip-width apart, and then root them to the floor by twisting them slightly apart. Maintain a relatively vertical shin angle, bring your shoulders over the bar, then hinge your hips backward by driving your butt behind you.
- Step 2 — Drive through the floor with the legs, keeping the bar against the body, to lift the weight off the floor. The barbell should very lightly graze your shins.
- Step 3 — As the barbell passes your knee, explosively thrust your hips forward to lock the bar out. Hold at the top for a beat before letting the weight down.
Sets and Reps
- For Beginners: 3 x 5
- To Build Strength: 5 x 3
- To Build Endurance: 3 x 10
Deadlift Standards
You’re probably asking, “How much should I deadlift?” See the below chart for deadlift standards, which we compiled based on our own research and the input of _BarBend_’s credentialed experts. These numbers represent the one-rep max (1RM) you should aim for as you progress in your training.
| Fitness Level | Male Standard | Female Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Beginner | BW | 0.50 x BW |
| Novice | 1.35 x BW | BW |
| Intermediate | 1.75 x BW | 1.25 x BW |
| Advanced | 2.15 x BW | 1.50 BW |
| Elite | 2.70 x BW | 2.00 x BW |
*BW refers to body weight
Modifications
- To Reach the Bar: If you’re having trouble getting your hands on the bar when it’s on the ground due to limitations in your flexibility, you can rest the bar and plates on a pair of low risers, lifting blocks, or even bumper plates laid flat. Unless you’re a powerlifter, there’s no rule stating you need to deadlift the bar from the floor.
- Improve Your Grip: If you’re having trouble holding on to the bar, try a “mixed” grip, with one hand’s palm facing forward while the other points behind you. You can also use lifting straps to secure your grip altogether.
- Avoid Back Pain: If the conventional deadlift aggravates your lower back, you might want to try the sumo deadlift instead. Sumo deadlifts put your torso in a more upright position, which may limit discomfort in that area.
Video Guide
If you’re a visual learner, we recommend our step-by-step deadlift tutorial on YouTube:
Below are four deadlift variations that you can perform to increase overall deadlift strength, address limitations and sticking points, and regress or progress the deadlift so it matches your personal experience level and goals.
- Stiff-Leg Deadlift: Ideal for lifters hoping to integrate deadlifting into a program to increase the hamstrings’ size and strength. You can also do stiff-leg deadlifts as an accessory exercise if you’re a strength athlete.
- Rack Pull: Rack pulls can address sticking points at the top of your deadlift and be used as a regression for lifters who may struggle to maintain back tension from the floor.
- Deficit Deadlift: This is a good variation to use if you want to add some quad training to your deadlift, or you find it difficult to break the bar off the floor when starting your sets.
- Sumo Deadlift: Use this one if you struggle to properly set up for conventional deadlifts due to flexibility issues, or if you want to limit the amount of stress on your lower back.
Deadlift Alternatives
The three variations below can increase unilateral strength and hypertrophy and add variety to a workout program.
Trap Bar Deadlift

- Stand inside the trap bar frame after loading it with some plates. Your feet should be close, under your hips.
- Sink down by bending at both the knees and hips and lowering your body until you can grasp either set of handles within the frame.
- Your torso should be more upright than during a standard deadlift, similar to that of a partial squat position.
- Inhale, brace your core, and push directly downward with your legs to lift the bar up to a standing position.
Hip Thrust

- Set up by sitting with your back to a stable surface like a weight bench or plyo box.
- Load a barbell with plates and roll it over your hips with your legs straight.
- Grasp the bar for stability, kick your feet back until your knees are bent, and brace your core.
- Thrust the bar up off the ground by contracting your glutes until your torso and legs form a straight line.
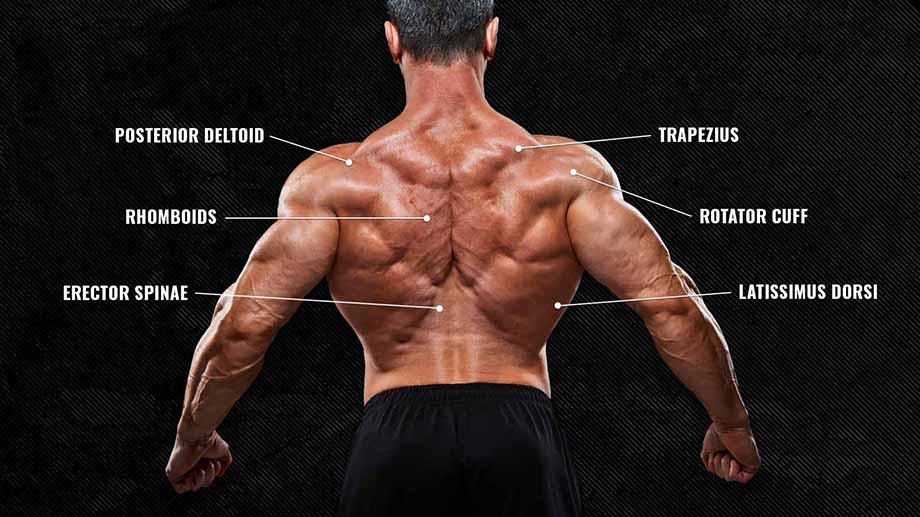
What Muscles Do Deadlifts Work?
Credit: Master1305 / Shutterstock
The deadlift is a top compound exercise precisely because of how many muscles it works at once.
In a 2018 study from the Journal of Exercise and Fitness, authors noted that the gluteus maximus, rectus femoris, and biceps femoris were highly active during the conventional deadlift. (1) Besides being an excellent movement for working these major muscles, the deadlift is fantastic for targeting these synergistic and stabilizer muscles:
Glutes
The deadlift is primarily a hip extension exercise. As such, the glutes do a lion’s share of the work in helping you stand tall with the barbell. Your glutes are active from start to finish, but engage primarily to straighten your body once the barbell passes your knees.
Hamstrings
Your hamstrings work alongside your glutes in the deadlift to help right your torso. That said, they’re also active from the very beginning of the lift. When you set up for a deadlift, depending on the height of your hips, you should feel a decent stretch throughout the back of your thigh.
Quads
Your quads have a limited role during most types of deadlift, but they’re crucial for getting the movement going. As knee extensors, your quadriceps work to help break the barbell off the floor in the beginning of the lift, but their engagement does decrease as you move to a standing position.
Lats
Your lats work isometrically to stabilize your torso during the deadlift. To be an effective puller, you need to stabilize your shoulder girdle from start to finish. Contracting your lattisimus dorsi muscles will help you achieve a solid, “locked-in” feeling during your pull.
Traps
Your traps also come into play isometrically in the deadlift. Even though you shouldn’t shrug your shoulders during the pull, you’ll undoubtedly feel a massive amount of stress across your traps as you lift. The primary function of your traps is to physically keep your shoulders in place against the heavy resistance of the bar.
Lower Back
Even though you maintain a rigid, unmoving spinal column in the deadlift, your lower back gets plenty of work.
[Read More:_** **_Best Lower Back Exercises for Strength and Reduced Pain]
Much like your lats and mid-back, your erector spinae muscles have one simple but important job — to protect your spine by contracting hard to keep everything aligned and in place. The deadlift is one of the best ways to develop an ironclad back that will assist and support you in and out of the gym.
Core & Other Muscles
Alongside the main movers in the deadlift, your body calls to action many of the smaller, supportive muscles as well. Your forearms work hard to maintain an airtight grip on the bar. Your abdominals brace hard against the impulse to collapse your trunk. Your rhomboids, middle traps, and serratus all assist your lats in stabilizing your shoulder while you pull.

[Read More: The Best Shoulder Exercises, Workouts From a CPT]
Even though the deadlift may not stimulate all these tissues in a way that will create long-term growth, the exercise is still unbelievably effective at training your body to work as a unit.
Benefits of the Deadlift
There are many deadlift benefits, which is why this movement, or one of its variants, is a staple in nearly every training program. Below are just four of the many, many benefits that come with deadlifting.
Better Functional Movement
Break down the deadlift to its core, and it’s picking something up off the ground. That’s a life skill. Think about how many times you’ve bent over to pick up your kid or something you’ve dropped — a lot, right?
That’s not to say that you need maximal deadlift strength to pick up your child, but the core mechanics are the same. A deadlift mimics proper hip hinging, driving your hips back and lowering your torso toward the floor with a tight back.
[Read More: The Best Glute Workout Exercises, With Tips From Our Experts]
Deadlifting somewhat regularly (even with light weight) will help reinforce proper hinging patterns to help you stay supple and mobile.
Strength Sport Specificity
There’s no beating around the bush on this one. If you want to compete in strength sports, you need to deadlift. Powerlifters compete to see who can deadlift (and bench press and back squat) the most weight. Strongmen and strongwomen compete in various deadlift variations, too, and weightlifters need to deadlift the barbell off the floor to complete both the snatch and clean & jerk.
A Bigger Back
Deadlifts should be in your training toolbox for those on the quest to build a strong and big upper back. You can load the deadlift heavier than other back movements, making it fantastic for strength and muscle hypertrophy.
[Read More: The Ultimate Workout Split, Created by Our Experts]
Because the deadlift recruits so many muscles, it’s a great option if you’re pressed for time. Say you only have 20 minutes to work out your muscles. Quickly warm up, load up a barbell with moderate weight, set a timer for 12 minutes, and do six reps at the top of every minute. Rest for the remainder of the minute and then repeat at the top of the next minute. Before you know it, you’ve just done 72 reps that targeted your back, hamstrings, core, and glutes.
More Maximal Strength
The deadlift is a good indicator of absolute raw strength. While there are other great ways to increase strength and power, the deadlift is considered a solid test of true strength, and so in the process of building a big deadlift, you’ll gain a lot of strength along the way.
Common Deadlift Mistakes
Below are three of the most common deadlift mistakes, which can lead to loss of positional strength, failed lifts, and potential injury if you’re not careful.
Poor Bar Path
As the name implies, bar path refers to the barbell’s path from start to finish. Ideally, you want the bar to remain in as straight of a line as possible. A straighter bar path means the bar has to travel less distance and is, therefore, easier to pick up. Second, a barbell that juts outward can throw your body out of alignment, which may lead to a failed lift or, in extreme cases, injury.
Set a foam roller six to eight inches before the barbell and practice reps without touching or knocking down the roller to fix the poor bar path. If it gets knocked over, film yourself from the side and analyze where the barbell might be shooting forward.
Not Pulling the Slack Out
Pulling the slack out of the bar means to create tension with the body, barbell, and floor before any movement is initiated. This ensures that you are bracing correctly and setting yourself up for mechanical success by producing tension. Otherwise, you’ll pull the barbell with loose form and either not move the weight or potentially hurt yourself.

[Read More: Powerbuilding Workout Routine, With Tips from a CPT]
Address this issue by progressively pulling tension into the barbell before liftoff and holding for a full second before lifting. Actively feel the tension and what it feels like to produce tightness before physically moving weight. Focus on the cues used, then repeat them every rep.
Your Hips Rise Too Quickly
If the hips shoot up once you start the movement, then there’s a good chance you’re losing power due to poor mechanical positioning, or your quadriceps are too weak to begin the exercise properly.
Try taking a video of yourself from the side and practice bringing the hips up slightly each set to highlight different positions and which feels most comfortable. Assuming the rest of your form is okay, then one position will generally feel best, and that’s what you’ll end up going and experimenting further with.
If you feel your legs are underpowered, you can benefit from deficit deadlifts to emphasize leg engagement at the start of the movement.
The Big Picture
The deadlift is unparalleled. While there are certainly other movements that excel in improving specific areas of your fitness, a good deadlift is among the highest-value actions you can perform in the gym. The beauty of the lift lies in its simplicity. The deadlift is easy to learn, but difficult to master. Convenient to adjust to suit your body, but challenging if you load up on weight.
No matter your goal, the deadlift deserves a home in your programming household. You can pull hard and heavy to improve your strength, turn your power output up, or perform well in a powerlifting meet competition. Dial back on intensity and ante up on repetitions to build work capacity and add new muscle. No matter what your target is, when it comes to the deadlift, you get out what you put in.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can beginners deadlift?
Absolutely. Everyone can deadlift at any fitness level. What’s most important is considering form and variations when progressing with the deadlift safely. Dumbbell and kettlebell deadlifts are a great option for beginners working towards the barbell.
It’s also worth hiring a coach to properly learn form and technique.
Do deadlifts work your back?
Yes! The deadlift is primarily a back exercise, though it does use your legs as well. Bending over at the hips to pick a weight up off the floor will engage your entire posterior chain, especially the back muscles that surround your spine like your erector spinae (lower back), latissimus dorsi (lats), and scapular muscles like the trapezius and rhomboids as well.
What are some benefits of the deadlift?
The deadlift has a ton of benefits for every fitness enthusiasts. For starters, the deadlift is fantastic for building total body strength and muscle. In addition, nailing the deadlift is a great way to produce carryover to sport and longevity in everyday life.
How should I warmup for deadlifts?
There’s no “one-size-fits-all” for a deadlift warm-up, but we do have a couple of pieces of advice.
1. Keep the warmup somewhat time-conscious. You don’t need to spend half an hour getting warm.
2. Focus on the muscle groups and joints needed most in the deadlift.
3. Spend the most time targeting areas that need the most activation per your needs.
References
- Lee, S., Schultz, J., Timgren, J., Staelgraeve, K., Miller, M., & Liu, Y. (2018). An electromyographic and kinetic comparison of conventional and Romanian deadlifts. Journal Of Exercise Science & Fitness, 16(3), 87-93.
Featured Image: puhhha / Shutterstock