CUDA Deep Neural Network (original) (raw)
NVIDIA cuDNN
NVIDIA® CUDA® Deep Neural Network library (cuDNN) is a GPU-accelerated library of primitives for deep neural networks. cuDNN provides highly tuned implementations for standard routines, such as forward and backward convolution, attention, matmul, pooling, and normalization.
Download cuDNN
Download cuDNN LibraryDownload cuDNN Frontend (GitHub)
cuDNN is also available to download via one of the package managers below.
Quick Install with conda
conda install nvidia::cudnn cuda-version=12
Installs the cuDNN library
Quick Pull with Docker
docker pull nvidia/cuda:12.8.1-cudnn-devel-ubuntu22.04
Installs the cuDNN lLibrary
Quick Install with pip
Installs the cuDNN library
pip install nvidia-cudnn-frontend
Installs the cuDNN Frontend API
How cuDNN Works
- Accelerated Llearning: cuDNN provides kernels, targeting Tensor Cores whenever it makes sense, to deliver best- available performance on compute-bound operations. It offers heuristics for choosing the right kernel for a given problem size.
- Fusion Support: cuDNN supports fusion of compute-bound and memory-bound operations. Common generic fusion patterns are typically implemented by runtime kernel generation. Specialized fusion patterns are optimized with pre-written kernels.
- Expressive Op Graph API: The user defines computations as a graph of operations on tensors. The cuDNN library has both a direct C API and an open-source C++ frontend for convenience. Most users choose the frontend as their entry point to cuDNN
cuDNN API Code Sample
The code performs a batched matrix multiplication with bias using the cuDNN PyTorch integration.
import torch import cudnn
Prepare sample input data. nvmath-python accepts input tensors from pytorch, cupy, and
numpy.
b, m, n, k = 1, 1024, 1024, 512 A = torch.randn(b, m, k, dtype=torch.float32, device="cuda") B = torch.randn(b, k, n, dtype=torch.float32, device="cuda") bias = torch.randn(b, m, 1, dtype=torch.float32, device="cuda")
result = torch.empty(b, m, n, dtype=torch.float32, device="cuda")
Use the stateful Graph object in order to perform multiple matrix multiplications
without replanning. The cudnn API allows us to fine-tune our operations by, for
example, selecting a mixed-precision compute type.
graph = cudnn.pygraph( intermediate_data_type=cudnn.data_type.FLOAT, compute_data_type=cudnn.data_type.FLOAT, )
a_cudnn_tensor = graph.tensor_like(A) b_cudnn_tensor = graph.tensor_like(B) bias_cudnn_tensor = graph.tensor_like(bias)
c_cudnn_tensor = graph.matmul(name="matmul", A=a_cudnn_tensor, B=b_cudnn_tensor) d_cudnn_tensor = graph.bias(name="bias", input=c_cudnn_tensor, bias=bias_cudnn_tensor)
Build the matrix multiplication. Building returns a sequence of algorithms that can be
configured. Each algorithm is a JIT generated function that can be executed on the GPU.
graph.build([cudnn.heur_mode.A]) workspace = torch.empty(graph.get_workspace_size(), device="cuda", dtype=torch.uint8)
Execute the matrix multiplication.
graph.execute( { a_cudnn_tensor: A, b_cudnn_tensor: B, bias_cudnn_tensor: bias, d_cudnn_tensor: result, }, workspace )
Sample Operation Graphs Described by the cuDNN Graph API
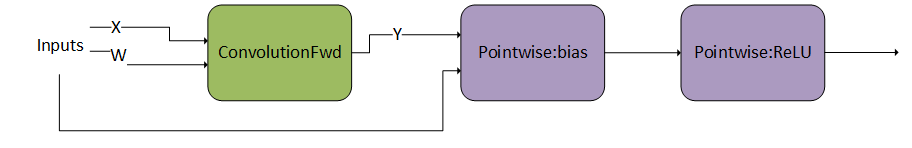
ConvolutionFwd followed by a DAG with two operations
Documentation
Complete guides on installing and using the cuDNN frontend and cuDNN backend.
Frontend Samples
Samples illustrate usage of the Python and C++ frontend APIs.
Latest Release Blog
Learn how to accelerate transformers with scaled dot product attention (SDPA) in cuDNN 9.
cuDNN on NVIDIA Blackwell
Learn about new/updated APIs of cuDNN pertaining to NVIDIA Blackwell’s microscaling format and how to program against those APIs.
Key Features
Deep Neural Networks
Deep learning neural networks span computer vision, conversational AI, and recommendation systems and have led to breakthroughs like autonomous vehicles and intelligent voice assistants. NVIDIA's GPU-accelerated deep learning frameworks speed up training time for these technologies, reducing multi-day sessions to just a few hours.
cuDNN supplies foundational libraries for high-performance, low-latency inference for deep neural networks in the cloud, on embedded devices, and in self-driving cars.
- Accelerated compute-bound operations like attention training/prefill, convolution, and matmul
- Optimized memory-bound operations like attention decode, pooling, softmax, normalization, activation, pointwise, and tensor transformation
- Fusions of compute-bound and memory-bound operations
- Runtime fusion engine to generate kernels at runtime for common fusion patterns
- Optimizations for important specialized patterns like fused attention
- Heuristics to choose the right implementation for a given problem size
cuDNN Graph API and Fusion
The cuDNN Graph API is designed to express common computation patterns in deep learning. A cuDNN graph represents operations as nodes and tensors as edges, similar to a dataflow graph in a typical deep learning framework.
Access to the cuDNN Graph API is conveniently available through the Python/C++ Frontend API (recommended) as well as the lower-level C Backend API (for legacy use cases or special cases where Python/C++ isn’t appropriate).
- Flexible fusions of memory-limited operations into the input and output of matmul and convolution
- Specialized fusions for patterns like attention and convolution with normalization
- Support for both forward and backward propagation
- Heuristics for predicting the best implementation for a given problem size
- Open-source Python/C++ Frontend API
- Serialization and deserialization support
cuDNN Accelerated Frameworks
cuDNN accelerates widely used deep learning frameworks, including PyTorch, JAX, Caffe2, Chainer, Keras, MATLAB, MxNet, PaddlePaddle, and TensorFlow.
Related Libraries and Software
NVIDIA NeMo™
NeMo is an end-to-end cloud-native framework for developers to build, customize, and deploy generative AI models with billions of parameters.
NVIDIA TensorRT™
TensorRT is a software development kit for high-performance deep learning inference.
NVIDIA Optimized Frameworks
Deep learning frameworks offer building blocks for designing, training, and validating deep neural networks through a high-level programming interface.
NVIDIA Collective Communication Library
NCCL is a communication library for high-bandwidth, low-latency, GPU-accelerated networking.
More Resources
Ethical AI
NVIDIA believes Trustworthy AI is a shared responsibility, and we have established policies and practices to enable development for a wide array of AI applications. When downloading or using a model in accordance with our terms of service, developers should work with their supporting model team to ensure this model meets requirements for the relevant industry and use case and addresses unforeseen product misuse.
Please report security vulnerabilities or NVIDIA AI concerns here.